How To Use The Zig Zag Indicator



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
The zig zag indicator filters out minor price fluctuations to help traders focus on meaningful trends and structural shifts. It connects major highs and lows based on percentage or point changes, revealing swing patterns and trend strength. While not predictive, it offers powerful insights into momentum and trend health when combined with price action or Fibonacci tools.
The zig zag indicator is not built to forecast. It is made to cut the noise and help you focus on structure. Traders often worry about every minor move and end up missing the bigger picture. Zig zag filters that out and highlights the major turning points based on the size of the moves. But its real value is not in the lines, it is in what they say about how the market breathes. If those swings start getting shorter in an uptrend or stretch longer in a downtrend, that can hint the trend is shifting before it becomes obvious. In this article, we will discuss this trend-filtering indicator in detail, covering its origin, key components, and top trading strategies.
Introduction to zig zag indicator
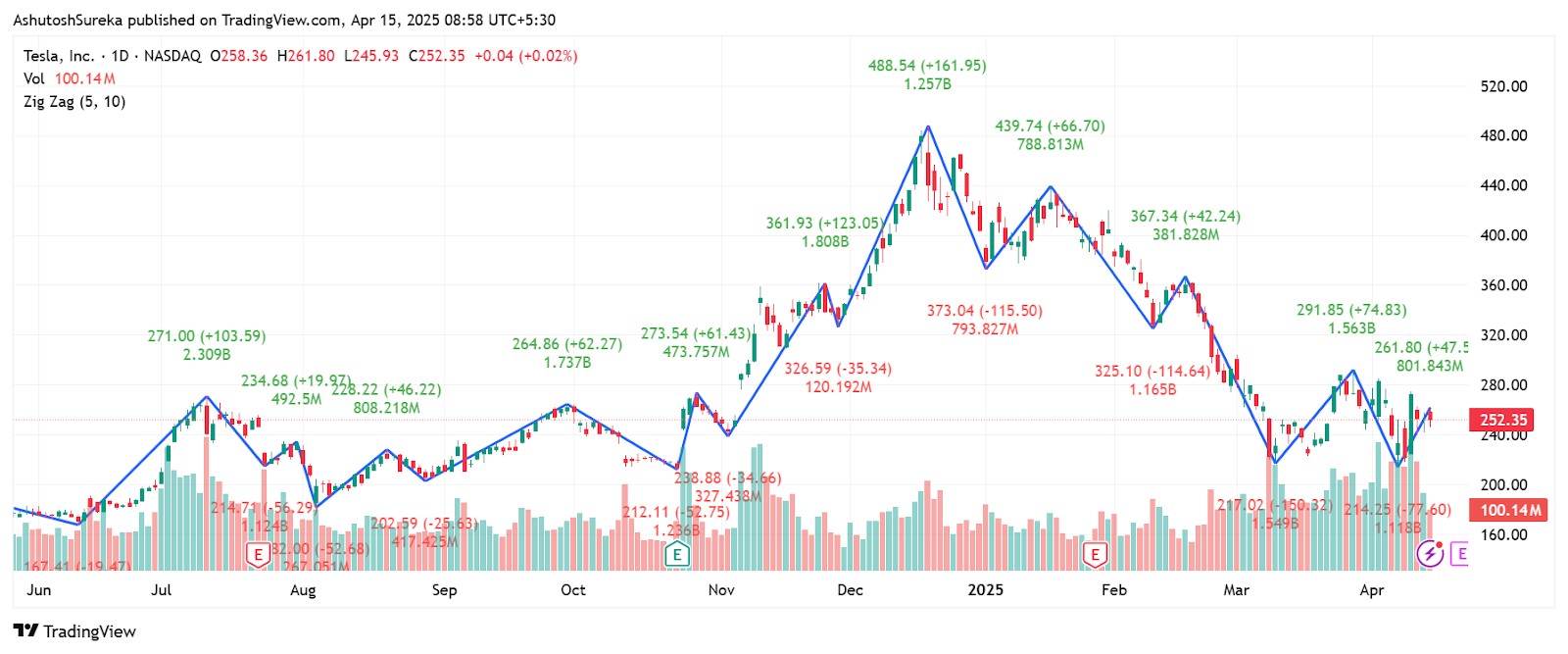
The zig zag indicator is a chart analysis tool used to filter out minor price movements and highlight major trends. It simplifies market structure by drawing straight lines between significant highs and lows, making it easier to spot patterns, swings, and overall direction.
Unlike moving averages or oscillators, this indicator does not predict future movement; it reacts only after price changes. This makes it useful for analyzing historical swings, measuring retracements, or confirming chart patterns like head and shoulders or Elliott waves.
What does zig zag show
Filters out small, random price noise.
Connects swing highs and swing lows with clean lines.
Helps identify wave patterns, support and resistance levels.
Makes trend direction and reversal zones easier to spot.
Origin and development of zig zag indicator
This trend filtering tool (zig zag) indicator has been around since the early days of technical charting. It was created to help analysts and traders visually separate meaningful market moves from insignificant fluctuations. Though it isn’t attributed to a specific person, it evolved over time through early market theory and price action analysis.
Why it was introduced
Traders needed a way to reduce chart clutter and highlight clean price movement.
The tool was designed to ignore minor fluctuations and help focus on key swing points.
It became popular as part of Elliott Wave Theory and pattern recognition strategies.
How it became useful
Originally used in manual chart drawing, later built into charting platforms.
Became a core part of swing trading, wave analysis, and pattern studies.
Still widely used to confirm structure, measure retracement levels, and analyze past trends.
Understanding the components of zig zag indicator
Zig zag indicator is built around one simple idea: filtering out smaller price movements and focusing only on major turning points. It does this by connecting significant highs and lows based on a set percentage or value, making the chart easier to read for trend and pattern recognition.
Although it appears as just a set of angled lines on the chart, this indicator depends on a few core components that control how it behaves and what it shows.
Key components of zig zag
1. Deviation or threshold
This setting defines the minimum price change needed for the indicator to draw a new line.
It can be set as a percentage (like 5 percent) or in points.
If the price does not move beyond this amount, the indicator ignores it.
2. Depth or lookback period
This controls how far back the indicator searches to find highs and lows.
A longer depth smooths the chart and focuses on major swings.
A shorter depth makes the indicator more sensitive to smaller moves.
3. Reversal amount
This value tells the indicator when to switch direction and plot the next leg.
For example, if set to 10 percent, the price must reverse by at least 10 percent from a high or low for the next point to be drawn.
It helps determine when a swing is large enough to matter.
How it all works together
The tool starts by plotting the first confirmed high or low.
It then connects the next valid swing only if the price has changed enough based on the reversal setting.
The result is a cleaner view of the trend, removing minor fluctuations that distract from the big picture.
How to apply zig zag on a chart
Zig zag indicator is available on most trading platforms and is very easy to use. It draws lines between key highs and lows based on a set percentage or point change. Once added to the chart, you can adjust the sensitivity using a few simple settings.
Access the indicator
Setting up the Zig Zag indicator on your chart is simple and quick.
Steps to follow
Open the indicators or tools section on your trading platform.
Search for “Zig Zag” in the available options.
Select and apply it to your chart; the line will show in a separate panel beneath the main chart area.
Platform availability
You will find Zig Zag already built into platforms like TradingView, MetaTrader 4 and 5, ThinkorSwim, and most major charting software; no extra downloads or installations needed.
Changing the inputs
While the indicator is simple, tuning the parameters helps match it to your timeframe and strategy.
What you can adjust
Deviation (percentage or points)
Sets the minimum move required before a line is drawn. A higher value means fewer, more meaningful swings.Depth (or lookback)
This defines how far back the tool looks to compare price. A longer depth gives a smoother line that focuses only on larger moves.Backstep (if available)
A setting used in some versions of zig zag to prevent very small reversals from being counted
Tips for setup
Use a higher deviation on higher timeframes to avoid noise.
Test on different charts to see which values give a clean, useful structure.
Combine with Fibonacci, support and resistance, or trendlines for better trade setups.
Trading strategies using zig zag indicator
Zig zag is a great tool for identifying market structure, spotting patterns, and filtering out noise. While it doesn’t give signals on its own, it works well when combined with support and resistance levels, Fibonacci tools, or candlestick formations. Traders mainly use it to analyze trends, confirm breakouts, and measure pullbacks.
Fibonacci retracement with zig zag confirmation
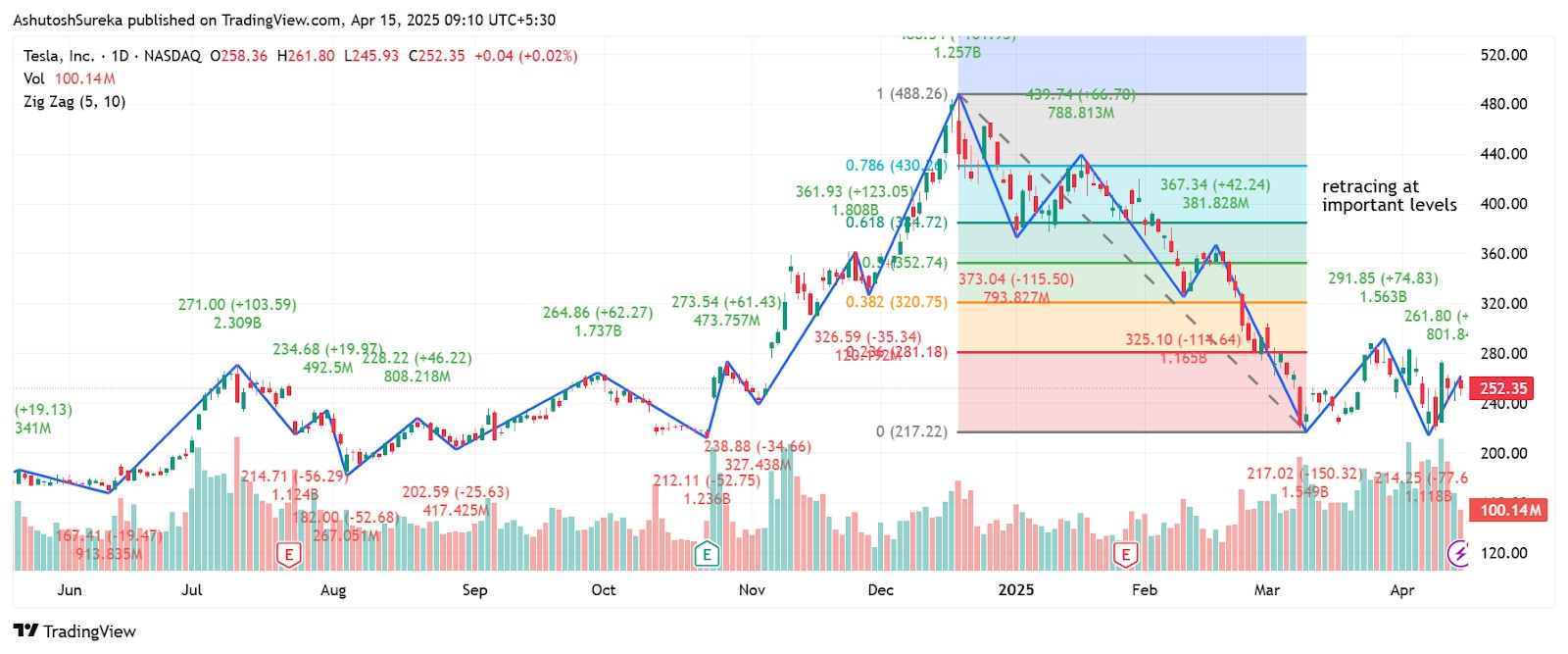
Zig zag helps mark the swing points needed to draw accurate Fibonacci levels.
How to apply it
Use the tool to mark a clear high and low.
Draw a Fibonacci retracement from swing low to swing high (or vice versa).
Watch for price to react at 38.2, 50, or 61.8 levels.
Confirm with a bounce or candlestick signal.
Why it helps
Avoids guessing on where to draw your Fib levels.
Matches structure with common retracement zones.
Gives more confidence in pullback trades.
Chart pattern recognition strategy
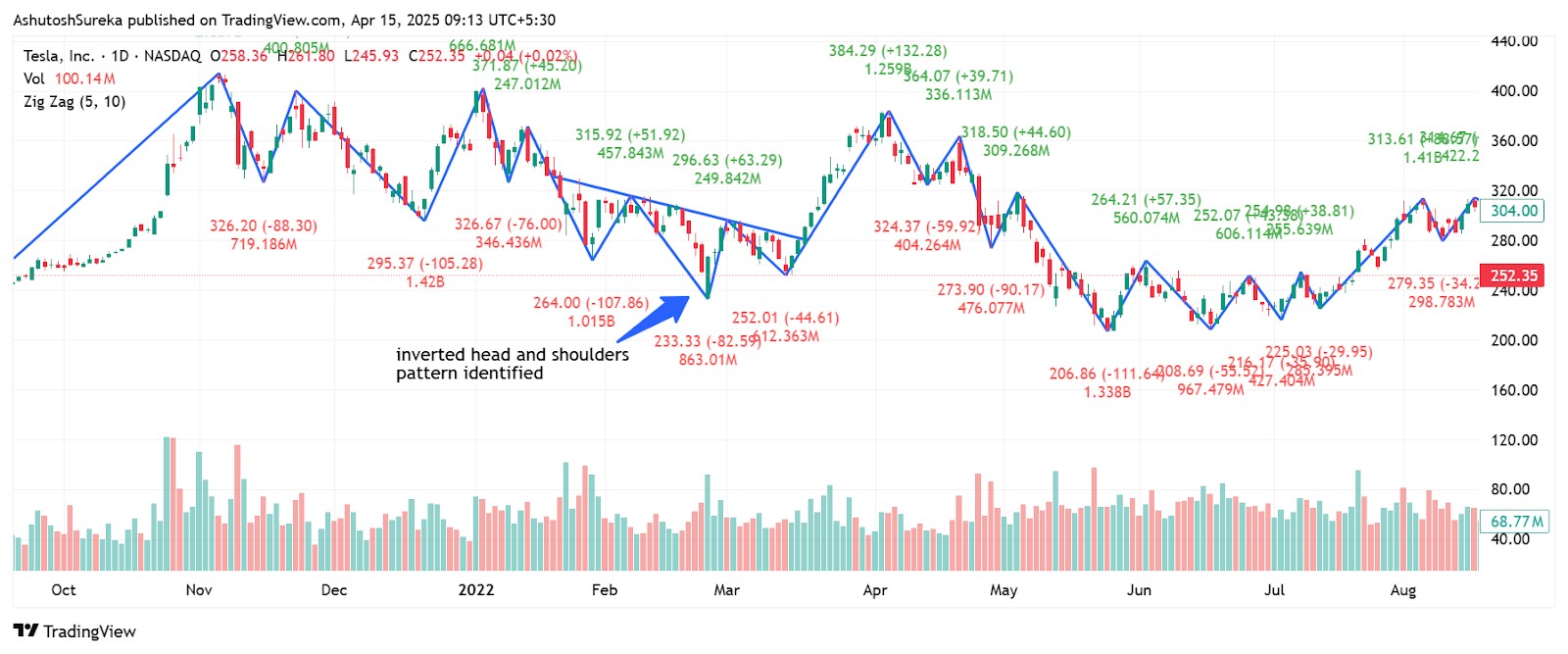
Zig zag makes it easier to see patterns like double tops, head and shoulders, or triangles.
How to apply it
Let zig zag outline the price structure.
Look for repeating shapes like M and W patterns, triangles, or channels.
Wait for a breakout beyond the pattern before entering.
Use price action to time your entry and stop placement.
Why it helps
Clears up the visual clutter on your chart.
Makes pattern spotting faster and more accurate.
Great for traders who prefer structure-based setups.
Traders who depend on multiple technical indicators should consider brokers that provide access to platforms like TradingView, MT5, or cTrader. These platforms come equipped with a wide range of professional charting tools and indicators that suit nearly any trading style. Below, you will find a comparison table showcasing the top brokers that offer these platforms, making it easier for you to find and select the one that matches your specific trading needs.
| Currency pairs | Crypto | Stocks | Min. deposit, $ | Max. leverage | TradingView | MT5 | cTrader | Regulation | TU overall score | Open an account | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | Yes | Yes | No | 1:500 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ASIC, FCA, DFSA, BaFin, CMA, SCB, CySec | 7.17 | Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
|
| 52 | Yes | Yes | 25 | 1:1000 | No | Yes | Yes | MISA, FSC (Mauritius) | 8.2 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 70 | Yes | Yes | 100 | 1:500 | No | Yes | Yes | FCA, CYSEC, FSCA, SCB, FSA (Seychelles) | 7.9 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 56 | Yes | Yes | 50 | 1:1000 | No | Yes | Yes | CySEC, FSC (Mauritius), SVG FSA | 7.87 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 61 | Yes | Yes | 200 | 1:500 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ASIC, CySEC, and FSA | 7.46 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
We at Traders Union have analyzed financial markets for over 14 years, evaluating brokers based on 250+ transparent criteria, including security, regulation, and trading conditions. Our expert team of over 50 professionals regularly updates a Watch List of 500+ brokers to provide users with data-driven insights. While our research is based on objective data, we encourage users to perform independent due diligence and consult official regulatory sources before making any financial decisions. Learn more about our methodology and editorial policies.Why trust us
Pros and cons of zig zag indicator
- Pros
- Cons
Filters out market noise. The indicator cuts through small, random price movements and focuses only on major highs and lows. This makes it easier to see what’s really happening without getting distracted by minor fluctuations.
Makes trend structure clearer. It connects turning points with clean lines, which helps you spot higher highs, lower lows, and overall trend direction. This is useful for identifying reversals or confirming ongoing moves.
Supports pattern recognition. Zig zag lines simplify chart patterns like head and shoulders, double tops, or channels. You can spot these more easily when price is outlined with clear swings.
Helps with drawing Fibonacci levels. It gives you clean reference points for swing highs and lows, which makes it easier to apply Fibonacci tools accurately and with confidence.
Lagging by design. The zig zag only draws after the price has moved by a set amount, so it shows what happened in hindsight. This means you can’t rely on it for real-time entries.
Not suitable for standalone signals. It doesn’t give buy or sell signals on its own. You need to combine it with price action, volume, or other tools to make informed decisions.
Can repaint with new price action. As new candles form, the indicator may shift or adjust recent lines. This can be confusing if you’re using it for live decision-making without understanding how it works.
Highly sensitive to settings. If your deviation or depth settings are too low, it may show too many swings. If they’re too high, it may miss key turns. Tuning it takes trial and error based on timeframe and asset.
Zig zag can be a trend strength mirror when used right
Most people treat the zig zag indicator as something that just makes the chart look neat. But what beginners often overlook is that zig zag can tell you if a trend is starting to fade. Watch the size of the swings. If the rallies in an uptrend get smaller while the dips get deeper, the strength behind the move is thinning out, even if price still climbs. And in a pullback, if buyers start showing up earlier and making stronger pushes, that is your sign to pay attention. With zig zag, you compare move size instead of just direction. That is where the real insight comes in.
Another detail most traders miss is how the angle of those moves tells you about the market’s tone. If your same zig zag setting suddenly starts drawing steeper legs or softer drops, the market is shifting. A sharp rally with only a mild dip shows momentum picking up fast. That is more than just a trend holding, it is gaining speed. When you stop thinking of zig zag as just a drawing tool and start using it to read the personality of the trend, it starts helping you notice who is really pushing the move and what they are trying to do.
Conclusion
The zig zag indicator is not meant to show you entry points. It is there to help you feel the pace of the market. When you start using it to understand how each move behaves, how far it runs, how quickly it turns, and how that compares to the last leg, you stop reacting and start observing. A steady run with deeper dips says something different than a sharp rally with no follow-through. Each move has meaning.zig zag becomes a way to listen to price and see when a trend is pushing hard or fading quietly. It is a tool that shows how strong the move really is underneath the surface.
FAQs
Can the zig zag indicator predict future price action?
No, the zig zag indicator does not predict future prices. It filters out market noise and highlights past trends or swings, making it a tool for analysis rather than forecasting.
Is zig zag suitable for day trading or long-term investing?
The zig zag indicator can be used in both day trading and long-term investing, but its effectiveness depends on the settings. Traders often adjust it for short-term patterns, while investors use it to view major market cycles.
Is the TDI suitable for all asset classes?
Yes, the zig zag indicator can be applied to any asset class including stocks, Forex, commodities, and crypto. It works well wherever price swings and trend analysis are relevant.
Should I use the zig zag indicator alone or with other indicators?
The zig zag indicator works best when combined with other tools like RSI, MACD, or volume indicators. This helps confirm trend strength and improves the reliability of trading signals.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Anton Kharitonov is an active trader and analyst. He employs both short- and long-term trading strategies, primarily based on fundamental factors, supported by technical indicators and intermarket analysis. Anton trades major and minor currency pairs, while his primary focus is on oil futures and index CFDs.
As a financial expert and analyst at Traders Union since 2013, Anton performs thorough internal broker evaluations, referred to as “test drives.” He examines website and account interfaces, client support, software stability, deposit and withdrawal processing speed, legal documentation, and additional broker services such as VPS, affiliate programs, contests, bonuses, and training programs.
New knowledge is the key to expanding our horizons and unlocking new opportunities. Every step in learning, every new understanding empowers us become better, smarter, and stronger. Knowledge provides an advantage, enabling informed decisions, confident actions, and forward momentum. In a changing world, only those who embrace learning and adaptation can truly thrive.
Based on these evaluations, Anton prepares expert reports on the operation of Forex, stock, binary options, and cryptocurrency exchanges.
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Xetra is a German Stock Exchange trading system that the Frankfurt Stock Exchange operates. Deutsche Börse is the parent company of the Frankfurt Stock Exchange.
The deviation is a statistical measure of how much a set of data varies from the mean or average value. In forex trading, this measure is often calculated using standard deviation that helps traders in assessing the degree of variability or volatility in currency price movements.
Forex leverage is a tool enabling traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital, amplifying potential profits and losses based on the chosen leverage ratio.
An investor is an individual, who invests money in an asset with the expectation that its value would appreciate in the future. The asset can be anything, including a bond, debenture, mutual fund, equity, gold, silver, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real-estate property.
Day trading involves buying and selling financial assets within the same trading day, with the goal of profiting from short-term price fluctuations, and positions are typically not held overnight.






























































































































