SEC | The U.S. Financial Regulator
SEC is one of the 4 primary U.S. regulators and has the broadest powers to regulate the country’s financial sector. The regulator was created in 1934 and cooperates closely with government authorities.
A financial regulator is a government or non-government organization, which ensures that financial market participants observe the laws, norms, rules, and requirements of the jurisdiction. The regulator’s tasks are to maintain the integrity of the country’s financial system, stop violations, assist in the development of the risk management system, and promote the attractiveness of the jurisdiction in the eyes of international companies.
For a broker, holding a license means:
-
Competitive advantages. A license, as a documentary confirmation of the right to render brokerage services, improves the status and reputation of the broker in the eyes of potential clients.
-
Access to legal operations in the country’s financial ecosystem and the international community. The broker can count on its regulator and government bodies in resolving various issues, such as disputes, additional funding during a crisis, etc. Independent audits can help reveal potential risks before a problem occurs.
For a trader, a license is a guarantee that the broker indeed exists, goes through audits, and is supervised by the regulator. If there is a problem, the trader can always seek help from the regulator. A license testifies that the broker can be trusted.
In this post, TU explores the Commission’s objectives, resources, advantages, procedures for finding licenses on the website, and procedures for filing complaints, as well as reviews and an expert’s opinion of this regulator.
Description and functions of the SEC
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is one of the 4 primary U.S. regulators and has the broadest powers to regulate the country’s financial sector. The regulator was created in 1934 and cooperates closely with government authorities. The Commission’s executives are appointed by the U.S. President and approved by the Senate. One of the regulator’s main objectives is to set and enforce securities registration and compliance with its rules. The SEC oversees all companies, brokers, and investment and insurance funds that trade securities and derivatives in the exchange market. Recently, the regulator has also begun seeking leverage over the cryptocurrency market. Since 2008, the trading of CFDs (contracts for price difference that are popular in Forex ) in the USA has been strictly limited or banned.
Tasks and purposes of the SEC in the Forex market:
-
Enforce federal laws regarding financial markets.
-
Control the disclosure of corporate information that licensees must provide to investors.
-
Oversee private regulators and auditors.
-
Stop violations of clients’ rights and conflicts of interest.
-
Stop manipulations involving affiliated entities or financial statements.
-
Ensure that licensees operate transparently.
-
Supervise corporate acquisitions.
-
Develop legislation that regulates the issuance and turnover of securities and related assets.
-
Ensure that the U.S. securities market information is updated promptly. Inform investors and licensees’ clients about their rights, options, risks, etc.
The SEC controls all U.S. financial market participants: stock and commodity exchanges; over-the-counter (OTC) markets; all issuers of securities (shares, bonds, derivatives); hedge funds and asset management companies; exchange-traded, investment, retirement, and insurance funds; and all brokers and investment banks. Any transaction with securities is subject to supervision. The SEC also oversees investors. Every private investor that buys over 5% of shares of a company quoted on U.S. exchanges must register with the Commission.
To obtain an SEC license, a broker has to:
-
-
Pass qualification tests.
-
Comply with the Commission’s regulations. In particular, the SEC prohibits its licensees from cooperating with clients and investors from some countries and regions, such as Iran, Sudan, North Korea, and Crimea.
There are separate requirements for each type of activity that can be reviewed on the regulator’s website. Outside the U.S., the SEC is also one of the most influential regulators. It has over 4,500 people on the staff, 5 departments, more than 20 offices, and 10 regional branches across the USA.
Official website and available information
Overview of the SEC website:
-
Upper main menu.

Upper main menu
1FINRA – The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority;
NASAA – The North American Securities Administrators Association
-
An information section that consists of several parts and provides a brief description of the regulator’s primary objectives,: which are to inform and service consumers, enforce federal laws, regulate markets, etc. Here you can also find the latest legal proceedings, investigations, and news.
An information section
-
Footer. It partially repeats information from the upper menu and includes contacts and the site map.
The Footer
Main menu structure:
-
About the SEC. Information about the regulator’s objectives, tasks, and management team.
-
Divisions & Offices. The Commission has several departments responsible for separate fields of supervision. This section contains contact information and links to the Commission’s divisions and offices.
-
Enforcement. Investigations, administrative proceedings, information for harmed investors, etc.
-
Regulation. Principles and guidelines.
-
Education. Information for novice investors.
-
Filings. Licensees' documentation, EDGAR2 search rules, and requests for public information about licensees.
-
News. An information section about current events, changes in regulations, etc.
“Filings” and “Enforcement” are the most important sections for investors. “Filings” feature the rules for using EDGAR. All this regulator’s information about its licensees is public. Every investor can find licenses, statements, information about securities, and a lot more. The “Enforcement” section features links, filters for searching for investigations, and complaint submission forms.
How to confirm a broker’s license on the SEC website
The U.S. system for registration and licensing differs drastically from the European system. The U.S. market is strictly structured and regulated not only by special laws, but also bylaws. Finding information about a broker by its name or license number is not enough. You also need to understand what this information means and how it can help a trader.
To confirm a broker’s license on the SEC website, do the following:
Option A:
-
1
Find an SEC-licensed broker. It is preferable to know the license number or other details by which the license could be found on the SEC website. Redirection is even better. The license number can be in the About Us the SEC section or the footer of the broker’s website.
2EDGAR – the Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis, and Retrieval system
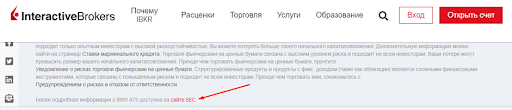
Information about SEC regulation in the footer of the website
-
2
Go to the SEC website via the link and find the license by the broker’s legal name.
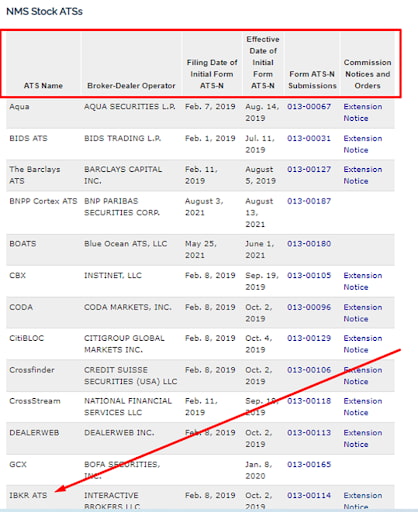
The information about broker’s licence on the SEC website.
-
3
View the information. In this case, the document includes the date until which the SEC can refuse to register the broker after reviewing the Form ATS-N.

The information about broker’s licence
Form ATS-N comprises 21 pages and contains a few dozen questions.

Form ATS-N
Option B:
-
1
On the SEC website, go to “Company Filings”.

The SEC website
-
2
Click “More Options”.
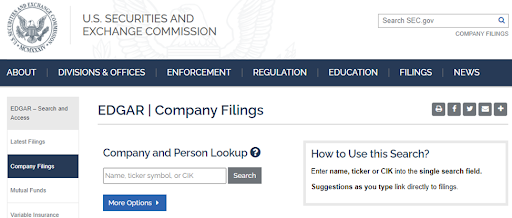
Company Filings section
-
3
Enter the broker’s legal name or other details.
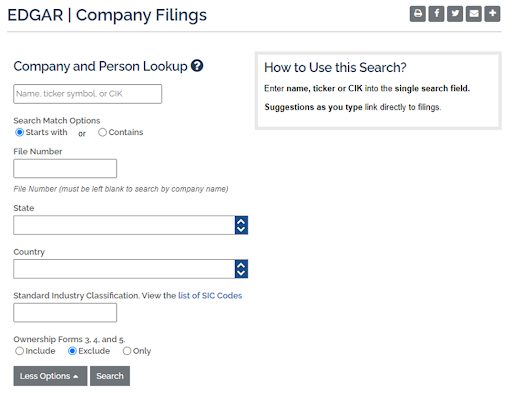
EDGAR Company Filings
-
4
Review the results.
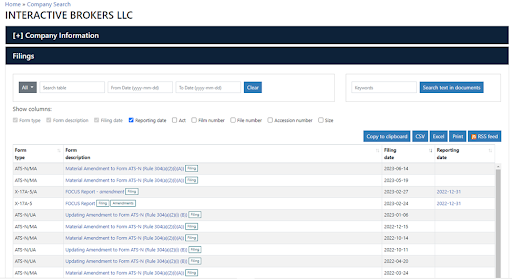
The results of searching
The broker has a Central Index Key (CIK) number that is uniquely assigned by the SEC. It means the company is registered with the SEC and has an individual number by which the broker’s documentation can be found in EDGAR.
Commission’s basic requirements for brokers
Basic requirements to obtain a license:
-
Fully disclose information about the company, its operation, plans, and risk management system.
-
Register with authorities associated with the SEC.
-
The broker’s executives must confirm their qualifications.
Brokers must operate as transparently as possible and meet the regulator’s requirements. The SEC can raise claims in cases of manipulations with liquidity or segregated client accounts, withheld information that could influence a trader’s decisions, misinformation, fraud, etc. The Commission’s objective is to protect the rights and interests of traders.
SEC license | Pros and cons
An SEC license is a broker’s pass to U.S. markets. For European brokers that are not going to operate in the USA, obtaining an SEC license makes no sense, as it would be uneconomic and would take away several competitive advantages due to the strictness of its requirements. But without an SEC license, a broker does not have the right to operate in the USA. That is why brokers do the following. They open several branches and obtain licenses from several regulators. A broker’s division in the U.S. acquires an SEC license and renders securities trading services in the exchange and OTC markets. A European division acquires a license from CySEC, the FCA , or BaFin and offers CFD trading, which is practically prohibited in the USA. A trader should make sure that the license corresponds to the broker’s division with which he concludes an agreement.
Advantages of trading with an SEC-licensed broker:
-
Access to the U.S. stock market. Due to the closed nature of the country’s financial system, brokers with licenses from other countries cannot operate in the USA. Their clients don’t trade actual securities, but CFDs on securities. However, if a broker has an SEC license, it can provide real assets for trading.
-
Segregation of accounts. Punishment for violating the account segregation rules is strict – the license is revoked.
-
Brokers are audited by the “Big Four” accounting firms. A system of private regulators and auditors is also developed in the USA.
An SEC license confirms that the broker is registered in the U.S., has a CIK number, is in the EDGAR database, and is registered in databases of other regulators. A trader only has to understand which types of services the broker can render in compliance with the license.
Disadvantages of trading with an SEC-licensed broker:
For a trader, an SEC license means more expenses that are partially passed on to him by the broker. Stock market participants pay repository, exchange, and clearing fees and have to cover contributions to the regulator. The U.S. has an investor grading system intended to prevent novice investors from putting all their money into high-risk assets. To obtain a status analogous to “a qualified/accredited investor”, a trader has to show an annual turnover of at least $200,000 and confirm his qualification. Without this status, traders are granted limited access to assets and leverage. Becoming a market participant may cost several thousand U.S. dollars.
SEC jurisdiction
The SEC is a government regulator that supervises the whole U.S. stock market and controls all exchange and OTC transactions with assets defined as “stock instruments”. The Commission cooperates closely with other government and non-government regulators (such as the CFTC3 and FINRA), can get information from the Federal Reserve and the FBI, and works with whistleblowers.
An SEC license only applies to the USA. Most brokers with registrations and licenses from other countries are prohibited from providing services in the USA. In the same way, there are limits on operating in Europe for U.S. brokers with SEC licenses.
Submission and consideration of complaints
The SEC website offers various ways to file complaints: through social media, at an address included in the website’s footer, and with separate departments and offices depending on the type of complaint and the investor’s location. The SEC considers complaints by private traders and offers monetary awards to everyone who can point at law violations by brokers. Below is an optional method.
-
1
In the main menu, go to “Enforcement” and select “Information for Harmed Investors”.
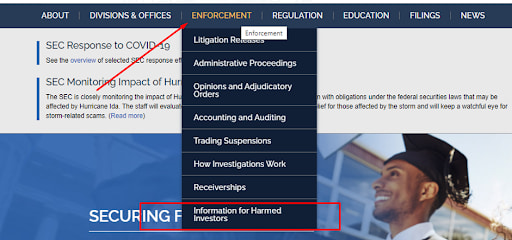
Information for Harmed Investors
3The CFTC – The Commodity Futures Trading Commission
-
2
In the left menu, select “Tips & Complaints”.
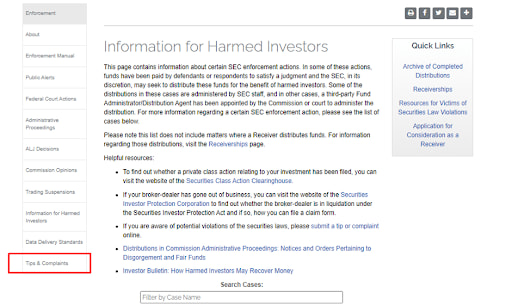
Tips & Complaints
-
3
Read the recommendations.
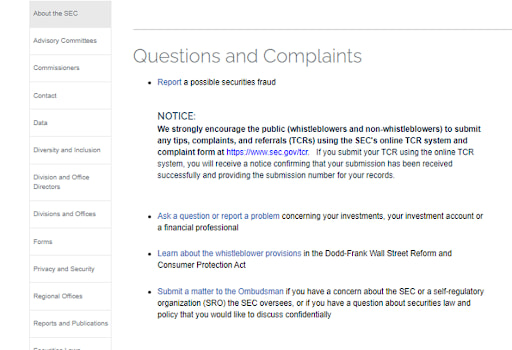
The recommendations
The two previous screenshots show recommendations and links to complaint submission forms. A section in which you can file a complaint is in the screenshot below.
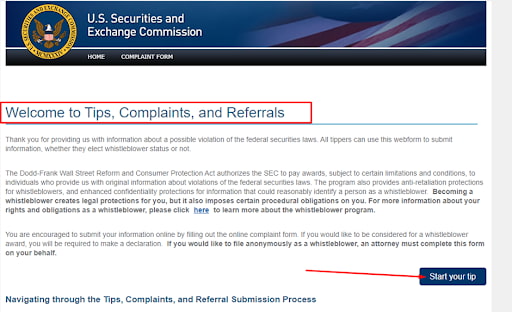
Complaint submission form
How to research an SEC-licensed broker
In this section, you can view all valid licenses held by brokers, including SEC licenses. Every month, TU’s analysts visit regulators’ websites and update information in broker reviews. If a broker has several licenses, you don’t need to look for information about them on several websites. You don’t need to compare legal names in an offer and license. TU’s analysts do all this for you. And if a regulator publishes a warning to a broker, you will learn about this at once.
Reviews of the SEC by complaining investors and traders
This is what private traders think about the SEC.
Anton, trader, St. Petersburg
I haven’t heard about any other regulator as much as I’ve heard about the SEC. There are hundreds of stories on the internet about the way the Commission works. For me, this is the main reason to trust SEC-licensed brokers.
Sergey, trader | Vladikavkaz, Russian Autonomous Republic of Alania
An SEC license is great, but only U.S. brokers can have it. For our traders, it’s easier to trade CFDs on currency pairs or stocks with traditional brokers and pay minimal fees. Initial deposits aren’t high and leverage isn’t 1:20 like in the USA. And for those who want to buy stock indexes or Facebook shares directly, there is FinEx ETF (exchange-traded funds). The SEC is for U.S. residents only.
Roman, cryptocurrency trader, Moscow
I think the SEC is a manipulator. I’ve been dealing with crypto for more than 3 years and I haven’t seen the Commission do anything good – they only get in the way of making money. Here’s why I think so:
-
As before, the cryptocurrency market works without any regulators. All the Commission's attempts to prohibit something are like fighting windmills. Crypto develops at a huge speed. ICOs (initial coin offerings) were followed by DeFi (decentralized finance) and IDOs (initial coin offerings on decentralized exchanges). The SEC has no control over these processes, but tries to intervene.
-
There are hundreds of fake crypto startups! Where is the regulator? I would understand if the SEC admitted they couldn’t do anything and didn’t intervene. But the regulator keeps getting involved. Consider complaints against Ripple in 2021, for example. The case went to court where it will probably stay for several years. Does anyone benefit from that?
-
On many occasions, the Commission’s allegations stirred the pot. And it seems like it all was done solely to increase crypto’s volatility so that someone could profit from it.
Cryptocurrency laws still haven’t been developed in the USA. Bitcoin ETF is another long story in which the SEC keeps having difficulties. In summary, the SEC may be useful in the stock and currency markets, but as far as crypto goes, the Commission causes nothing but trouble.
Igor, trader, Moscow
The thing I like the most about the U.S. regulatory system is its closed nature. European Forex brokers acquire offshore licenses and it supposedly means they are licensed and can render services to residents of Europe and Asia. This is partially true, but, in Europe, they are simply not controlled by anybody. In the U.S., no broker can operate without an SEC license. The regulator doesn’t let any strangers into its territory; you either get a license or don’t work there. While a broker with an FSC Belize license, for example, can provide services to residents of Russia, U.S. brokers work with non-residents only through an “introducing brokers” program. The SEC doesn’t care whose license a broker holds. Licensing in the U.S. is mandatory. And for European brokers, obtaining an SEC license and not operating in the U.S. makes no sense; it’s too expensive. In short, regulation in the USA is truly reliable. But considering the fees, trading in the U.S. market is costly for ordinary traders like us.
Constantin, trader, Kharkiv
I agree that, on the internet, there are a lot of examples of the Commission’s positive work. But for every 10 small victories, the SEC has 1 big failure. For example, in 2011, the regulator missed violations and bankruptcy of MF Global, the 7th largest U.S. broker by the value of assets; and not just missed it. The broker played too long with government debt instruments to which it had access through repurchase agreements. As a result of a crisis in Greece that affected other European countries, MF Global had insufficient proprietary assets to cover the debts and used client money, breaking the client funds segregation rule. The SEC didn’t notice the risks or the segregation rule breach. Consequently, $700 million went missing from clients’ accounts. MF Global had $41 billion worth of assets and a $39.7 billion debt. Plus, the broker’s auditor was PwC, one of the “Big Four” accounting firms. Neither the auditor nor the regulator noticed anything askew.
Expert’s assessment
The SEC is deemed to be the strictest, most reputable, and most serious regulator in the world, although its mandate only applies to the USA. The Commission is subordinate to the U.S. President and Senate and, alongside the Federal Reserve, embodies the stability of the country’s financial system. For this reason, the SEC has unlimited powers. The Commission imposes fines, initiates bankruptcies, represents prosecutions in courts, etc. Every month, there is new information on the internet about the regulator’s high-profile investigations or fines. And the licensee’s reputation doesn’t matter. If you commit a violation, you have to pay or leave the market. FXCM , formerly the largest Forex broker in the U.S., is a case in point. In 2017, after 4 years of investigation, the SEC revoked the company’s license and fined it $7 million for deceiving its clients. The broker lost the whole U.S. market.
The SEC is unique in the way it influences global financial markets. The Commission’s reports, high-profile investigations, and fines are fundamental factors that affect quotes of indexes or currencies. Lately, the regulator has been putting pressure on cryptocurrencies that are equated with securities. Notable examples include Pavel Durov’s TON (Telegram Open Network) and Mark Zuckerberg’s Libra which had to shut down after being inspected by the regulator.
Conclusion
By strictly enforcing its mandate and regulation and U.S. federal laws, the SEC is comparable to European National Banks. Every year, the Commission imposes fines in the amount of $3-4 billion. In Europe and Asia, regulators are more like assistants to National Banks; they have no leverage over licensees. In the U.S., the SEC is an independent regulator and one of the central authorities that undergirds and protects the country’s entire financial system.
FAQs
What is the SEC?
The SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission) is a government agency that supervises all stock market participants, including exchanges and brokers, and monitors transactions with assets treated as securities. The regulator’s tasks are to ensure maximal market transparency and equal conditions for competition; protect investors’ rights; and take measures to prevent manipulations. The Commission imposes a fine for any violation by a broker or an investor.
What do I get from trading with SEC-licensed Forex brokers?
-
1
An SEC license means that the broker is fully controlled by the U.S. government regulatory system, its details are in the Commission’s EDGAR database, and it’s registered with FINRA. Mandatory external audits are an additional guarantee for traders.
-
2
Accounts are segregated. Traders are protected from the broker’s bankruptcy or violations.
For traders, an SEC license is proof that a broker has the right to render services in the USA and can have direct access to U.S. stock and commodity exchanges. If the broker doesn’t have such a license, it cannot operate in the USA or provide services to residents of the USA.
How to check if a broker holds a a SEC license?
Two options:
-
1
Use the broker’s legal name or CIK number to find all documents with correspondence between the broker and the SEC. In the information found, see which type of activity the broker can perform and for how long.
-
2
Find a review of the broker on the Traders Union website. Every month, TU analysts update information about all valid licenses held by brokers. If the regulator issues a warning to the broker or takes other action, you will see it in its review on the TU website.
How to submit a complaint against a broker to the SEC?
-
1
On the SEC website’s homepage, go to “Enforcement” and select “Information for Harmed Investors”. Follow recommendations to open and fill out a complaint submission form.
-
2
Before going through the long procedure for lodging a complaint with the SEC and verification, contact TU’s legal department. Every TU member is entitled to free help in cases of disputes with brokers. TU’s lawyers are ready to defend investors’ interests and help you properly prepare a complaint against a broker on the SEC website.
Team that worked on the article
Oleg Tkachenko is an economic analyst and risk manager having more than 14 years of experience in working with systemically important banks, investment companies, and analytical platforms. He has been a Traders Union analyst since 2018. His primary specialties are analysis and prediction of price tendencies in the Forex, stock, commodity, and cryptocurrency markets, as well as the development of trading strategies and individual risk management systems. He also analyzes nonstandard investing markets and studies trading psychology.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
The topics he covers include trading signals, cryptocurrencies, Forex brokers, stock brokers, expert advisors, binary options. He has also worked on the ratings of brokers and many other materials.
Dr. BJ Johnson’s motto: It always seems impossible until it’s done. You can do it.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO). Mirjan is a cryptocurrency and stock trader. This deep understanding of the finance sector allows her to create informative and engaging content that helps readers easily navigate the complexities of the crypto world.









