Day Trading Taxes Guide



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.

eOption - Best stock broker for 2025 (United States)
Day trading taxes apply to traders buying and selling financial instruments within the same day. They are primarily short-term capital gains taxed at varying rates depending on the country's tax laws (range from 10% to 37%). However, traders can reduce their tax liability through deductions, proper trading status classification, and strategic planning.
In this guide, you'll learn how day trading taxes work, what tax rates apply, and how to pay less through deductions and strategic planning. We'll answer common questions and provide insights from expert traders to help you maximize your after-tax returns.
What are day trading taxes in different countries?
Profits made from day trading are taxable. Whether you're trading stocks, Forex, cryptocurrencies, or commodities, any gains from these transactions are subject to federal, state, or regional income taxes.
Understanding how your gains are taxed based on your residence is crucial for maximizing your after-tax returns and staying compliant with the law. Whether you're in the United States, Canada, Germany, or any other region, it's essential to grasp the specific rules and reporting requirements for your location.
In this section, we'll explore how day trading taxes work in different countries, providing insights into tax rates, reporting forms, and practical examples. We'll also compare the various tax treatments globally to give you a comprehensive understanding of your potential tax liability.
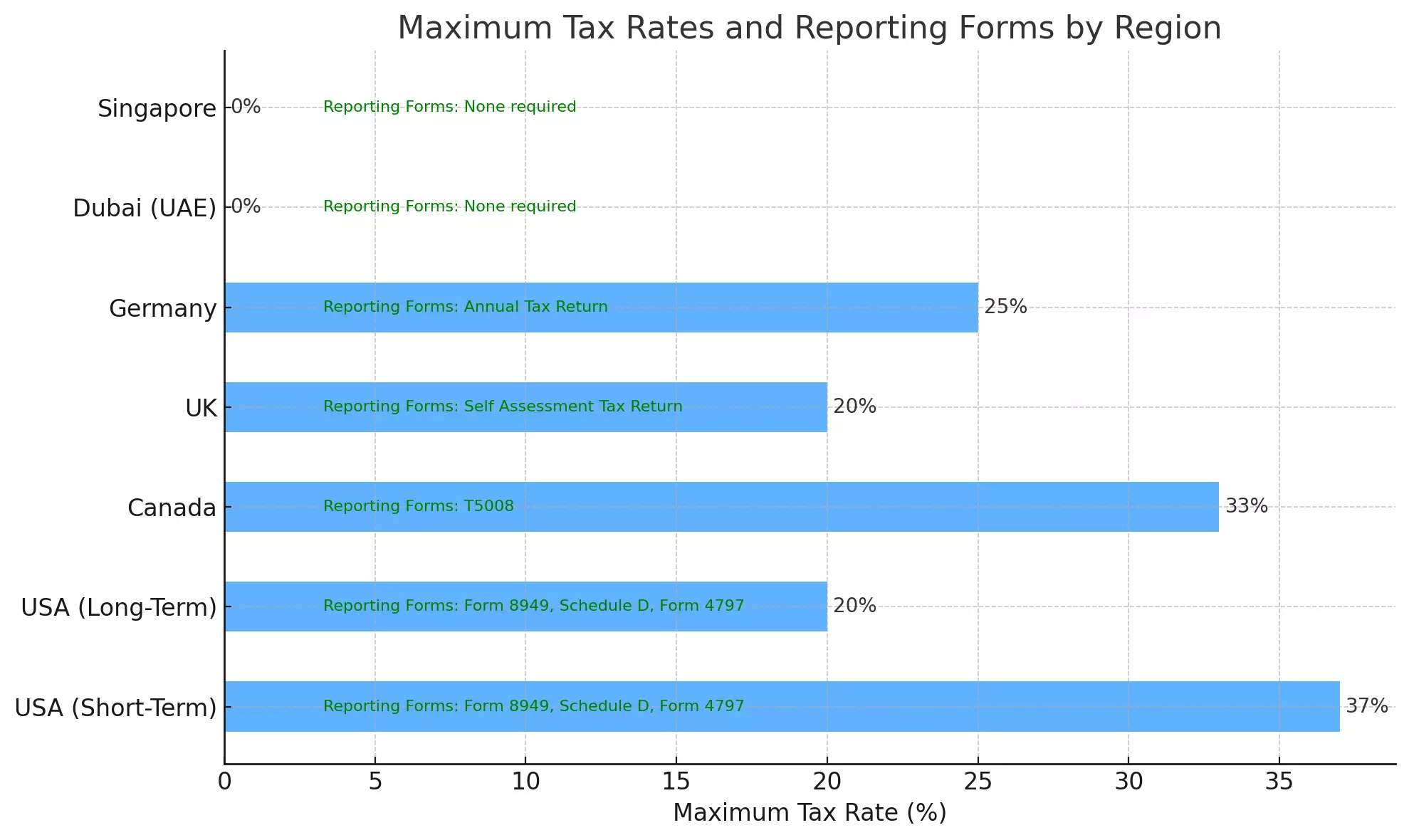
USA
Tax Rates:
Short-term: 10% - 37%
Long-term: 0%, 15%, 20%
Reporting Forms:
Form 8949
Schedule D
Form 4797 (for TTS traders)
Canada
Tax Rates:
Capital gains: 50% of gains included as taxable income
Ordinary income tax rates (15% - 33%)
Dubai (UAE)
Tax Rates:
No personal income tax on trading profits.
Singapore
Tax Rates:
No capital gains tax on trading profits.
Reporting Forms:
None required for day trading activities.
Europe
United Kingdom:
Tax Rates:
10% - 20% (Capital gains tax rates)
Reporting Forms:
Self Assessment Tax Return
Germany:
Tax Rates:
25% flat rate plus solidarity surcharge
Reporting Forms: Annual Tax Return
Best Stock Brokers
Day-Trading Tax Rates
There are two types of capital gains taxes for day trading: short-term and long-term.
Short-Term Capital Gains
Definition: Profits from trades held less than a year;
Taxed as ordinary income based on your country's tax laws;
Reported on relevant tax forms (for example, IRS Form 8949 in the USA, T5008 in Canada);
Ordinary income tax rates based on local laws.
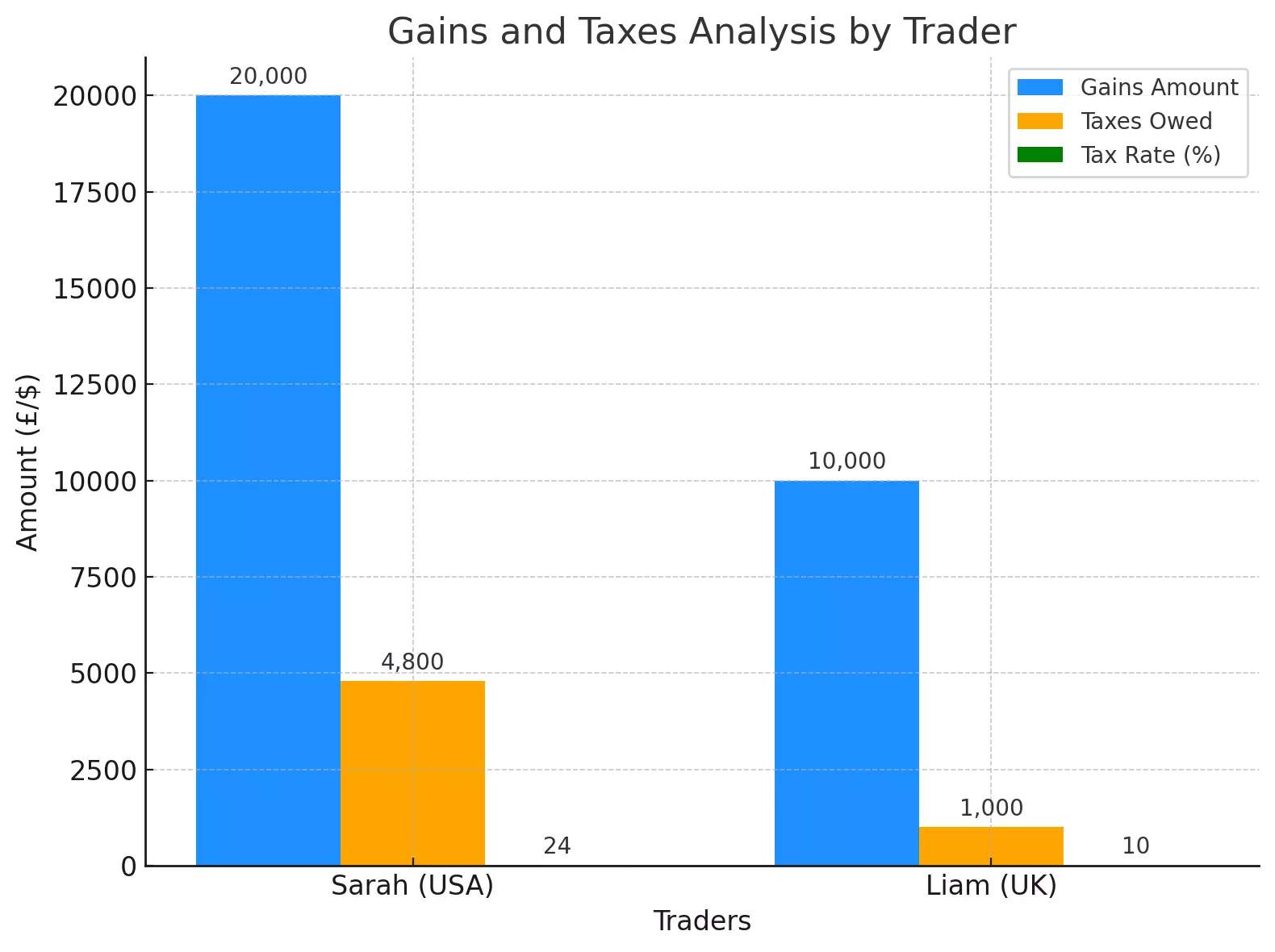
Example:
Sarah is a full-time day trader in the USA who focuses primarily on tech stocks like Apple, Tesla, and Google. She made $100,000 in total income from her trading activities last year, including $20,000 in short-term gains. According to U.S. tax laws, her short-term gains are taxed as ordinary income at a rate of 24%. As a result, she owes $4,800 in taxes on her short-term gains alone.
Income: $100,000
Short-term gains: $20,000
Tax rate: 24%
Taxes Owed: $20,000 x 0.24 = $4,800
Long-Term Capital Gains
Definition: Profits from trades held longer than a year;
Taxed at a lower rate than short-term gains in many countries;
Reported on relevant tax forms;
Typically lower than short-term rates, ranging from 0% to 20% or more.
Example:
Liam is an investor based in the UK who prefers holding stocks for the long term. He earned £80,000 in total income, including £10,000 in long-term gains. In the UK, long-term gains are taxed at a lower rate of 10%. Therefore, he owes only £1,000 in taxes on his long-term gains.
Income: £80,000
Long-Term Gains: £10,000
Tax Rate: 10%
Taxes Owed: £10,000 x 0.10 = £1,000
How to file day trading taxes
Filing day trading taxes can be simplified with the help of tax software. Here are five options, each with features beneficial for day traders:
TurboTax Free Edition
TurboTax is one of the most widely used tax preparation software solutions in the USA and many other countries.

Features:
Free Federal and State Returns: Offers free filing for federal and state returns;
W-2 Import: Easily imports W-2 data directly from your employer;
Guided Questions: Asks simple questions to help you complete your tax return accurately;
Investment Income Reporting: Handles basic investment income, including dividends and interest.
Day Trader Benefits:
Form 8949 & Schedule D: Supports basic capital gains and losses reporting;
Investment Portfolio Overview: Summarizes investment income for easy tax preparation.
H & R Block Free Online
H & R Block is a reliable tax preparation solution offering various products, including a free online edition. It is optimal for day traders with basic investment income and W-2 employment.
Features:
Free Federal and State Returns: Offers free filing for federal and state returns for W-2 employees;
Deduction Finder Tools: Guides you to identify eligible deductions and credits;
Import Capabilities: Imports last year's tax data and W-2 information directly from your employer.
Day Trader Benefits:
Basic Investment Income Reporting: Handles reporting of interest and dividends;
Multiple Sources of Income: Suitable for freelancers and those with multiple income streams;
Audit Support: Provides guidance in case of an IRS audit.
Credit Karma Tax
Credit Karma Tax is a completely free tax filing solution offering federal and state tax returns. It is best for day traders with simple returns, including basic cryptocurrency transactions.
Features:
Free Federal and State Returns: 100% free for all federal and state returns;
Audit Defense: Provides free audit defense services;
Multiple Forms Support: Handles multiple forms, including self-employment and investment income.
Day Trader Benefits:
Form 8949 & Schedule D Support: Easily reports capital gains and losses;
Cryptocurrency Income Reporting: Supports the reporting of cryptocurrency gains;
W-2 Import: Automatically imports W-2 information directly.
FreeTaxUSA
FreeTaxUSA is a budget-friendly tax software offering free federal tax returns and low-cost state returns.It is best for day traders looking for a low-cost solution with comprehensive features.

Features:
Free Federal Returns: Free filing for federal returns with a small fee for state returns;
Investment Income Reporting: Supports Schedule D for reporting stock and cryptocurrency transactions;
Prior Year Imports: Imports data from previous years for returning users;
Advanced Deduction Finder: Identifies potential deductions for optimal tax savings.
Day Trader Benefits:
Form 8949 & Schedule D Support: Handles capital gains and losses reporting;
Cryptocurrency Income Reporting: Suitable for traders with basic cryptocurrency transactions;
Multiple Sources of Income: Supports W-2 and self-employment income.
TaxAct Free Edition
TaxAct offers a range of tax preparation products, including a free edition for basic tax returns. Ideal for day traders with basic stock trading income and W-2 employment.
Features:
Free Federal Returns: Free filing for federal returns with a fee for state returns;
Investment Income Reporting: Supports reporting of dividends, interest, and stock sales;
Prior Year Imports: Imports previous years' data for returning users;
Guided Questions: Simplifies the tax filing process by asking straightforward questions.
Day Trader Benefits:
Form 8949 & Schedule D Support: Reports capital gains and losses for basic stock trades;
Audit Support: Offers free basic audit support for users;
W-2 Import: Automatically imports W-2 data directly.
How to save on day trading taxes
As a day trader myself, understanding tax-saving options can significantly impact your overall profitability. Here are the key strategies and how each can be applied:
Qualify for Trader Tax Status (TTS)
In the U.S., Trader Tax Status (TTS) allows you to treat your trading activity as a business, enabling you to deduct trading expenses like a company.
How to Qualify TTS:
Trade Frequently: Execute at least four trades daily on most trading days.
Holding Period: Majority of trades should be short-term (less than 31 days).
Trading Hours: Spend a minimum of four hours daily trading or analyzing markets.
Capital Requirement: Have substantial capital dedicated to trading.
Other countries also offer ways for active traders to reduce their tax liability. Consult a tax professional in your jurisdiction to understand your eligibility and maximize deductions.
Offset Gains with Losses:Selling losing positions to offset gains, also known as tax-loss harvesting, can significantly reduce your taxable income.
How It Works:
Identify positions with unrealized losses and sell them before the end of the tax year.
Refrain from repurchasing the same security within 30 days before or after selling it.
Maximize Retirement Contributions
Contributing to retirement accounts like IRAs can provide immediate tax benefits.
How It Works:
Traditional IRA: Contributions are tax-deductible, reducing taxable income.
Roth IRA: Contributions are made after-tax, but withdrawals are tax-free in retirement.
Self-Employed Retirement Accounts: Self-employed traders can consider Solo 401(k) or SEP IRA for higher contribution limits.
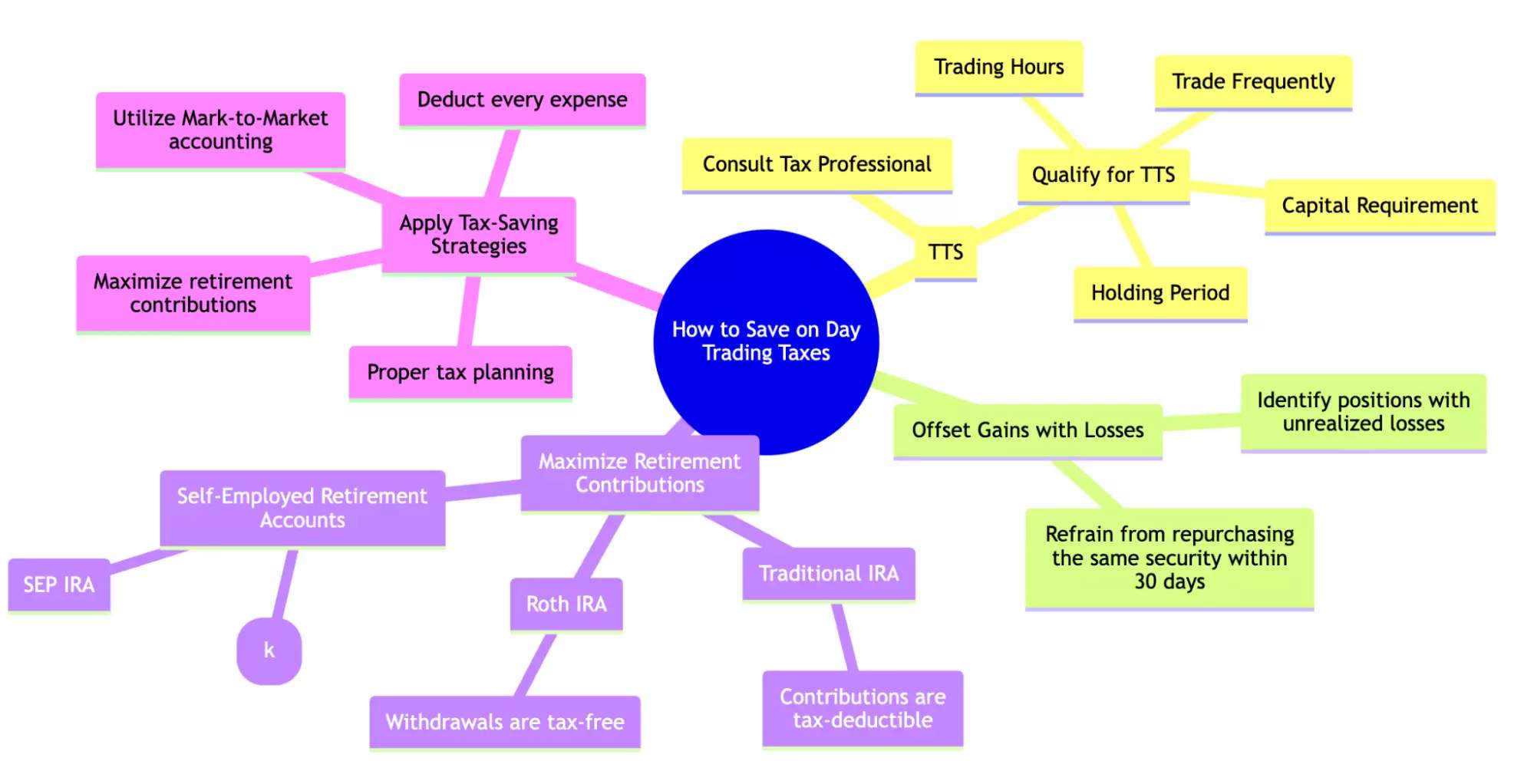
Tax-saving strategies can make a significant difference in your net returns as a day trader. Whether you're just starting or have years of experience, understanding your tax-saving options and implementing them can help you minimize your tax burden and keep more of your profits. Deduct every expense, utilize Mark-to-Market accounting, and maximize retirement contributions. Proper tax planning can make a significant difference in your overall profitability.
Expert opinion
Managing day trading taxes can be challenging, but it's crucial for maximizing your net returns. Learn from my mistakes, plan ahead, and seek professional advice to navigate the complexities of tax laws:
Lesson 1:
In my early trading days, I underestimated the complexity of calculating taxes. I believed I could handle everything myself and didn't need specialized software. When tax season arrived, I was overwhelmed by the number of trades and the need to categorize them accurately. This led to mistakes in reporting and a higher-than-expected tax bill.
Lesson Learned:Use specialized tax software that automates trade categorization and reporting.
Lesson 2:
At one point, I was actively selling losing positions and repurchasing them within a short timeframe, unknowingly triggering the Wash-Sale Rule. This rule disallowed my losses, which meant I couldn't use them to offset my gains, resulting in a much higher tax bill than anticipated.
Lesson Learned:Understand the Wash-Sale Rule and avoid repurchasing the same security within 30 days.
Lesson 3:
I failed to keep detailed records of my trading expenses, including software subscriptions, education, and travel. When it came time to file my taxes, I couldn't accurately account for these deductions, leaving potential tax savings on the table.
Lesson Learned:Maintain meticulous records of all trading expenses throughout the year.
Conclusion
Day trading taxes can be challenging, but understanding the different tax rates and how to reduce your tax liability through deductions and strategic planning can help you save money. By accurately reporting your trading income and following the tips in this guide, you'll be better prepared to handle your day trading taxes and minimize your tax burden.
FAQs
Do you pay taxes on day trading?
Yes, profits from day trading are taxable as short-term capital gains.
How many trades do you need to be a day trader for taxes?
There is no set number of trades, but consistent trading activity is essential to qualify as a day trader.
Is day trading profitable?
Yes, but not for everyone. A University of Berkeley study found that 75% of day traders call it quits within two years, and the majority of trades, up to 80%, lose money. So, is it worth it? The decision is up to you, but going in with clear eyes about the challenges is important.
How much money do day traders with $10,000 accounts make per day on average?
Earnings vary widely, but a well-disciplined day trader might aim for a 1-2% daily return, or $100-$200 per day.
How does the Wash-Sale-Rule work?
If you sell a security at a loss and buy the same or a substantially identical security within 30 calendar days before or after the sale (totaling 61 days including the sale date), you won't be able to take a loss for that security on your current-year tax return.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Anastasiia has 17 years of experience in finance and content marketing. She believes that the support of information and expert opinion is very important for the success of investors and new traders. She is ready to share her knowledge of forex, stock and cryptocurrency trading, as well as help choose the right investment products and strategies to achieve active or passive income.

Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Day trading involves buying and selling financial assets within the same trading day, with the goal of profiting from short-term price fluctuations, and positions are typically not held overnight.
A day trader is an individual who engages in buying and selling financial assets within the same trading day, seeking to profit from short-term price movements.
Social trading is a form of online trading that allows individual traders to observe and replicate the trading strategies of more experienced and successful traders. It combines elements of social networking and financial trading, enabling traders to connect, share, and follow each other's trades on trading platforms.
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is the practice of buying and selling currencies in the global foreign exchange market with the aim of profiting from fluctuations in exchange rates. Traders speculate on whether one currency will rise or fall in value relative to another currency and make trading decisions accordingly. However, beware that trading carries risks, and you can lose your whole capital.
Options trading is a financial derivative strategy that involves the buying and selling of options contracts, which give traders the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price, known as the strike price, before or on a predetermined expiration date. There are two main types of options: call options, which allow the holder to buy the underlying asset, and put options, which allow the holder to sell the underlying asset.
































































































































