FINRA | U.S. Financial Regulator
FINRA, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, is a non-governmental organization responsible for regulating securities markets and brokerage firms in the United States. It plays a crucial role in ensuring transparency and compliance within the financial industry by overseeing the activities of brokers and enforcing regulatory standards.
The foundation of any country’s regulatory system is one or several controlling authorities. They can be governmental or non-governmental. The national bank or another body can serve as a regulator. Besides government regulators, a country can have a system of private regulators and auditors. Also, in a number of countries, licensees are required to be members of self-regulatory organizations (SROs).
For a broker, holding a license means:
-
Permission to render certain types of services in the exchange, over-the-counter (OTC), and Forex markets.
-
Necessity to operate transparently.
-
Traders’ trust and respect.
For a trader, a license means understanding which types of services a broker is permitted to provide and a guarantee that the broker operates in the legal framework of the country or region issuing the license. In some jurisdictions, insurance funds are formed from licensees’ contributions. In case of a conflict of interest with a broker, a trader can get help from a regulator or an ombudsman, depending on the broker’s place of registration.
In this post, TU explores FINRA’s objectives, functions, mandate, procedure for confirming licenses on the website, and the procedure for filing complaints, as well as reviews and an expert’s opinion of this regulator.
Description and functions of FINRA
FINRA was established in 2007 as a successor to the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc. (NASD) which had operated since 1939. FINRA’s mandate includes oversight of the OTC market. FINRA belongs to a type of non-governmental self-regulatory organizations. Membership in such SROs is mandatory for every broker that accesses the U.S. exchange markets. The Authority has around 3,600 employees, 20 regional representative offices, and about 704,000 members (4,000 financial organizations and 700,000 brokers). Every day, approximately 42 billion financial transactions go through FINRA’s processing center.
Tasks and purposes of FINRA in the Forex market:
-
Issue certificates to corporate market participants.
-
Ensure that the law is observed by participants in securities markets, partially including the exchange market.
-
Run information campaigns intended to improve the qualifications of professional investors.
-
Consider disputes and impose fines in cases of violations.
-
Present cases to the SEC when there is evidence of a criminal offense.
-
Monitor and audit the NYSE and Nasdaq stock exchanges.
FINRA is a non-government regulator that supervises the OTC market with the consent of NYSE and Nasdaq. Exchanges let FINRA conduct audits because they are interested in resolving disputes between investors and brokers without the participation of a court. FINRA is fully subordinate to the SEC and provides it with all information about exposed violations.
To obtain a FINRA license, a broker has to:
-
Disclose information about its executives. The CEO provides detailed information about their family’s property.
-
Provide a business plan, development strategy, and a plan of activities for force-majeure cases.
-
Provide a trial balance.
-
Provide other documents required by FINRA, depending on the type of the broker’s activity. The list may include over 30 documents.
A FINRA certificate confirms a broker’s membership in an independent SRO as per the SEC requirements. FINRA is financed from its members’ contributions and fines paid.
Official website and available information
The website has a convenient structure. Needed information can be located quickly just by following the sections and subsections on the website.
Overview of the FINRA website:
-
The upper main menu consists of two parts.
-
Central part. Introductory information about the regulator, links to annual reports, etc.
-
The Footer repeats the upper menu and contains the site map, links to the regulator’s social media profiles, etc.

FINRA website

FINRA website
FINRA website
Main menu structure:
-
About FINRA contains general information: mission, functions, and organizational structure.
-
Careers. Jobs with the regulator.
-
Brokercheck. Here you can find all public information about the Authority’s licensees.
-
Media Center. News, releases, and information about upcoming events.
-
Rules & Guidance. Theoretical framework, laws, and rules that govern FINRA’s work. Links to the National Adjudicatory Council and other organizations. Disciplinary actions, guidelines on how to apply sanctions, and a list of barred entities.
-
Filing & Reporting. Reporting tools, regulatory information filing system, e-Bill, etc.
-
Compliance Tools. Tools for control and cybersecurity.
-
For Investors offers information about personal finance, calculators to determine financial results, investment courses for beginners, counteractive methods against fraud, filing complaints, writing to the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), etc.

FINRA website
“For investors” provides a theoretical framework and complaint forms. The second most useful section is “Brokercheck” (FINRA clients database).
How to confirm a broker’s license on the FINRA website
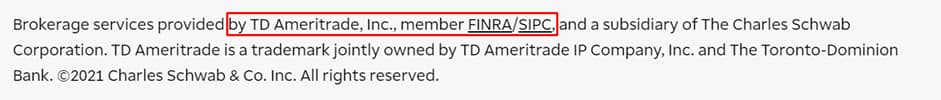
FINRA issues certificates without which it’s impossible to obtain a license from the SEC. Direct search by a broker’s legal name allows you to find mentions of the company in articles, reviews, and releases on the FINRA website. This information can be useful for preliminary analysis of the broker before you open an account.

FINRA website
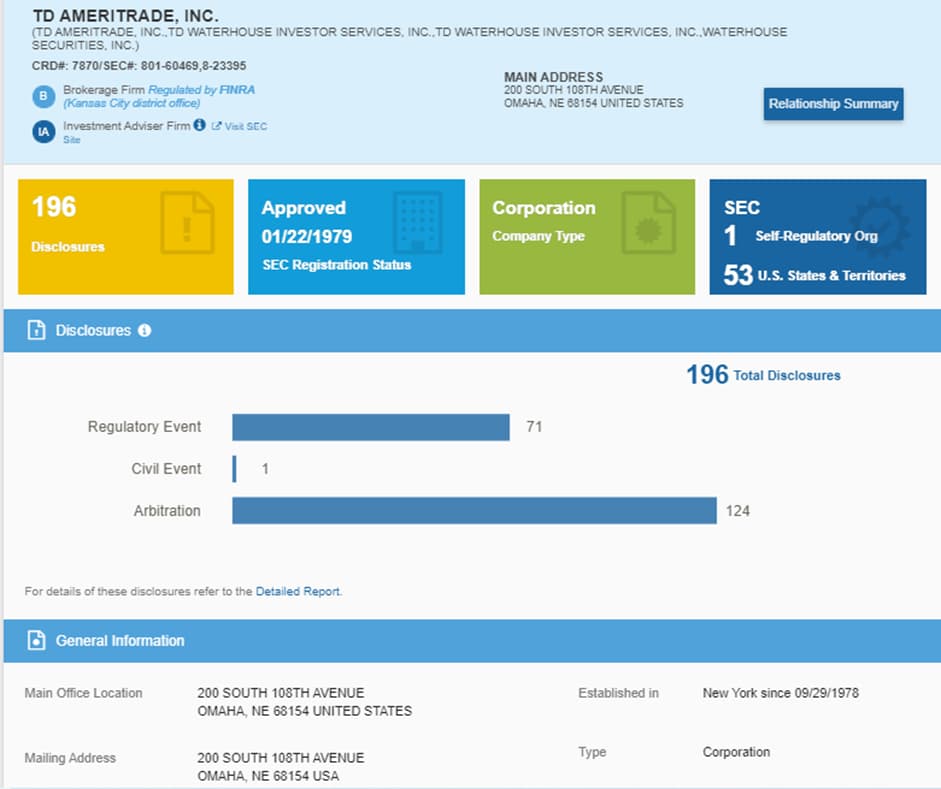
For example, in the screenshot above, the TD Ameritrade broker, well-known thanks to its trading platform Thinkorswim, is mentioned in connection with a fine imposed on it by FINRA in 2013.
To find a broker’s license on the FINRA website, do the following:
-
1
On the broker’s website, find confirmation that the company is a FINRA member.
-
2
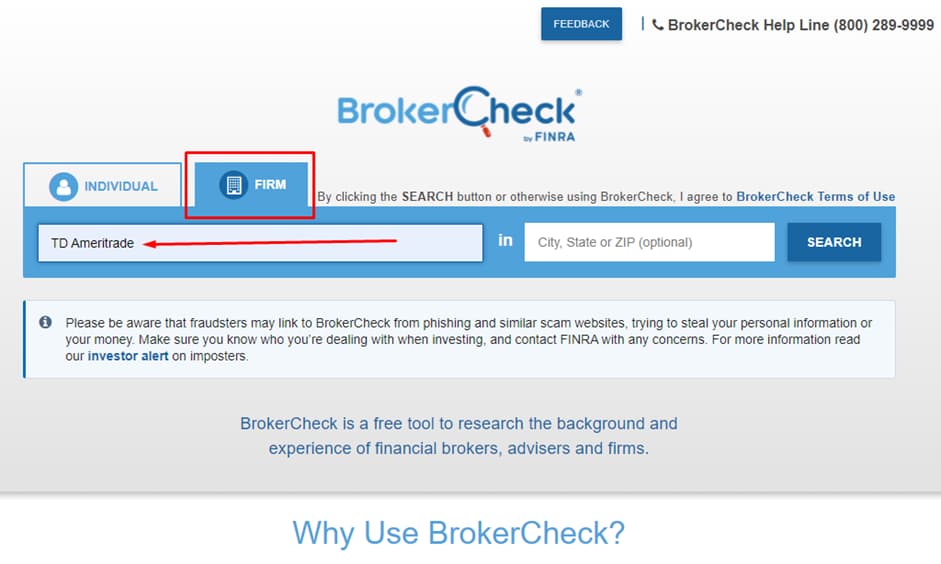
In the upper menu on the FINRA website’s homepage, select “Brokercheck”. This is a separate resource (database) of the regulator. Here you can find any information about brokers and companies whose shares are traded in the OTC market.
-
3
Open the “Firm” tab. In the “Name or CRD” field, enter the broker’s full legal name. It is best to take it from the company’s website.
-
4
Analyze the results.
-
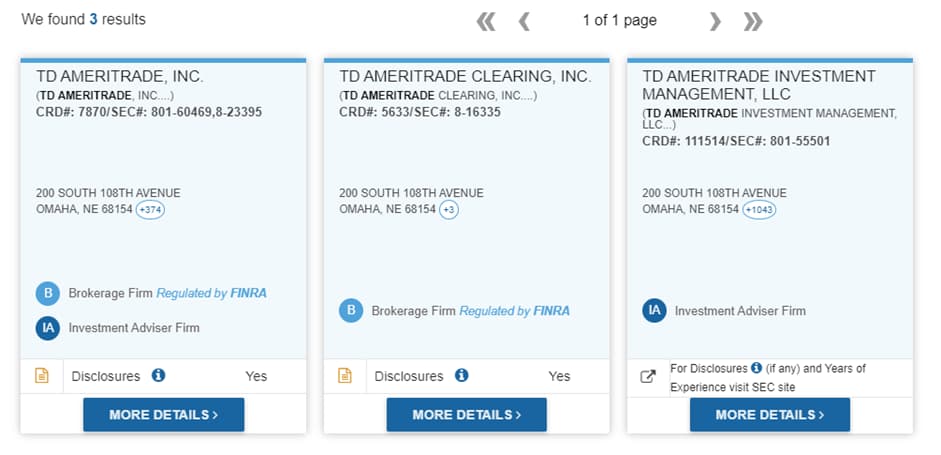
5
Open the broker’s page. In this case, you need the first page. The second is about clearing and the third is about investing.
FINRA website
If this information is not on the website, it does not mean that the broker is not registered. If you are going to trade in the U.S. market, TU recommends checking every broker on the FINRA website to avoid dealing with blacklisted companies.

FINRA website
FINRA website
FINRA website
FINRA website
Here you will find all information about the broker such as registration with other regulators, states in which the license is valid, types of permitted services, and much more.
FINRA’s basic requirements for brokers
Basic requirements to obtain a license:
-
Fully disclose information about the company’s executives, plans, development strategy, and risk management system.
-
Provide documents in accordance with the planned areas of focus in the OTC market.
-
Employees must pass a qualification exam.
FINRA’s mission is to apply the following three market regulation principles: uphold justice and fair competition; inform investors about their rights and available resources; and enforce the law. The regulators’ tools include the Investor Education Foundation (2003) and a dispute resolution forum divided into platforms for different states. In cases of violations, FINRA can apply disciplinary measures such as imposing fines, obligating offenders to pay damages, and sending information about violations to the SEC.
FINRA license | Pros and cons
FINRA is one of the most reputable non-government SROs. During the establishment of the U.S. stock market, brokers would unite and create SROs to protect their interests when dealing with government bodies and exchanges. Later, membership in SROs became a mandatory condition to operate in the U.S. stock market. SROs, in their turn, became more or less answerable to government regulators.
👍 Advantages of trading with a FINRA-licensed broker:
• Protection of investors’ rights. Government regulators monitor brokers and consider applications from private individuals only as reasons to fine offenders. FINRA is a non-government organization that primarily aims to protect the interests of private clients.
• Guarantees the security of trades in the U.S. OTC market.
FINRA is the first instance with which a trader should file a complaint before going to government regulators.
👎 Disadvantages of trading with a FINRA-licensed broker:
• Brokers’ registration with FINRA does not have any downsides for traders. All members of the Authority pay annual contributions. In theory, brokers could partially pass those expenses on to traders, but there is no direct evidence of that.
FINRA’s jurisdiction
FINRA is fully accountable to the SEC and registration with it is mandatory for every stock broker. Like the SEC, FINRA controls the whole OTC market and part of the exchange market. Mandates of the regulators differ:
-
The SEC oversees the exchange and OTC market participants. The Commission can open criminal cases and initiate brokers’ bankruptcy. The SEC is mostly focused on forcing offenders to comply with the law.
-
FINRA protects the rights of investors and financial service users. It considers issues of compensating clients for financial and moral damage. FINRA is mostly focused on the protection of investors’ interests.
Complaints can be filed by any client (including non-residents of the USA) of a broker that has a FINRA certificate and an SEC license. A complaint can be filed with both regulators simultaneously, but it is better to consult FINRA lawyers first.
Submission and consideration of complaints
Membership in an SRO and a FINRA certificate are mandatory conditions for every licensee of the SEC. For this reason, investors can file complaints with both FINRA and the SEC at the same time. But since it is FINRA that specializes in protecting the rights of private investors, TU recommends filing a complaint with this organization first.
How to file a complaint with FINRA:
-
1
In the “For Investors” section, select “File a Complaint”.
-
2
Review the recommendations before filling out a complaint form.
-
3
Fill out the form.
FINRA website
FINRA website
FINRA website
How to check on a FINRA-licensed broker's legitimacy
Brokers can have an unlimited number of licenses and certificates. Most brokers have licensed representative offices in several regions. In this section, you can find current information on all valid licenses of every broker. Every month, Traders Union’s analysts visit regulators’ websites, checking on the following information:
-
Expiry dates of FINRA licenses and the absence of suspensions.
-
Lists of services that brokers are permitted to render.
-
Warnings or investigations in relation to brokers and their executives.
Save your time by checking on brokers’ licenses on the TU website.
Reviews of FINRA by complaining investors and traders
This section provides additional information about FINRA shared by traders and analysts.
Mikhail, private investor, St. Petersburg
As far as I understand, FINRA supervises all transactions involving shares and bonds that a private individual can buy from banks or investment companies. It means an investor does not need to trade on an exchange and confirm his qualification. He just goes to a bank, opens a securities account, and buys what he wants. I see many benefits in this:
-
Investors can buy securities that, for some reason, are not traded on exchanges. Banks get fees and investors get additional earning opportunities.
-
Investors can file complaints with banking oversight agencies and the SEC/FINRA. Someone will definitely respond.
This is a good cross-checking system.
Vitaly, analyst and trader, Moscow
I wouldn’t rely completely even on the U.S. regulatory system. I agree that European regulators are far less strict and don’t have such powers as U.S. authorities. But failures happen to everyone. The SEC, for example, failed in the Enron scandal, the dot-com bubble, and WorldCom’s bankruptcy. FINRA had failures as well:
-
In 1996, the U.S. Department of Justice and the SEC conducted an investigation in relation to several Nasdaq market makers. It was revealed that the market makers had conspired to set prices of assets for large trades, thereby breaking the principles of fair, competitive, and transparent pricing. FINRA’s predecessor, NASD, was supposed to control the situation, but the regulator’s permissiveness made it possible to manipulate the market.
-
In 2010, the Goldman Sachs investment bank became involved in a scandal with violations of investors’ rights. In theory, when acting as a broker, the bank was supposed to protect its clients’ interests. And FINRA’s task was to control it. But the bank did otherwise. It sold its clients' mortgage fund bonds, knowing that the mortgage funds would promote a decline in real estate prices. Buying those bonds was very risky because of the high chance that the issuer would default. The bank cared about its fees, not its clients’ interests. During the proceedings, the bank’s lawyers argued that the clients themselves had decided on buying, and the bank had only generally informed them about the risks. Eventually, the bank agreed to pay one of the largest fines in the history of the U.S. financial system – about $550 million. And the question of how FINRA overlooked it remains unanswered.
Speaking of the dot-com bubble, it’s worth remembering that shares of many IT-startups were traded over the counter as well. It was easier because there were no exchange fees and there was no exchange control. Perhaps at that time, the SEC was paying more attention to securities trading on exchanges. But NASD should have noticed that the prices of securities were too high and the bubble was swelling.
Query. If regulators reveal violations by separate financial system participants but fail to see risks and prevent the collapse of the whole stock market, can you trust them?
Ruslan, trader | Smolensk, Russia
To obtain a FINRA license, the CEO of a company has to provide his fingerprints and declare all property holdings of his family. A licensee must have a plan of activities for emergency situations. Every employee of a company has to take a 12-hour course and pass a proficiency exam. If brokers with offshore licenses went through similar procedures, I think there would be a lot fewer deceived traders.
Yury, trader | Perm, Russia
I wish Russia had a regulatory system like in the USA. Our regulator is the Central Bank that first issues 5 licenses, then revokes them, and then issues them again. And our SROs are simply useless. At first, we had self-regulatory organizations that essentially worked for certain brokers. Membership in such SROs was granted even to binary options brokers, i.e., organizers of casinos! And what do we have now? About 1,000 pyramids and fraudulent companies are revealed every year. And this is just what the Central Bank makes public.
Regulation in the U.S. is a whole other story. The SEC is the highest regulator that partially delegates its powers to the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the futures market and to FINRA in the OTC market. All brokers are actually cross checked because the SEC periodically inspects the ОТС market participants and FINRA is empowered to find violations on NYSE and Nasdaq. All regulators work consistently and effectively. The SEC imposes fines amounting to several billion USD a year and FINRA imposes $200-300 million a year. And in Russia, we just block websites.
Alexander, trader | Kemerovo, Russia
The U.S. regulatory system is beneficial for traders in that they can consult all authorities simultaneously. If you are a client of a bank or a management company, go to the SEC, FINRA, and an ombudsman. If you trade with a stock broker, go to the SEC, the CFTC, and the National Futures Association (NFA). Someone will eventually respond. Operating under the oversight of all these regulators is hard for brokers. But the U.S. financial system is trusted much more than licenses from European regulators.
Expert’s assessment
Oleg Tkachenko is an economist-analyst and a risk manager with a practical experience of working in financial institutions for over seven years. Oleg specializes in the analysis of commodities, Forex, stock markets and non-standard investment markets (cryptocurrency, hypes, peer-to-peer lending). He holds a Master’s Degree from the Ukrainian Academy of Banking of the National Bank of Ukraine, Kharkiv Banking Institute. Oleg became an author for Traders Union in 2018; in 2020 he joined the TU’s team of financial experts.
FINRA (NASD until 2007) is a non-government self-regulatory organization (SRO) that supervises the OTC securities market in theory and significantly influences the exchange market in practice. According to regulators’ statistics, less than 50% of U.S. securities are traded on exchanges, while the rest of securities are bought and sold through OTC Markets Group and OTC Bulletin Board. These markets are also regulated by FINRA, but, compared to exchanges, they offer softer terms of securities listing. After its establishment in 2007, FINRA was entrusted with part of the supervisory and adjudicatory functions of NYSE Regulation (“NYSER”) that regulates the New York Stock Exchange. Also, FINRA periodically audits NYSE and Nasdaq under the agreements concluded with these exchanges.
FINRA is fully accountable to the SEC and cannot exceed the authority provided to it by the government regulator. FINRA’s task is to assist the SEC in regulating the OTC market by carrying out judicial functions. One of the reasons to create FINRA was the need for an agency that would be entitled to hear arbitration cases in the stock market instead of in the courts, which do not have deep knowledge of financial markets.
Conclusion
FINRA is the main regulator of the U.S. OTC market. It operates under full control of the SEC, which oversees the exchange and OTC markets. And although the SEC was created to primarily supervise the exchange sector and FINRA was supposed to oversee the OTC sector, both regulators actually influence exchanges and the OTC market at the same time. The only difference is that FINRA is subordinate to the SEC which makes final decisions regarding violations.
About the author of this review
Oleg Tkachenko, Author and analyst at TU
Oleg Tkachenko has been TU’s financial analyst and economic observer since 2016. During this time, he has prepared more than 100 reviews of financial companies and analytic articles on technical and fundamental analysis, as well as developed over 10 proprietary trading strategies. Oleg’s motto is to help everyone come all the way from a novice trader to a professional.
FAQs
What is FINRA?
FINRA is the largest non-government financial regulator in the USA, whose objective is to protect investors’ rights. FINRA controls the OTC market and audits NYSE and Nasdaq as per agreements with them. It is a self-regulatory organization that reports to the SEC.
What do I get from trading with FINRA-licensed Forex brokers?
A guarantee that your broker is also controlled by the SEC and is a FINRA member. For a trader, it means that the broker has the right to render services in the exchange and OTC markets.
You can see which types of services the broker can provide in the OTC market.
For a trader, a FINRA license is the protection of his interests. While government regulators mostly work on revealing fraud and apply sanctions to offenders practically without the participation of private individuals, FINRA specializes in the protection of the rights and interests of private investors in disputes with brokers.
How to check if a broker holds a FINRA license?
Two options:
On the FINRA website, go to the “Brokercheck” section. Open the “Firm” tab and enter the broker’s legal name in the search box.
Find the broker’s page on the Traders Union website. Information about all valid licenses is updated monthly. This option is convenient in that you don’t have to go to websites of every regulator and SRO. The broker’s page on TU’s website contains all relevant information.
How to submit a complaint against a broker to FINRA?
In the upper menu on the FINRA website, open the “For Investors” section, select “File a Complaint”, and fill out a complaint form.
Register on the Traders Union website and refer to TU’s lawyers for help and free representation. TU aims to protect all its members. Legal advice is free for every TU member and applications are considered within 24 hours.
Glossary for novice traders
-
1
Broker
A broker is a legal entity or individual that performs as an intermediary when making trades in the financial markets. Private investors cannot trade without a broker, since only brokers can execute trades on the exchanges.
-
2
Investor
An investor is an individual, who invests money in an asset with the expectation that its value would appreciate in the future. The asset can be anything, including a bond, debenture, mutual fund, equity, gold, silver, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real-estate property.
-
3
Trading
Trading involves the act of buying and selling financial assets like stocks, currencies, or commodities with the intention of profiting from market price fluctuations. Traders employ various strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management practices to make informed decisions and optimize their chances of success in the financial markets.
-
4
Index
Index in trading is the measure of the performance of a group of stocks, which can include the assets and securities in it.
-
5
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that relies on cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology.
Team that worked on the article
Oleg Tkachenko is an economic analyst and risk manager having more than 14 years of experience in working with systemically important banks, investment companies, and analytical platforms. He has been a Traders Union analyst since 2018. His primary specialties are analysis and prediction of price tendencies in the Forex, stock, commodity, and cryptocurrency markets, as well as the development of trading strategies and individual risk management systems. He also analyzes nonstandard investing markets and studies trading psychology.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).









