How To Trade Using Order Blocks



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
An order block is a term used in liquidity analysis to describe the concentration of trading orders placed by large market participants:
-
In Level 2 order books. This is the primary meaning. It refers to the price levels where traders place limit orders with high total volumes
-
On market profiles. Sometimes, the term “order block” refers to the levels at which trades with high total volumes were executed
Order block is a sign of presence of large players in the market, who need active liquidity. These are the price zones where "market whales" manipulated the price and where some of their orders are in drawdown at the moment. This is their shadow "trace" - open positions that should be closed. Prices will definitely return to these levels and we can prepare for that. So for us the Order Block zone is a level for entry or exit.
The concept of order blocks comes from supply and demand analysis in order books (Level 2 data). Traders focus on assessing the changes in supply and demand that cause even the slightest price fluctuations, thereby getting a competitive advantage over other market participants.
The problem is that such thorough analytical work is rather complicated – much more complicated than searching for moving average crossovers. Moreover, the internet offers little expert content on order block trading with chart examples. In this post, I will share valuable information, including trading examples with detailed descriptions, that will be useful for those who want to know what order blocks are.
Example of an order block
Here is what order blocks on a Bitcoin chart look like:
 Order blocks on a chart
Order blocks on a chartThe brighter and bolder the lines that mark the levels, the larger the order blocks. In this case, the bold red lines mark the most evident order blocks.
The number 1 shows a current buy order block:
-
The Depth of Market indicator on the right displays an evident spike. It means that market participants are ready to buy a large number of Bitcoins at $60,400 per coin. Regular (retail, small) market participants cannot bid such an amount or create a pronounced spike on the indicator.
-
The order block stays at the $60,400 level during the whole time displayed on the chart, which can be interpreted as a steady interest.
The number 2 shows an order block that worked. The price descended to the $60,500 level where a buy order block was placed. After all the orders were executed (the large player accumulated a long position), the price went up.
Best Forex brokers


How to confirm an order block
In my opinion, to confirm an order block, it is more rational to use classic volume indicators (or Deltas) and price action patterns:
-
Vertical volume indicators (under the value area) directly confirm that the limit orders have been filled, signifying the satisfaction of institutional participants’ interest. The Delta indicator provides more details.
-
Price action patterns help confirm the price’s reactions and make trading decisions – for example, to enter a position expecting that it will be in harmony with a large market participant’s actions.
I mean if you trade reversals from order blocks, confirmation tools should help you make sure that a reversal is really happening and you have a reference point to make a trading decision.
Also, to make sure that an order block is strong, it is important to monitor its behavior over time. The order block should not become thinner when the price nears it. Thus, you confirm that the large player is confident about his intention.
But no matter how big it is, an order block can never guarantee that the price will bounce off it and the market trend will change.
How to trade order blocks
Order blocks can be traded in various ways. In this post, I offer three approaches:
-
Reversal;
-
Breakout;
-
Driving.
But you can explore charts more thoroughly using depth of market analysis tools to build your own, more versatile strategies with unique trading rules.
All the screenshots below are from the ATAS platform that I discussed here: ATAS Review: The Order Flow Trading Platform's Pros and Cons.
Order block trading strategy # 1 – Reversal
A reversal is a trend change – it’s often short-term, but sometimes lasts longer – that occurs after the price interacts with an order block.
Here is an example of trading a reversal from an order block:
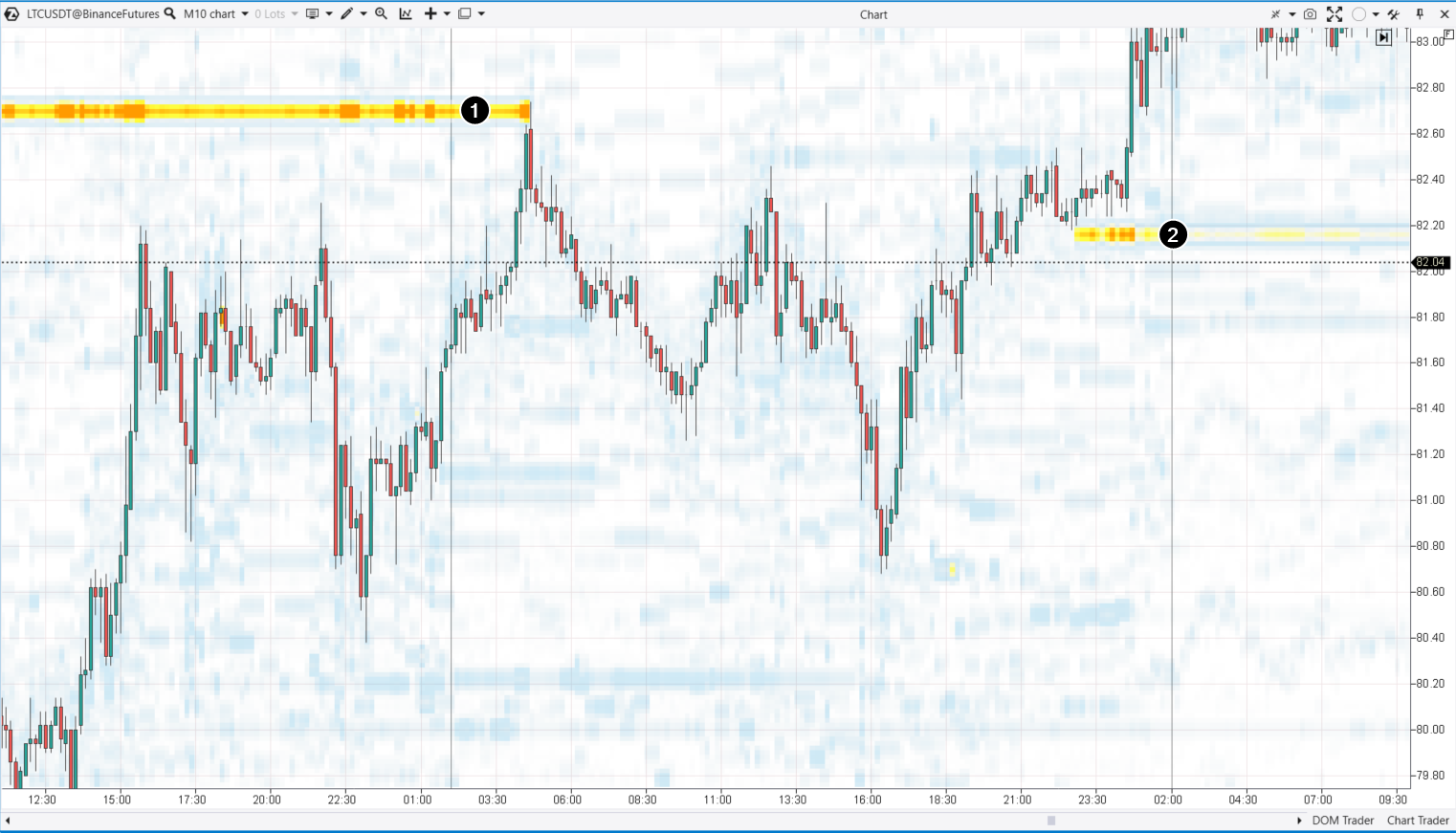 Order blocks on an LTC/USD chart
Order blocks on an LTC/USD chartA buy order block (1) placed at 82.70 made the price reverse and descend as soon as it touched the 82.70 level. The bold line disappeared, which means the large player fulfilled his intention to enter a short position. The large size of his trade changed the sentiment and established a short-term trend.
The number 2 shows a demand driving signal that will be considered later.
How to trade reversals from order blocks
When you see the price approaching an order block, be ready to enter a position on clear signals that the trend is changing. You can:
-
use the oscillators you prefer;
-
simply place your orders next to the large player’s orders using stop losses as insurance and remembering that nobody can guarantee a future price movement or resist the whole market.
Order block trading strategy # 2 – Breakout
Below is an example of an order block breakout.
 An order block breakout on an ETH/USD chart
An order block breakout on an ETH/USD chartThe chart shows that a buy order block was placed near a psychological level of 2000. However, the downward impulse was strong enough for the price to break through the large buy orders and keep dropping.
Here traders could join the downward impulse. On a lower timeframe, you would clearly see that as the price broke through the order blocks, its movement formed a bounce trajectory shown by the black arrow.
Traders could use it to find short position entry points:
-
at the top of the bounce after the first contact with the order blocks;
-
at the downward breach of the first bottom followed by the bounce.
Whichever approach you apply, it is important to protect your capital so that possible mistakes that nobody can be insured against will not entail extremely negative consequences.
Order block trading strategy # 3 – Driving
The chart below shows what price driving is. In simple terms, when a large player places large orders above and below the price, he thereby influences the sentiment and can capitalize on it.
If the large player wants the price to go down, he will place a large sell order. The other market participants will see this order and will probably want to enter short positions as well, pushing the price down with their sells. This way, the large player will achieve his goal.
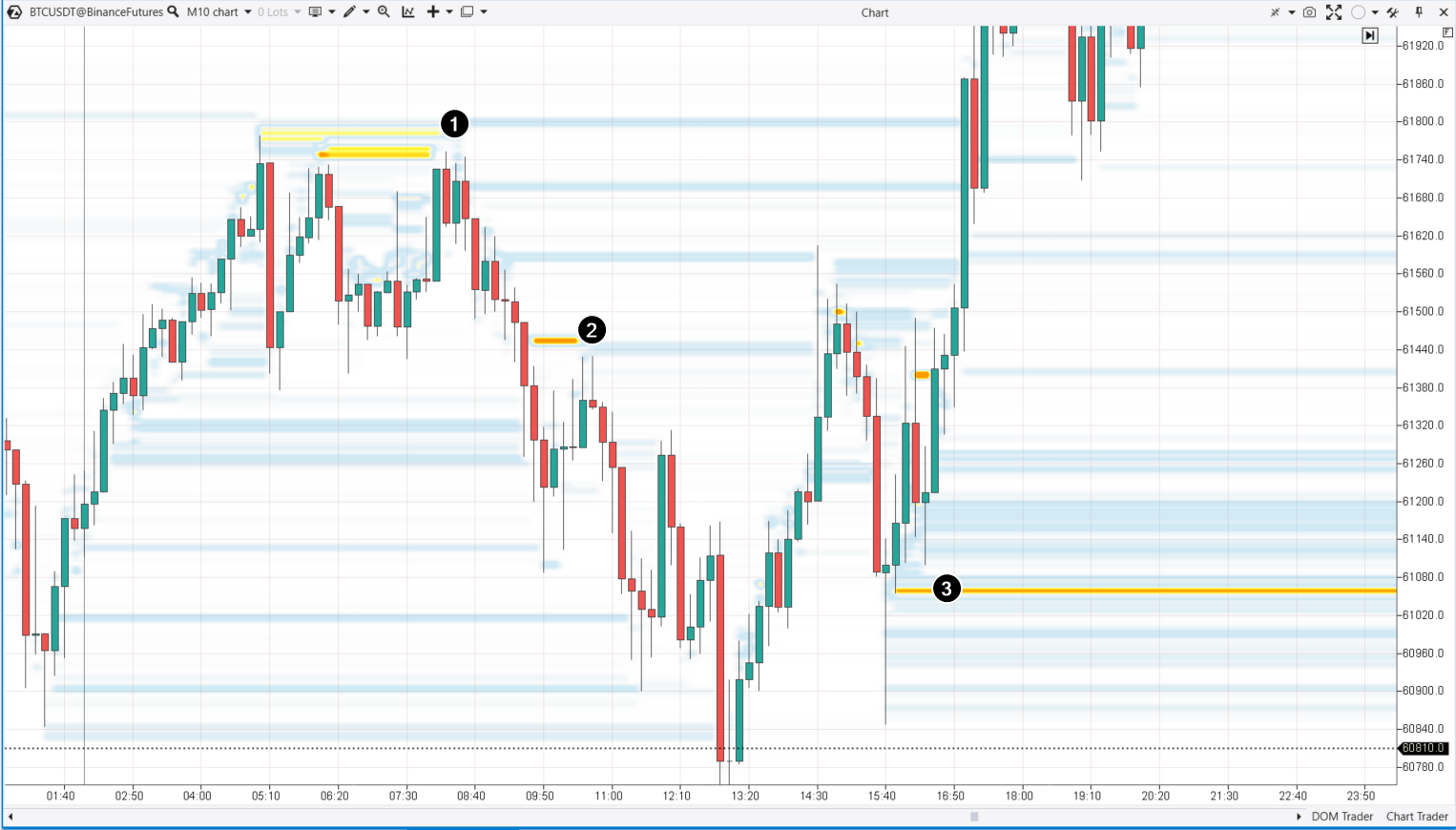 Trend driving on a BTC/USD chart
Trend driving on a BTC/USD chartThe number 1 on a 10-minute Bitcoin price chart above, shows that the large sell orders near 61750-61800 prompted selling and stopped the upward impulse that started at 01:40.
The number 2 shows that the large sell orders resulted in a bearish breach of the 61440 short-term support. Then, this level was tested.
The number 3 shows the driving of demand followed by the active buying of Bitcoin, a price rise, and a breach of the 61750-61800 resistance area.
Order block trading – One more example
Sometimes, the term “order block” refers to price levels with high volumes on the Market Profile indicator.
Essentially, order blocks in order books displayed by the Depth of Market indicator are the orders that appear on the Market Profile indicator after execution. In other words, high volume levels on the Market Profile are practically the same order blocks, but they are already executed.
 Order blocks on a profile indicator
Order blocks on a profile indicator
But as sellers overcame the support, the price dropped lower and the volumes moved from the order book to a high volume level on the profile indicator. Later, this level effectively worked as resistance, which is shown by the numbers 2 and 3.
Is order block trading profitable?
Yes, it can be profitable if your interpretation of the interaction between the price and order blocks is mostly correct. Order block trading requires proper discipline.
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- More accurate identification of the price levels that really matter due to the placement of large orders that reflect the interests of important market participants.
- Improvement of the risk/reward ratio.
- Applicable to various markets for intraday trading
- Indicators are the source of raw market data that is provided in real time and does not change.
- Interpreting Level 2 data is complicated.
- Order blocks cannot be used for investing because they are displayed on low-scale charts ignored by long-term investors.
- Real-time reception of exchange data may require the use of paid software and services.
- It is difficult to establish trading algorithms when analyzing history. The ever-changing market requires you to analyze it yourself rather than use advisors that work by simple “if–then” rules.
Advice:
The ATAS platform has the Market Replay feature allowing you to use past data to trade order blocks in training mode without risking real funds.
Summary
Order block trading can be a powerful tool in a trader’s arsenal, but it’s important to approach it properly. The price will most likely react to order blocks (pending or executed), but traders should take into account that actual price action will differ from predictions.
FAQs
What does an order block mean?
Put simply, an order block is a large number of limit orders at one or several closely positioned price levels.
Why is it called an order block?
Probably because this name accurately conveys the phenomenon’s essence. A cluster (block) of orders reflects market participants’ interest and usually results in a significant price change.
Is order block the same as supply and demand?
It is about the same. For example, a buy order block signals a pronounced demand for an asset or buyers’ readiness to pay money for it. The same goes for supply, which involves traders’ interest in selling an asset.
How to identify order blocks?
Order blocks can be identified through the Depth of Market (DOM) indicator or related liquidity analysis tools in order books.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
For over 15 years, Oleg worked as a copywriter and journalist at advertising and marketing agencies, as well as radio and television companies. His writing style is aimed at using simple terms to explain only those things that matter to the reader – benefits, risks, and realizable ideas. During the 2008 financial crisis, Oleg got interested in the stock and Forex markets and thoroughly explored price action to start working as an independent expert in 2018.

Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital cryptocurrency that was created in 2009 by an anonymous individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a technology called blockchain, which is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers.
CFD is a contract between an investor/trader and seller that demonstrates that the trader will need to pay the price difference between the current value of the asset and its value at the time of contract to the seller.
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is the practice of buying and selling currencies in the global foreign exchange market with the aim of profiting from fluctuations in exchange rates. Traders speculate on whether one currency will rise or fall in value relative to another currency and make trading decisions accordingly. However, beware that trading carries risks, and you can lose your whole capital.
Index in trading is the measure of the performance of a group of stocks, which can include the assets and securities in it.
A limit order is a type of order used in trading where an investor specifies a particular price at which they want to buy or sell a financial asset. The order will only be executed if the market price reaches or exceeds the specified limit price, ensuring that the trader gets the desired price or better when the trade is executed.





























































































































