IIROC | Investment Industry Regulatory Organization Of Canada
IIROC is a non-governmental self-regulatory organization in Canada that oversees and facilitates interactions in the securities market across the entire country. It collaborates with provincial regulators and other structural organizations. It reviews claims from private traders when there are clear violations of legislation and manipulations.
A regulator is a governmental or non-governmental organization responsible for enforcing A regulator is a governmental or non-governmental organization responsible for enforcing market participants' compliance with legislation, establishing rules for operation in various financial markets, ensuring transparency in relationships, aiding in dispute resolution, and protecting clients' rights. The regulatory system can encompass central banks, separate structures accountable to the central bank or executive authorities, self-regulatory organizations, and a system of private regulators and auditors. The distinction between regulators lies in their authority.
For a broker, holding a license means:
-
Mandatory compliance with local and international legislation, and adherence to regulator-established norms and standards. Maintaining transparency, and providing information about operations upon request, including financial documentation.
-
Safeguarding investor rights. Obligatory disclosure of potential risks, prevention of conflicts of interest, and the use of insider information.
In a trader's eyes, a regulatory license represents the broker's status and authority. The more reputable the regulator, the more trust a broker gains, leading to a larger client base for the company. A license serves as evidence that a broker complies with legislation and is unlikely to be interested in violating its clients' rights.
This review covers the role of the self-regulatory organization IIROC as a performing regulator, its functions, authority, reviews, and an expert’s opinion.
Description and functions of the IIROC
IIROC stands for Investment Industry Regulatory Organization of Canada. It is a non-governmental self-regulatory organization (SRO) with the authority to oversee participants and their operations in the stock and investment markets of Canada. IIROC establishes requirements for minimum capital, ensures an attractive investment climate, fosters fair competition, and mediates corporate disputes by tracking situations and transmitting results for consideration by other regulatory bodies. While the SRO doesn't regulate client services, it does address complaints from private individuals.
IIROC’s mission and objectives in the Forex market:
-
To develop rules, norms, and provisions mandatory for compliance by all accountable companies;
-
To develop legislation and audit licensees;
-
To check brokers for compliance with quality-of-service requirements, and to ensure adherence to international business conduct rules;
-
To regularly assess investment consultants and verify employees' qualification levels at broker-licensees;
-
To set a minimum capital requirement. Individual requirements might be established based on a broker's operational specifics.
In Canada, there is a regional division among regulatory bodies. In each province, its own regulator is in place, often represented by the Securities Commission. IIROC is an SRO that operates nationwide, overseeing the work of local SRO representatives, regulators, and accountable entities. IIROC is a non-profit organization that deals with pre-trial dispute resolution between legal entities and acts as an arbitrator.
To obtain an IIROC license, a broker has to:
-
Meet the requirements of local regulators;
-
Incorporate investment consultants into the organizational structure, whose qualification is overseen by IIROC;
-
Meet the minimum capital size requirements.
IIROC is a coordinating regulator. The primary demands are set by provincial regulators for brokers. IIROC acts as an independent auditor and mediator. The SRO monitors licensees and promptly informs provincial regulators about problems if they arise. While IIROC has the authority to impose fines and initiate legal proceedings, in practice, these matters are handled by government bodies. IIROC also reviews complaints from private traders. If a matter falls outside the regulator's authority, IIROC redirects it.
IIROC’s official website and available information
The regulator's website primarily serves as an informational hub. IIROC regularly publishes reports about its operations, ratings, local legislative changes, licensee requirements, and more. The site features a complaint submission form and a participant list, indicating that around 174 investment dealers and 31,000 registered individuals are licensees according to the site.
Overview of the website:
-
The upper auxiliary menu.

IIROC Website Sections
-
Informational sections. There is news about changes, disciplinary hearings, quick useful links, and report references.

IIROC Website Sections
-
Financial offers and the footer. There are regulator's services, links to other sites, privacy policy, and links to the regulator's social media accounts.

IIROC Website Sections
Main menu structure:
-
About IIROC. Regulator’s charter, organizational structure, and leadership.
-
Investors. This section contains information about choosing investment consultants, licensee lists, investor protection theory, and filing complaints.
-
Markets. This section provides info about regulated markets, trading oversight, corporate and government bond information, and statistics.
-
Rules and enforcement. This section provides Universal Market Integrity Rules (UMIR), regulatory standards, and legislation. This is the section with information governing relationships between broker-licensees and their clients.
-
Members. This section provides rules for registering individuals and securities market dealers, and obtaining licenses.
-
News & publications. Here are published annual reports, releases, strategic development data, etc.
For traders, the informational sections will be of primary interest. The news sections periodically publish warnings and updates on the progress of disciplinary hearings, investigations, and penalties. For instance, the regulator might identify and caution against pyramid schemes, reveal brokers falsely claiming IIROC licenses, or highlight elevated broker risks.
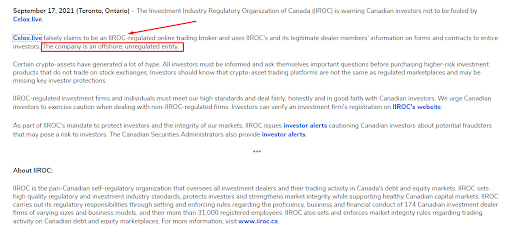
IIROC Website Sections
The "Investors" section, which includes information on complaint resolution procedures, will also be valuable.
Another notable section is the registry of disciplinary actions and unpaid fines. You can find it on the main page under the "Advisor Report" link in the informational sections.
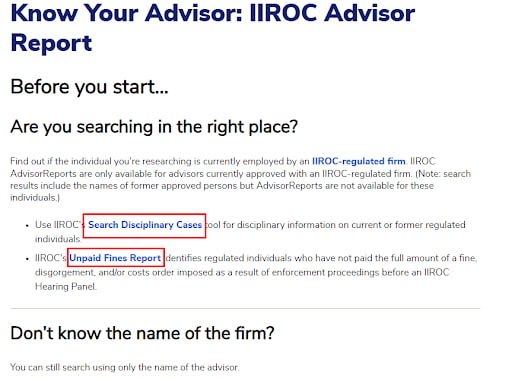
IIROC Website Sections
For guidance on locating a broker's license on the IIROC website, refer to the next section.
How to confirm a broker’s license on the IIROC website
Membership in the self-regulatory organization IIROC is mandatory for every broker. The IIROC license is issued after registration with the provincial regulator and enrolment in the Canadian Investor Protection Fund (CIPF).
To confirm a broker’s license on the VFSC website, do the following:
-
1
On the broker's website, find confirmation that the company is registered in Canada and is a member of IIROC. If a broker is not part of IIROC but provides services in Canada and deals with Canadian residents, they are likely in violation of the jurisdiction's financial laws. Note that a broker might have a Canadian subsidiary, and if it plans to enter the Canadian exchange market, it should establish a client agreement specifically with them. Alternatively, the obligations of the broker's parent company for the subsidiary should be legally defined.
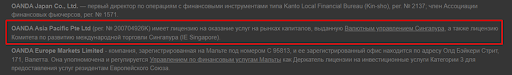
Screenshots from broker’s website
-
2
On the main page of the regulator's website, use the search bar to enter the broker's name.
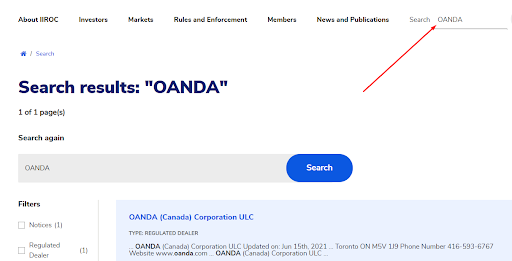
IIROC Website Sections
-
3
Compare the information in the broker's profile with the details provided on their website.

IIROC Website Sections
IIROC’s basic requirements for brokers
The basic requirements to obtain a license are to:
-
Comply with the UMIR rules.
-
Comply with provincial regulatory requirements.
IIROC has a reputation as a serious regulator. Unlike offshore regulators, IIROC genuinely audits and monitors licensees, and detects violations through its representatives in each province. However, IIROC has two drawbacks:
-
The regulator is a non-governmental self-regulatory organization. This means it lacks the authority to impose stringent penalties on violators. Instead, IIROC relies on provincial regulators and governmental organizations;
-
Canada's regulatory system is decentralized compared to analogous systems in the U.S., U.K., or Germany.
This complicates the adaptation to the Canadian market for brokers preferring to work in Europe, Asia, or the U.S.
IIROC license | Pros and cons
IIROC's primary role is coordinating, and secondarily, providing information. The regulator develops sets of rules, and norms, and establishes individual financial reporting requirements for each licensee, adjusting them as necessary. IIROC's mission is to integrate Canadian business regulations into the international economic society. For now, Canada remains relatively closed, and regulatory licenses apply only within its jurisdiction.
Advantages of trading with an IIROC-licensed broker:
Advantages of an IIROC license for traders:
-
In case of rights violations, traders can file a complaint with the regulator, which can impose fines on brokers after reviewing the claim;
-
For complaints about the quality of provided services, traders can turn to the provincial regulator. A valid IIROC license automatically confirms a broker’s registration;
-
In the event of a broker's bankruptcy, traders can anticipate compensation from the CIPF fund.
An IIROC license guarantees that a broker is registered with a provincial regulator, is an SRO and investor protection fund member, and is under the supervision of the Bank of Canada.
Disadvantages of trading with an IIROC-licensed broker:
The regulator acts as a mediator and assistant to official provincial regulators. It coordinates interactions between regulators of different provinces and brokers, and financial companies operating across the country but regulated in one province. IIROC reviews complaints from individual traders and is ready to examine them in specific cases. The regulator doesn't consider complaints related to the quality of trader service but helps redirect grievances to the appropriate authority.
IIROC’s jurisdiction
IIROC is a non-governmental self-regulatory organization in Canada. A broker's membership in the SRO means it is subject to the exclusive and independent control of Canada. This doesn't imply that the broker operates according to international legislation or has the right to provide services in other jurisdictions.
-
Credit, brokerage, and investment companies licensed by the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) operate under international legislation. The regulator is part of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS). Although brokers aren't related to the banking sector, this fact might streamline licensing for specific operations in Europe;
-
Some provincial regulators (Quebec, Alberta, etc.) are members of the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO);
-
Some provincial regulators are part of the Global Financial Innovation Network (GFIN). As of 2020, the organization had over 29 regulators and 60 organizations worldwide. Its goal is to establish a foundation for collaboration among regulators from different countries.
A broker with an IIROC license has the right to serve non-residents as long as it doesn't contradict their state's legislation.
Submission and consideration of complaints
On the internet, many sources state that the regulator doesn't entertain complaints from private individuals, redirecting them to other regulatory and judicial bodies. This isn't entirely accurate. IIROC does acknowledge complaints from individual traders. The regulator's website includes a complaint form in PDF format, along with contact details, and specifies specific scenarios in which IIROC can assist private traders. If the essence of the complaint doesn't align with the regulator's policies and jurisdiction, the grievance is redirected to other authorities. Limitations on the accepted claim amount aren't mentioned on the IIROC website.
Reviews of the IIROC by complaining investors and traders:
-
1
Go to the “Investors” section and select the subsection “How to Make a Complaint.” Review the information provided.
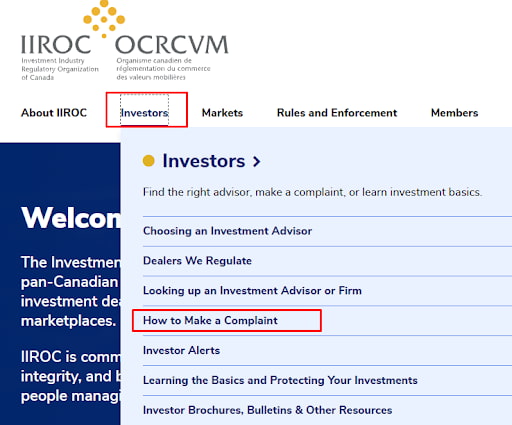
IIROC Website Sections
-
Broker executing actions on behalf of a trader without their knowledge and using their funds;
-
Persistent imposition of high-risk products by the broker that is not of interest to the trader;
-
Account, account access, or profile suspension;
-
Trading manipulations.
First and foremost, the regulator suggests attempting to resolve the issue directly with the company, warning that the complaint may be escalated to official authorities if necessary.
The regulator handles the following complaint types:
When filing a complaint, it's essential to provide personal details and thorough evidence, including screenshots, correspondence with the broker, and the client agreement. The regulator has emphasized multiple times that it does not address complaints related to client service.
Addresses and contact information for submitting complaints can be found below:
IIROC Website Sections
There is a complaint submission form available in the same section:

IIROC Website Sections
If the broker's violation falls within the jurisdiction and authority of the regulator, IIROC may initiate disciplinary hearings, impose fines, or consider the possibility of license revocation.
IIROC-licensed brokers | How to check on a broker
This section will be of interest to those who want to obtain information about all the active licenses of a broker with just a few clicks and don't have the time to monitor regulator websites. TU analysts analyze:
-
License validity, including its expiration date, and revocation/annulment status. Information is updated for all active licenses of the broker and its subsidiary structures, and branches;
-
Types of licenses and the corresponding services they cover;
-
Presence of disciplinary proceedings, violations, fines, and warnings.
Updates by TU are carried out monthly.
Expert’s assessment
In Canada, there's a complex multi-tiered regulatory system, which is both an advantage and a drawback. The advantage lies in each organization having its authority in a specific domain. That makes it clear who's responsible for what and where to turn for questions. The downside is the communication issues between regulatory bodies. Canada doesn't have a single federal regulatory authority; the securities market is regulated by provincial and territorial securities commissions.
Key Structures:
-
CSA (Canadian Securities Administrators);
-
IIROC is a self-regulatory organization that isn't government-based. It's organized by market participants themselves and somewhat resembles FINRA in the U.S., in essence. However, unlike the U.S. SROs, IIROC barely deals with retail clients. Its task is to ensure efficiency and communication among licensees;
-
CIPF is a fund tasked with investor protection in case of a broker's bankruptcy;
-
AMF is Autorité des marchés financiers. It oversees financial markets in Quebec and is an example of a territorial regulator;
-
Canadian Arbitration Court adjudicates disputes between brokers, clients, and other market participants.
IIROC serves as a regulator for brokers and the entire Canadian financial system, but not for traders. The organization develops operational Universal Market Integrity Rules (UMIR), oversees industry development departments, etc. The regulator also supervises investment administrators who conduct on-site assessments of companies and establish individual capital requirements and multipliers based on risk levels.
Conclusion
IIROC is a self-regulatory organization that coordinates the actions of local territorial regulators and its own regional representations. For a trader, a broker's membership in IIROC signifies the company's eligibility to operate in Canada. Complaints can be filed with IIROC, but they should also be duplicated to the territorial regulator at the broker's registration location or the jurisdiction's courts.
About the author of this review
Oleg Tkachenko, author and analyst at TU
Oleg Tkachenko has been TU’s financial analyst and economic observer since 2016. During this time, he has prepared more than 100 reviews of financial companies and analytic articles on technical and fundamental analysis, as well as developed over 10 trading systems. Oleg’s motto is to help everyone come all the way from a novice trader to a professional.
FAQs
What is the IIROC?
IIROC is a non-governmental self-regulatory organization in Canada that oversees and facilitates interactions in the securities market across the entire country. It collaborates with provincial regulators and other structural organizations. It reviews claims from private traders when there are clear violations of legislation and manipulations.
What do I get from trading with IIROC-licensed Forex brokers?
-
1
The ability to address disputes with the regulator in case of clearly violated investor rights such as the unauthorized use of funds, imposition of high-risk services, and manipulations.
-
2
The option to appeal to the Arbitration Court or the provincial regulator in case of service quality issues.
An IIROC license indicates that a broker operates within Canada's legislation, is registered with a provincial regulator, and is a member of the CIPF compensation fund.
How to check if a broker holds an IIROC license?
There are two options:
-
1
Search for the broker on the main page of the regulator's website.
-
2
Visit the broker's profile on the Traders Union website to see information about all current licenses. The second option saves time, as the TU website provides up-to-date information on all broker licenses and their representations.
How to submit a complaint against a broker to the IIROC?
-
1
Complete the complaint form on the regulator's website and send it to one of the specified addresses. If the complaint concerns service quality, it will be redirected to provincial regulators or OSFI and FCAC regulators.
-
2
Register with the Traders Union and seek assistance from the legal department.
The second option is free, takes less time due to fewer stages, and can be effective in resolving the issue at an early stage.
Team that worked on the article
Oleg Tkachenko is an economic analyst and risk manager having more than 14 years of experience in working with systemically important banks, investment companies, and analytical platforms. He has been a Traders Union analyst since 2018. His primary specialties are analysis and prediction of price tendencies in the Forex, stock, commodity, and cryptocurrency markets, as well as the development of trading strategies and individual risk management systems. He also analyzes nonstandard investing markets and studies trading psychology.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
The topics he covers include trading signals, cryptocurrencies, Forex brokers, stock brokers, expert advisors, binary options. He has also worked on the ratings of brokers and many other materials.
Dr. BJ Johnson’s motto: It always seems impossible until it’s done. You can do it.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO). Mirjan is a cryptocurrency and stock trader. This deep understanding of the finance sector allows her to create informative and engaging content that helps readers easily navigate the complexities of the crypto world.









