How Does The Martingale Strategy In Binary Options Work?



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
The Martingale strategy in binary options works by doubling your investment after each losing trade to recover previous losses and make a profit once a winning trade occurs. For example, if you lose a $10 trade, you invest $20 in the next trade, then $40 if that also loses, and so on. While it can recover losses in the short term, the strategy is risky, requiring significant capital to withstand losing streaks and is not guaranteed to be profitable.
In binary options trading, traders use various strategies to maximize their profits and minimize losses. One such strategy is the Martingale, which has gained attention and controversy. In this article, we will dive into the Martingale strategy in binary options, how it works, its profitability, and its associated risks, and answer some frequently asked questions.
Essentially, the Martingale strategy in binary options is a betting system that involves doubling your investment after each losing trade. While it may seem like a foolproof way to recover losses, it comes with inherent risks and is not guaranteed to be profitable.
What is the Martingale strategy?
The Martingale strategy is a popular strategyand trading system employed in various financial markets, including binary options trading. It is based on the principle of doubling your investment after each losing trade in the hopes of eventually recovering all losses and making a profit.
Here's how it typically works:
Initial trade. You start with an initial investment amount of $100
Trade. If your first trade results in a loss, you double your investment in the next trade, which would be $200 in this case
Repeat. If the second trade also results in a loss, you double your investment again, making it $400 for the third trade
Continue. You continue this process until you have a winning trade, at which point you return to your initial investment amount
In other words, the idea behind the Martingale strategy is that, statistically, a winning trade will eventually occur. When it does, it should cover the previous losses and result in a net profit.
Is Martingale allowed in binary options?
Yes, the Martingale strategy is typically allowed in binary options trading. Binary options platforms generally do not impose restrictions on specific trading strategies that traders can employ. This means that you are free to use the Martingale strategy and any other trading strategies you deem suitable for your objectives.
However, it's crucial to remember that while it may be allowed, using the Martingale strategy in binary options trading carries significant risks and may not be advisable for all traders due to its high-risk nature and potential for substantial capital losses. Before employing this method, you should carefully assess your risk tolerance and financial situation.
Is the Martingale strategy 100% profitable?
The Martingale strategy is far from being 100% profitable. To achieve 100% profitability with this strategy, one would need an infinite supply of capital, which is practically impossible. Let's take a look at how the Martingale trading strategy can play out in the real world. We started our simulation with $10,000 in our trading account.
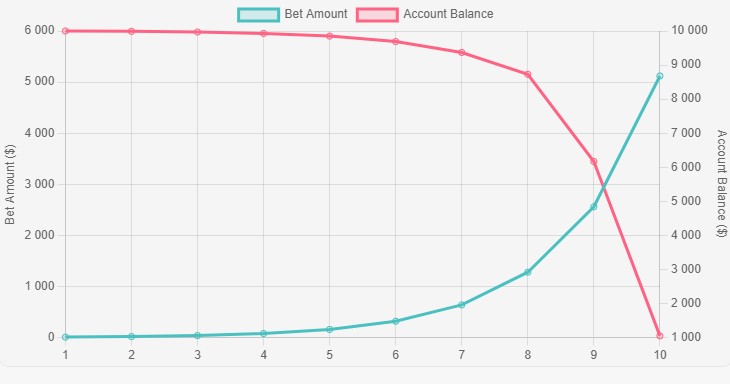
Our trades started small at only $10 risk per trade but doubled after each loss, as the Martingale strategy requires. You can see the trade amounts increasing exponentially along the left vertical axis.
While our account balance, shown on the right axis, decreased slowly at first, things took a turn as our losing streak continued. Larger and larger trades were not enough to overcome multiple losses in a row.
Additionally, it's crucial to note that the Martingale strategy can only potentially work with assets like Forex, which do not have an absolute zero value. In financial markets, where asset prices can fluctuate significantly and are influenced by various factors, there is no guarantee that a losing streak will end in a way that allows the strategy to recover all losses and yield a profit.
Is Martingale strategy risky?
Yes, the Martingale strategy is inherently risky. First and foremost, it demands a substantial capital base to endure a potential string of losses. A series of consecutive losses can quickly deplete your funds as you double your investment. Here are the steps that you can follow to minimize your risks:
Start with micro-investments to limit exponential loss. Start with the smallest possible trades instead of doubling large amounts. This keeps your losses from growing too fast, giving you more room to recover without draining your account.
Set a predefined loss cap before using the Martingale strategy. Plan ahead on how many losses you’ll take before stopping. This stops you from losing more by trying to win it back, a common mistake in the Martingale approach.
Combine the Martingale strategy with trend analysis. Check indicators like RSI to confirm the trend before using this strategy. Going against the trend makes losses add up quickly, so avoid using it in random or choppy markets.
Use Martingale only in specific market conditions. Use this strategy only when the market is calm, like during low-volatility periods. Try it with options that have short timeframes to limit risk and improve control over your trades.
Alternative strategies to the Martingale approach
For traders hesitant to take on the risks associated with the Martingale strategy, several alternative strategies provide a safer approach:
Anti-Martingale strategy (Reverse Martingale)
Instead of doubling after losses, traders double their investment after a winning trade. This helps to capitalize on winning streaks without exposing too much capital during losses.Paroli system
A more cautious strategy where you increase your investment incrementally after consecutive wins but reset to the initial amount after any loss.D’Alembert strategy
This involves increasing your trade size by a fixed amount after a loss and decreasing it after a win, offering a slower and steadier risk approach.
Tools and platforms for Martingale trading
Certain trading platforms provide features that support traders using the Martingale strategy:
Automated Martingale bots. Allow traders to implement the strategy without manual input, reducing stress.
Risk calculation tools. Some platforms offer calculators to estimate the capital required for Martingale trading based on expected market conditions.
Some of the best platforms for binary options that offer similar tools are:
| Demo | Min. deposit | Min. trade size | Min. Payout (%) | Max. Payout (%) | Foundation year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | 5 | 1 | 50 | 128 | 2017 | |
| Yes | 5 | 1 | 80 | 95 | 2012 | |
| Yes | 5 | 1 | 70 | 92 | 1999 | |
| Yes | 10 | 1 | 20 | 98 | 2019 | |
| Yes | 5 | 1 | 17 | 95 | 2013 |
Use scaled Martingale and trend tools for safer binary options trading
The Martingale strategy in binary options is not just about doubling after a loss — it’s about careful planning and smart risk-taking. Pick low-risk assets that stay steady, like currencies with low volatility. Start with small trades that can survive several losses in a row. Combine the Martingale strategy with tools like Bollinger Bands or Fibonacci levels to time your trades better. For instance, only double down when the price hits strong support or resistance levels confirmed by these indicators, so you’re not just guessing.
Try a “scaled Martingale” method instead of doubling every time. Increase your trade size by 50% or 75% instead of 100% to make losses smaller while still giving you a chance to recover profits. Use Martingale only when the market is calm, avoiding high-volatility sessions or major news events. With these adjustments, you can turn Martingale from risky into a smarter, more controlled strategy for binary options trading.
Conclusion
The Martingale strategy in binary options trading is both intriguing and polarizing. While its premise of recovering losses through incremental investments can seem appealing, the strategy comes with significant risks, including the potential for rapid capital depletion during losing streaks. It is not a foolproof method, and its effectiveness relies heavily on the trader's financial resources, market conditions, and risk tolerance.
For traders considering this strategy, incorporating robust risk management practices and setting clear boundaries is crucial. Exploring alternative strategies, such as the Anti-Martingale or D’Alembert methods, can offer more sustainable options for those looking to mitigate risks while aiming for profitability.
FAQs
Does Martingale work in trading?
The Martingale strategy can work in trading, but it is not foolproof. It carries significant risks and requires a substantial capital base to withstand potential losses.
What is the $10 Martingale strategy?
The $10 Martingale strategy is a variation of the Martingale strategy, where traders start with a $10 initial investment and double it after each losing trade. While the initial investment is lower, the same risks associated with the traditional Martingale strategy still apply.
How risky is Martingale in binary trading?
Martingale is very risky in binary trading. It can lead to rapid capital depletion and is not recommended for inexperienced traders or those with limited capital.
How profitable is Martingale?
The profitability of the Martingale strategy is not guaranteed. While it can be profitable in the short term, it is not a good long-term strategy due to the inherent risks involved.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Mikhail Vnuchkov joined Traders Union as an author in 2020. He began his professional career as a journalist-observer at a small online financial publication, where he covered global economic events and discussed their impact on the segment of financial investment, including investor income. With five years of experience in finance, Mikhail joined Traders Union team, where he is in charge of forming the pool of latest news for traders, who trade stocks, cryptocurrencies, Forex instruments and fixed income.
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Copy trading is an investing tactic where traders replicate the trading strategies of more experienced traders, automatically mirroring their trades in their own accounts to potentially achieve similar results.
Bollinger Bands (BBands) are a technical analysis tool that consists of three lines: a middle moving average and two outer bands that are typically set at a standard deviation away from the moving average. These bands help traders visualize potential price volatility and identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market.
Yield refers to the earnings or income derived from an investment. It mirrors the returns generated by owning assets such as stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments.
Risk management is a risk management model that involves controlling potential losses while maximizing profits. The main risk management tools are stop loss, take profit, calculation of position volume taking into account leverage and pip value.
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.






























































































































