Quantitative Trading - What Is It And How To Get Started



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
Quantitative Trading is an investment method that uses mathematical and statistical models to make trading decisions, with common types including:
- Statistical Arbitrage - uses statistical models to identify and exploit market anomalies.
- Mean Reversion - assumes that the prices of stocks and other assets will revert to their average value over time.
- Momentum Trading - assets showing high returns in the past will continue to show high returns in the future.
Quantitative Trading is a modern approach to investing that combines the power of mathematical models and computing technology. Using algorithms, quantitative traders analyze market trends and make decisions with high accuracy and speed. Due to its high objectivity and accuracy, this method provides automation of trading processes and allows for high efficiency and ability to quickly adapt to changing market conditions.
What is quantitative trading
Quantitative trading is a trading style based on the application of mathematical and statistical models. Unlike traditional methods that rely on intuition and subjective judgments, quantitative trading uses data and algorithms to analyze markets and predict future price movements.
The key steps for undertaking quantitative trading include collecting and processing large volumes of data, creating models to identify market patterns, and automating the trading process. Quantitative traders often use complex algorithms and programs to analyze historical data, identify trends and anomalies, and test hypotheses based on this data. One crucial aspect is backtesting, which is the process of validating a model on historical data to assess its effectiveness and reliability.
Quantitative trading has replaced the task of trend forecasting with the search for the optimal Sharpe ratio - a set of trading assets and strategies that will bring profits in any market conditions.
The advantage of quantitative trading is a long-established fact. Investment hedge funds have been creating quantitative algorithmic strategies for more than 50 years, and the most famous example is George Soros. He was the first retail trader who proved the ineffectiveness of fundamental and technical analysis: his success on the failure of British monetary policy was qualitatively modeled in advance.
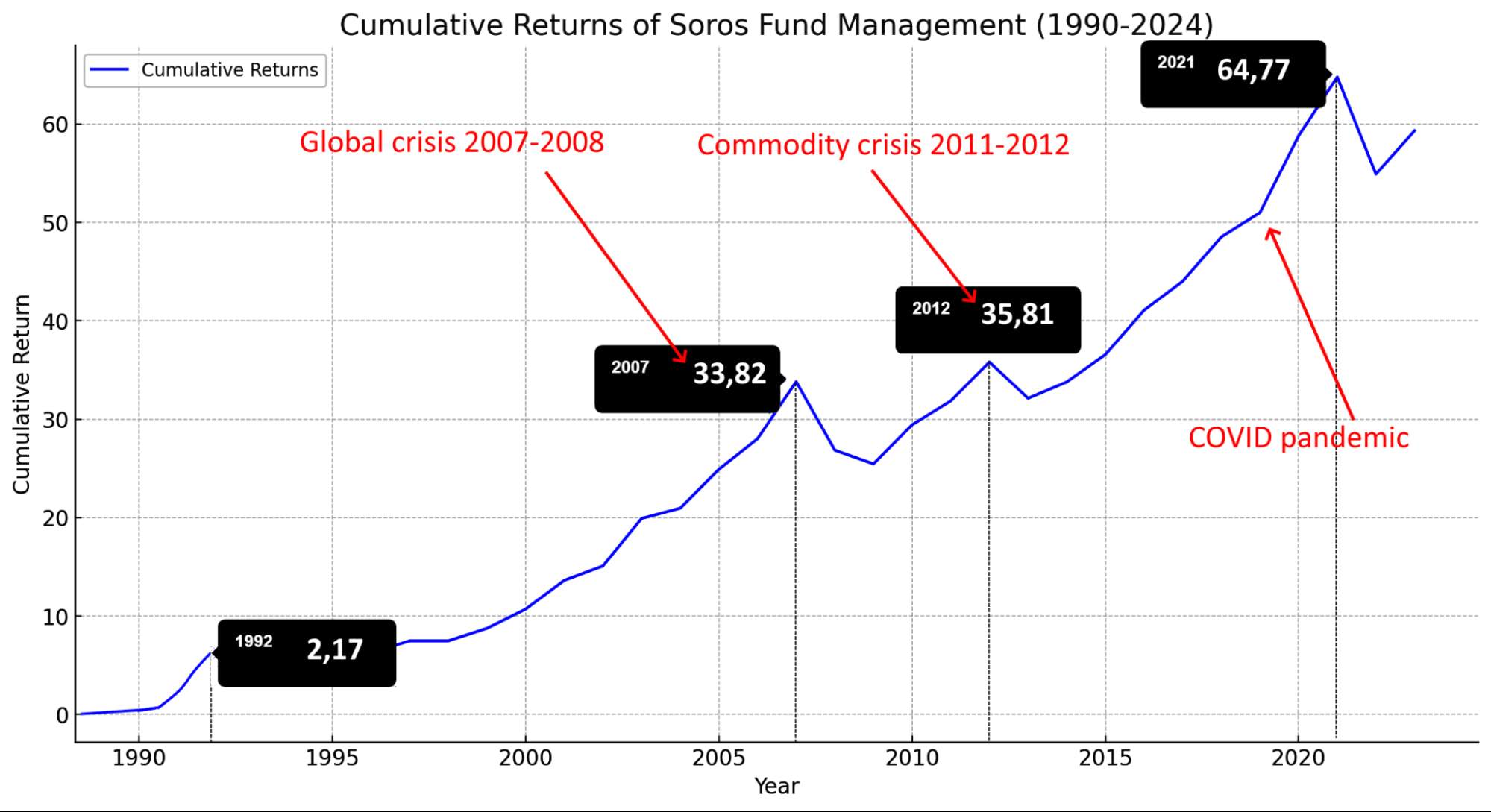
For almost 50 years, Soros Fund Management's stable annualized return is over 20%. Note: Soros, unlike other market monsters such as Berkshire Hathaway, successfully speculates on all types of market assets, including cryptocurrency (since April 2018).
The use of quantitative models in trading offers numerous advantages:
Objectivity and accuracy. Quantitative models eliminate human bias, reducing the likelihood of subjective errors and emotional decisions. Mathematical algorithms make decisions based on data, making the process more objective and reliable.
Speed and efficiency. Algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and make decisions in milliseconds, which is beyond human capability. This allows quantitative traders to respond quickly to market changes and capitalize on short-term opportunities.
Risk management. Quantitative models often include risk management mechanisms that help minimize potential losses. This is achieved through precise risk calculations and optimal capital allocation.
Access to new strategies. The use of sophisticated algorithms enables the implementation of strategies that are difficult to execute manually. This can include high-frequency trading, arbitrage, and other complex methods, which open up new opportunities for profit.
How to start quantitative trading — tips for traders
For those looking to start quantitative trading, the following tips can be highly useful:
Importance of backtesting and data analysis. Backtesting is the process of testing trading strategies on historical data. It helps evaluate the effectiveness and reliability of strategies. Using tools like Python and R can significantly improve the quality of analysis.
Risk management. Quantitative trading requires strict risk management. Develop capital management strategies and set rules to limit losses, including using stop-loss orders and hedging positions. Consider market volatility and be prepared for unexpected price changes.
Learning and self-education. Successful quantitative trading requires knowledge in mathematics, statistics, and programming. Study the basics of these disciplines through courses, books, and online resources to acquire the necessary skills.
Using specialized software. Leverage specialized software and trading platforms like MetaTrader, TradeStation, and QuantConnect for creating, testing, and automating strategies. These platforms also provide access to historical data and the ability to integrate custom algorithms.
Constant monitoring and adaptation. Markets constantly change, so strategies need to be flexible. Regularly analyze results and be prepared to adapt your models to maintain their relevance and effectiveness.
For you to test your skills and strategies in Quantitative Trading, we have provided a list of the top brokers offering a wide range of assets, including stocks, bonds and currency pairs.
| Plus500 | Pepperstone | OANDA | FOREX.com | Interactive Brokers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Availability of quantitative trading |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Min. deposit, $ |
100 | No | No | 100 | No |
|
Max. leverage |
1:300 | 1:500 | 1:200 | 1:50 | 1:30 |
|
ECN Spread EUR/USD |
No | 0,1 | 0,15 | 0,2 | 0,2 |
|
Scalping |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Trading bots (EAs) |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Open account |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Study review | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Key quant trading strategies
Statistical arbitrage (StatArb) is a trading method that uses statistical models to identify and exploit market anomalies. StatArb strategies are based on analyzing historical data to determine pairs trading opportunities, where one stock can be bought and the other sold based on historical correlations. An example of successful StatArb application is Renaissance Technologies, known for its highly successful trading strategies based on complex mathematical models and big data analysis. Learn more in our article Arbitrage Trading in Forex: The Ultimate Guide.
Mean reversion is a strategy that assumes that the prices of stocks and other assets will revert to their average value over time. This strategy uses statistical methods to identify deviations from the mean and trades based on the assumption that the price will return to the average level. For example, Bridgewater Associates, managed by Ray Dalio, successfully applies Mean Reversion strategies in its portfolio, using historical data and economic indicators to make trading decisions.
Momentum trading is a strategy based on the idea that assets showing high returns in the past will continue to show high returns in the future. Traders using the Momentum strategy buy assets with an upward trend and sell them when the trend starts to weaken. An example of successful application of this strategy is AQR Capital Management, which uses quantitative models to analyze market trends and execute trades based on momentum. You can find out more information about momentum trading on our website.
Types of quantitative trading
Quantitative Trading provides the foundation for the following forms of automation, providing the mathematical and statistical tools needed to develop effective trading algorithms and systems.
Algorithmic trading - involves performing trading operations with minimal human participation, relying on the use of algorithms and programs. The algorithms used in this method are based on mathematical and statistical models developed by quantitative traders. These models analyze large amounts of data, identify trading opportunities, and automatically execute trades based on predetermined conditions. An example is the use of Statistical Arbitrage and Mean Reversion strategies, which are used in algorithmic trading.
High-frequency trading (HFT) - is a form of algorithmic trading that involves executing a large number of trades in very short periods of time, often measured in milliseconds. HFT is also based on Quantitative Trading as it also relies on complex mathematical models and algorithms to quickly analyze market data and execute trades. HFT is used to profit from the slightest price fluctuations using high speed and low latency.
Automated trading - performing trading operations without the direct intervention of a trader using software. Automated systems can monitor markets, analyze data and execute trades in real time, providing high accuracy and speed. An example of automated trading is trading platforms such as MetaTrader and TradeStation. They allow you to create and run algorithmic strategies based on quantitative models.
Never compromise data quality as a quantitative trader
Quantitative trading has revolutionized the financial markets. As an expert in this field, I believe that using mathematical models and data analysis in making trading decisions can materially change the results achieved from your trading setup.
The most important piece of advice for new quantitative traders is to never underestimate the importance of data quality. Clean and accurate data is the foundation of any reliable trading model. Additionally, always prioritize risk management. Even the most sophisticated models can fail if risks are not managed properly. Implementing stop loss orders and diversifying your strategies can help mitigate potential losses.
Finally, always be open to new things and adaptable. Financial markets are dynamic, and strategies that work today may not work tomorrow. Constantly monitor your strategies, improve your models, and stay abreast of the latest developments in quantitative finance to gain a competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Quantitative trading is a powerful tool for modern traders that allows for the use of mathematical models and data to trade profitably. This approach provides objectivity, accuracy and the ability to automate, which significantly improves trading efficiency.
To get started successfully in quantitative trading, it is important to pay attention to backtesting, risk management and continuous learning. The use of specialized software and platforms also plays a key role in the development and implementation of strategies.
Quantitative trading requires discipline and analytical thinking, but with the right approach it can lead to significant financial gains. Be prepared to continually monitor and adapt your strategies to stay relevant in ever-changing market conditions.
FAQs
What are the main strategies used in Quantitative Trading?
Common strategies in quantitative trading include Statistical Arbitrage, Mean Reversion, and Momentum Trading. These strategies rely on complex algorithms and models to identify and exploit market anomalies and trends.
What skills are necessary for successful Quantitative Trading?
Successful quantitative trading requires knowledge in mathematics, statistics, and programming. Skills in data analysis and backtesting are also important. Traders need to develop and optimize trading models, manage risks, and adapt strategies to changing market conditions.
What advantages does Quantitative Trading offer?
Quantitative Trading offers objectivity and accuracy in decision-making, automation of the trading process, and the ability to analyze large volumes of data. This allows traders to respond quickly to market changes, manage risks, and use sophisticated trading strategies, potentially leading to increased profitability.
What data is used in quantitative trading?
Quantitative trading uses historical data such as prices, trading volumes, financial reports and market indicators. News and macroeconomic indicators may also be taken into account.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Parshwa is a content expert and finance professional possessing deep knowledge of stock and options trading, technical and fundamental analysis, and equity research. As a Chartered Accountant Finalist, Parshwa also has expertise in Forex, crypto trading, and personal taxation. His experience is showcased by a prolific body of over 100 articles on Forex, crypto, equity, and personal finance, alongside personalized advisory roles in tax consultation.

Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Economic indicators — a tool of fundamental analysis that allows to assess the state of an economic entity or the economy as a whole, as well as to make a forecast. These include: GDP, discount rates, inflation data, unemployment statistics, industrial production data, consumer price indices, etc.
Algorithmic trading is an advanced method that relies on advanced coding and formulas based on a mathematical model. However, compared to traditional trading methods, the process differs by being automated.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that relies on cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology.
The deviation is a statistical measure of how much a set of data varies from the mean or average value. In forex trading, this measure is often calculated using standard deviation that helps traders in assessing the degree of variability or volatility in currency price movements.
Quantitative trading consists of trading strategies based on quantitative analysis, which rely on mathematical computations and number crunching to identify trading opportunities.






























































































































