Working Orders | All You Need To Know



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
Working orders are a type of order that allows traders to specify the price and time conditions for entering or exiting a trade. They help traders execute their trading strategies more effectively, reduce the need for constant market monitoring, and improve risk management.
Working orders are trading orders that don't get filled immediately at the current market price. Instead, they wait on the order book until a specific price or time condition is met. These orders let you trade at your chosen price points or automatically close trades when you reach a profit or loss target.
Definition of working orders
Working orders, also known as pending orders, include stop and limit orders. They offer flexibility by allowing you to create more advanced trading strategies by combining them with other order types. You can set different expiry dates for working orders, such as same-day or "good 'til canceled," meaning they stay open until you cancel them or the condition is met. We have prepared this guide for you featuring the benefits of these orders, the different types, and how to use them.
Types of working orders
There are several types of working orders that traders can use to enhance their trading efficiency and profitability. Below, several of the more common working orders are described.
A limit order (reversal) is an order to deal at a certain price "better" than the market, i.e. to buy at a price below the market (BuyLimit) and to sell above the current price (SellLimit). These orders are executed only if the market performs a correction of the current trend and turns in the original direction.Limit orders can help traders enter or exit a trade at their preferred price level, but they may not be filled if the market does not reach the limit price.
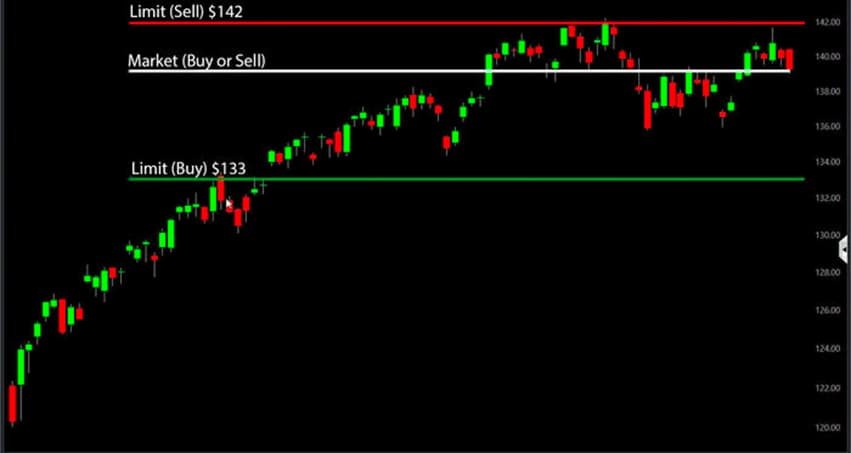 Limit order (buy/sell)
Limit order (buy/sell)A stop-limit order is an order to buy or sell an asset when it reaches a specified price, known as the stop-limit price. Stop orders can help traders protect their positions from adverse price movements or enter a trade in the direction of a breakout.
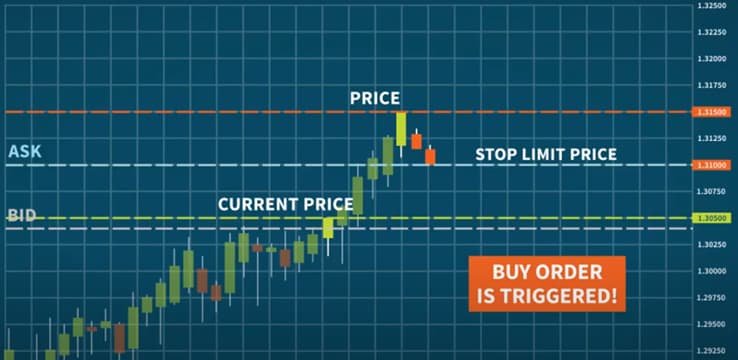 Stop-limit Orders
Stop-limit OrdersA one-cancels-the-other (OCO) is a pair of working orders that are linked together such that if one order is executed, the other order is automatically canceled. OCO orders can help traders to capture profits or limit losses in volatile markets without having to monitor both orders separately.
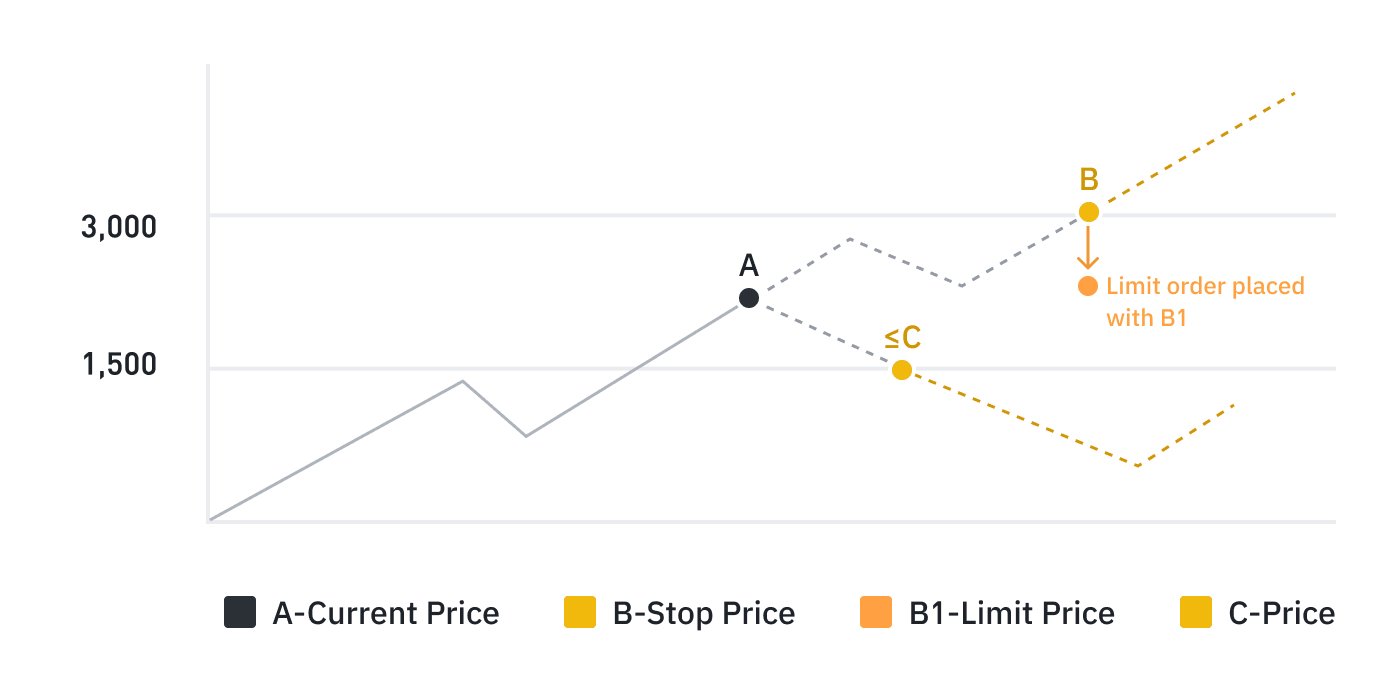 OCO (One-Cancels-the-Other) Order
OCO (One-Cancels-the-Other) OrderA take profit (TP) is an order to close an existing position at a specified profit level. TP orders can help traders to lock in their profits when the market reaches their target level without having to manually close their positions.
 Take-Profit Order
Take-Profit OrderA stop loss (SL) is an order to close an existing position at a specified loss level. SL orders can help traders limit their losses when the market moves against them without having to manually close their positions.
When you select a broker for trading orders, it's important to consider those that offer robust platforms, reliable execution, and a range of order types.
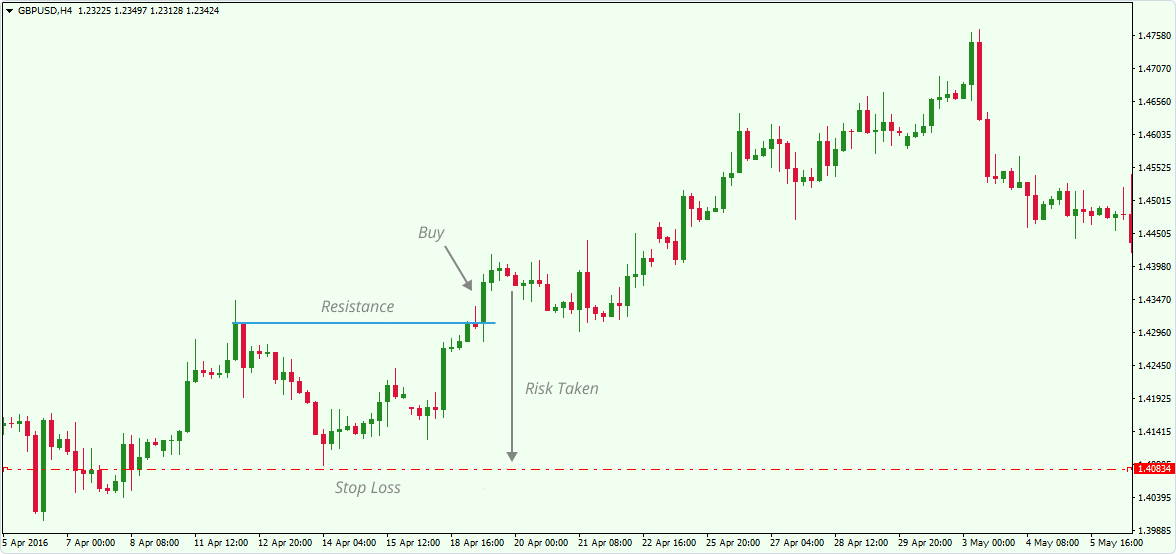 Stop Loss Order
Stop Loss Order| Trading platform | Orders execution | Min. deposit, $ | Min Order | Mobile trading | Account types | Open account | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile, Web, Desktop | Market Execution | 100 | 0,01 | Yes | 0.00 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| MT4, MobileTrading, WebTrader, cTrader, MT5, TradingView | Instant (30 ms) | No | 0.01 lot | Yes | 0.00 | Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
|
| WebTrader, MetaTrader4, Mobile platforms, MetaTrader5 | Market Execution | No | 0,01 lot | Yes | 0.00 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| FOREX.com, MT4, MT5 | Market Execution, Instant Execution | 100 | 0.01 | Yes | 0.00 | Study review | |
| Trader Workstation, IBKR Mobile, APIs | Instant Execution | No | 0.1 lot | Yes | 0.00 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Listed below are some of the benefits of using working orders:
Improved Efficiency
Working orders allow traders to set specific conditions for trades, which means they can automate parts of their trading process and reduce the time spent monitoring the market.Better Risk Management
By setting predetermined entry and exit points, traders can manage their risk more effectively. This helps limit losses and secure profits at desired levels.Price Control
Working orders let traders specify the exact price at which they want to buy or sell, helping them achieve better prices compared to market orders that execute at the current market price.Reduced Emotional Trading
Automated execution of trades based on set conditions can help reduce the emotional impact of trading decisions, leading to more disciplined and consistent trading.Flexibility in Trading Strategies
Traders can combine different types of working orders to create complex and sophisticated trading strategies, enhancing their ability to respond to various market scenarios.Time-Saving
Since working orders can execute trades automatically when certain conditions are met, traders can save time and focus on other important tasks or strategies.Market Opportunities
Working orders can capture market opportunities that may occur when traders are not actively watching the market, ensuring they don’t miss out on potential trades.Custom Expiry Options
Traders can set different expiry dates for their working orders, such as same-day or good 'til canceled, providing flexibility in how long their orders remain active. By using working orders, traders can enhance their overall trading experience, making it more efficient, controlled, and strategic.
Difference between working orders and market orders
Market orders and working orders are two types of trading orders that have different advantages and disadvantages for traders.
Different advantages and disadvantages
| Feature | Working Orders | Market Orders |
|---|---|---|
Execution Timing | Executes when a specific price or time condition is met | Executes immediately at the current market price |
Price Control | Allows traders to set a preferred price for execution | Executes at the best available price in the market |
Order Types | Includes stop orders, limit orders, and other conditional orders | Typically a straightforward buy or sell order |
Expiry Options | It can have various expiration dates (same day, good 'til canceled, etc.). | Usually executed immediately with no expiry options |
Monitoring | Traders do not need to constantly monitor the market as the order will execute when conditions are met | Requires traders to monitor the market for immediate execution |
Flexibility | Provides flexibility to create more sophisticated trading strategies | Simpler and more straightforward to use |
Use Case | Ideal for traders wanting to trade at specific price points or automate trade closures at certain conditions | Ideal for traders needing immediate execution |
Risk Management | Can help manage risk by setting predetermined profit or loss targets | Offers less control over the execution price |
Market Impact | Typically less immediate market impact as orders wait for conditions | Immediate impact on the market as they are filled |
Reducing the necessity for constant market monitoring
Working orders are an essential tool in a trader's arsenal, providing benefits that enhance trading efficiency and strategy execution. Unlike market orders, which execute immediately at the current market price, working orders are placed on the order book to be filled when specific price or time conditions are met. This strategic delay allows traders to aim for optimal entry and exit points, ensuring they trade at their preferred prices rather than accepting the prevailing market rates.
As I have noticed in my practice, one of the key advantages of working orders is their ability to reduce the need for constant market monitoring. By automating the execution based on predefined criteria, traders can manage their positions more effectively, even when they are not actively watching the markets. This is particularly beneficial in volatile markets where rapid price movements can occur.
If you understand and effectively utilize working orders, you can significantly improve a trader's ability to navigate the financial markets successfully.
Summary
Working orders are powerful tools that can help you trade more efficiently and profitably. With working orders, you can set specific price and time conditions for when to start or stop a trade. This means you don’t have to watch the market constantly. These orders also help you manage risk better.
You can combine working orders with other types of orders to create more advanced trading strategies. It’s important to learn about the different types of working orders and how they work and choose the ones that best match your trading goals and strategies.
FAQs
Can working orders be combined with other types of orders?
Yes, working orders can be combined with other order types to create more sophisticated trading strategies, enhancing flexibility and precision in trading.
Can working orders expire?
Yes, working orders can have different expiry dates, such as same-day or "good 'til canceled" (GTC), meaning they remain open until the trader cancels them or the condition is satisfied.
Are working orders useful for beginners in trading?
Yes, working orders are useful for beginners as they help manage trades without constant market monitoring and can automate trading strategies to achieve better prices and manage risks effectively.
How do I set up a working order?
Setting up a working order typically involves selecting the type of order (limit or stop), specifying the price or condition for execution, and setting an expiry date if applicable. This can be done through your trading platform's order entry interface.































































































































