FINMA | Financial Regulator Of Switzerland



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
The Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) is the regulatory body overseeing financial stability and integrity in Switzerland. It supervises banks, insurance companies, stock exchanges, Forex brokers, securities dealers, and other intermediaries, ensuring compliance with financial laws and maintaining market transparency. FINMA's responsibilities include licensing, supervision, and enforcement, aimed at protecting creditors, investors, and policyholders.
The guide below delves into FINMA's licensing system, detailing its various licenses and their impact on financial institutions and traders, aiding them in navigating the financial landscape effectively.
What is FINMA and how does it work
The Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) was established in 2009 as a result of reform in the wake of the global financial crisis, when it became clear that the existing regulatory bodies did not have sufficient competence to effectively control capital flows. FINMA is currently the only organization supervising the Swiss financial markets.
Areas of Supervision and regulatory scope - FINMA supervises various sectors, including banking, insurance, stock exchanges, and securities dealers. It ensures these sectors operate within the regulatory framework, maintaining financial stability and integrity across the market. FINMA regulates over 500 financial institutions, including approximately 250 banks and securities dealers, and around 200 insurance companies. It also oversees numerous fund management companies and financial market infrastructures.
Enforcement Actions - in 2022, FINMA took several enforcement actions, imposing fines and sanctions on institutions violating financial regulations. For example, it issued 25 enforcement decisions, reflecting its commitment to upholding market integrity.
Market Practices and Compliance - FINMA rigorously monitors market practices to ensure compliance with Swiss financial laws. In its 2022 assessment, FINMA found that while most institutions adhered to the required standards, some areas required further attention. Also it is useful to read FINMA's report on risk management practices and FINMA's investigations and reports on AML compliance.
International Collaboration - FINMA plays a significant role in international financial regulation, collaborating with global regulatory bodies such as the European Securities and Markets Authority ( ESMA) and the International Organization of Securities Commissions ( IOSCO). These partnerships help FINMA align Swiss financial regulations with international standards, enhancing global financial stability.
Types of FINMA licenses
FINMA issues several types of licenses to financial institutions, each with specific regulatory requirements. These include:
Banking licenses: For institutions accepting public deposits and providing lending services.
Securities licenses: For entities involved in securities trading and market making.
Fintech licenses: For innovative firms accepting deposits up to CHF 100 million without engaging in traditional banking activities.
Crypto licenses: For businesses dealing in digital assets and cryptocurrencies, including exchanges and custodians.
Insurance licenses: For companies offering insurance and reinsurance services.
Requirements for Forex brokers to obtain a FINMA license
Forex brokers aiming to obtain a license from the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) must meet a set of stringent requirements. These requirements (organizational, financial, operational, etc) ensure a high level of security, transparency, and reliability in their operations.
Organizational requirements
Structure and management: Brokers must establish a well-defined organizational structure with clearly assigned responsibilities for management and control. Executives must possess the necessary qualifications and experience to manage financial services effectively. This includes adhering to FINMA's requirements, which mandate that key personnel demonstrate integrity and professionalism, ensuring sound management of the firm’s operations.
Board of directors: Companies must have an independent board of directors responsible for overseeing the company’s activities and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. According to FINMA, the board must include members with diverse expertise who are capable of independently monitoring and guiding the firm's strategy and performance.
Financial requirements
Сapital adequacy: To meet the capital adequacy requirements set by the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA), brokers must adhere to specific guidelines detailed in the Capital Adequacy Ordinance (CAO). The key requirements include maintaining a minimum fully paid-up capital of CHF 1.5 million.
Liquidity: Brokers must demonstrate adequate liquidity to meet their financial obligations and support their trading activities. This includes maintaining sufficient liquid assets to cover potential client withdrawals and other liabilities.
Operational requirements
Risk management: Brokers must implement robust risk management frameworks to identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with their activities. This includes having policies and procedures for managing market, credit, operational, and other relevant risks.
Internal controls: Effective internal control systems must be in place to ensure the integrity and accuracy of financial and operational processes. This includes regular audits and compliance checks.
Client protection
Segregated accounts: Brokers are required to keep clients' funds in segregated accounts, separate from the broker's operational funds. This protects clients' money in case of the broker's insolvency.
Negative balance protection: Brokers must offer negative balance protection to ensure that clients do not lose more than their initial investment, safeguarding them from significant financial losses.
Transparency and reporting
Regular reporting: Brokers must provide regular financial and operational reports to FINMA. This includes detailed information on their financial condition, risk management practices, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Disclosure requirements: Brokers must disclose key information to their clients, including fees, charges, risks associated with trading, and terms of service. This ensures transparency and helps clients make informed decisions.
By meeting these stringent requirements, Forex brokers demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high standards of security, transparency, and integrity in their operations, thereby gaining the trust of clients and regulatory authorities alike.
Below is a comparative table of best Forex brokers, licensed and regulated by FINMA:
| Forex regulation | Min. deposit, $ | Leverage, 1:0 | Min Spread EUR/USD, pips | Trading Platform | Open account | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFSA, FCA, ASIC, FINMA, and SFC | No | Up to 1:30 | 0,2 | SaxoTraderGO, SaxoTraderPRO | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| FINMA | 100 | From 1:1 to 1:200 on weekdays/ from 1:1 to 1:20 on weekends | 0,1 | MobileTrading, WebTrader, JForex, Java | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| FCA, FINMA, DFSA, MFSA, MAS | No | Up to 1:400 | 1,1 | MT4, MobileTrading, WebTrader, Advanced Trader | Open an account Between 70 and 80%
of retail investors are losing money when trading forex instruments and CFDs. |
|
| FCA UK, ASIC, SEC, VFSC, TCSP Hong Kong, FSC Mauritius, FSA Seychelles | 100 | Up to 1:1000 | 0,1 | In Trade, MT4, MT5 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| FCA, BaFin, ASIC, MAS, CySec, FINMA, BMA, CFTC, NFA | 1 | Up to 1:200 | 0,6 | MetaTrader4, API, ProRealTime, IG Trading Platform | Study review |
This table highlights the regulation and key safety features of each broker, making it easier to compare and choose the right one.
How confirm a broker’s license on the FINMA website
Brief overview of FINMA website
The FINMA website (Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority) is a comprehensive resource for information on financial regulation in Switzerland. The homepage features key sections including:
About FINMA: Provides an introduction to the organization, its mission, and structure. It details FINMA's role in overseeing and regulating financial markets to ensure stability, transparency, and protection for investors.
 FINMA website
FINMA websiteAuthorization: This section contains laws, ordinances, and circulars governing financial activities. It is a valuable resource for understanding the regulatory framework and guidelines that financial institutions must adhere to.
 FINMA website
FINMA websiteSupervision: Outlines the supervisory activities of FINMA, including risk assessments, enforcement actions, and ongoing monitoring of financial entities to ensure compliance with regulations.
 FINMA website
FINMA websiteEnforcement: Describes FINMA's enforcement powers, processes, and case management. It includes information on investigations, sanctions, and legal actions taken against non-compliant entities.
 FINMA website
FINMA websitePublications & News: Offers access to FINMA's latest reports, press releases, and publications. This section keeps stakeholders informed about recent developments and regulatory updates.
 FINMA website
FINMA website
Each section is well-organized, providing clear and detailed information to help stakeholders navigate the complex landscape of financial regulation in Switzerland. The website also features a search function and multilingual support, enhancing accessibility for a diverse audience.
How to confirm broker’s license on FINMA’s website
To confirm a broker’s license on FINMA’s website, take these simple steps:
Visit the FINMA Website: Go to FINMA's official website.
 FINMA website
FINMA websiteNavigate to “Authorisation”: Click on the "Authorisation" section in the main menu.
 FINMA website
FINMA websiteSelect “Authorised or registered institutions”: Choose "Authorised or registered institutions, persons and products".
 FINMA website
FINMA websiteSearch for the broker: Use the search function to enter the name or registration number of the broker. You can also choose a category of the company you are searching for.
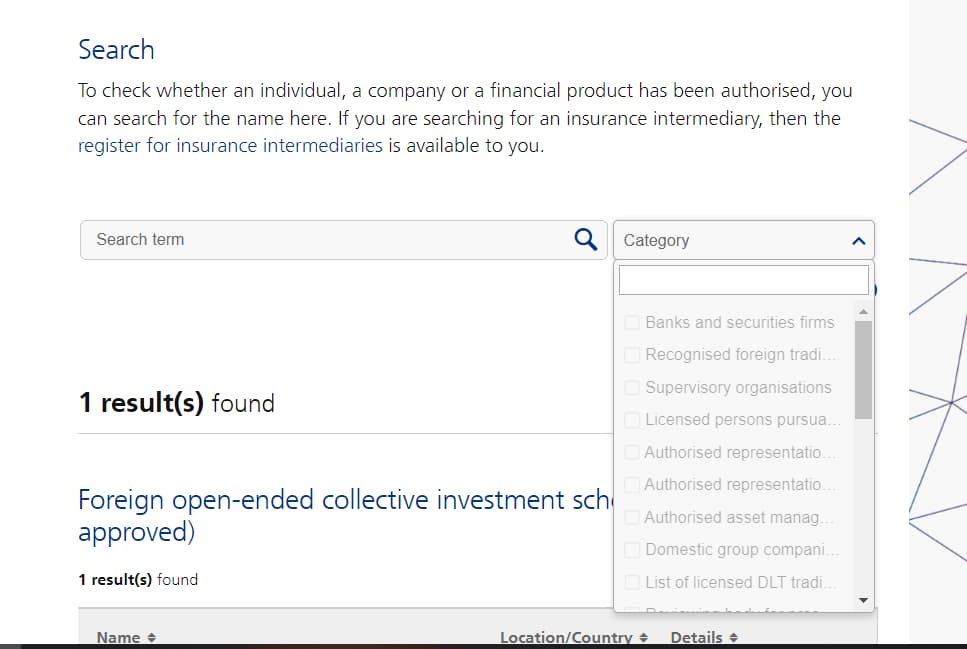 FINMA website
FINMA websiteVerify details: Review the search results to ensure the broker is listed and check their authorization status and details.
By following these steps, you can confirm whether a broker is authorised by FINMA.
The benefits I’ve found trading with FINMA-regulated brokers
As a trader with over a 10-year experience working with FINMA-regulated brokers, I can attest to the security and stability provided by this regulatory body. FINMA's rigorous oversight ensures brokers adhere to high standards, offering a safer trading environment. Notably, FINMA mandates that brokers maintain a minimum capital requirement of CHF 1.5 million, ensuring financial robustness.
For newcomers, I recommend thoroughly researching the specific FINMA licenses your broker holds, as this reveals the scope of their regulatory compliance. Utilize the advanced trading tools and educational resources often provided by FINMA-regulated brokers, which can significantly enhance your trading strategies and overall experience.
Additionally, FINMA’s enforcement actions underscore their commitment to integrity. In 2022 alone, FINMA issued 25 enforcement decisions, highlighting their proactive stance in maintaining market discipline. Pay close attention to the broker's capital adequacy and risk management practices. FINMA’s strict requirements ensure that licensed brokers are well-prepared to handle market volatility, safeguarding your investments. Choosing a well-regulated broker under FINMA is a strategic move that provides peace of mind and a solid foundation for your trading journey.
Conclusion
By regulating a diverse array of financial institutions, including banks, insurance companies, and Forex brokers, FINMA ensures compliance with rigorous Swiss financial laws. Its responsibilities encompass licensing, supervision, and enforcement actions aimed at safeguarding investors, creditors, and policyholders.
FINMA’s stringent regulatory framework demands high standards of transparency, financial stability, and risk management from licensed entities. For traders, understanding the various licenses and requirements helps in choosing reliable financial institutions. FINMA’s commitment to robust supervision and adherence to international standards ensures a secure and trustworthy trading environment, ultimately enhancing market confidence and protecting the interests of all stakeholders in the Swiss financial system.
FAQs
What is FINMA and what is its role in the Swiss financial market?
FINMA, the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority, is an independent regulatory body that oversees Switzerland's financial markets. Its roles include protecting investors, creditors, and policyholders, and ensuring financial system stability by supervising banks, insurers, stock exchanges, and other financial institutions.
What types of licenses does FINMA issue?
FINMA issues several licenses including banking, securities, fintech, crypto, and insurance licenses. These licenses come with specific regulatory requirements and varying levels of supervision depending on the financial activities involved.
What is the process for obtaining a FINMA license?
Obtaining a FINMA license involves submitting a detailed application, undergoing a review and assessment by FINMA, and meeting compliance and risk management criteria. The process varies based on the business model's complexity and risk.
How does FINMA ensure compliance and enforcement of its regulations?
FINMA ensures compliance through regular audits, risk-based supervision, and enforcement actions such as fines or license revocation. It also provides guidance and collaborates with international bodies to maintain regulatory standards.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.

Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.
Forex leverage is a tool enabling traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital, amplifying potential profits and losses based on the chosen leverage ratio.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that relies on cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology.
FINMA is a government body in Switzerland overlooking financial markets including banks, insurance companies, stock exchange, cryptocurrencies, etc
An investor is an individual, who invests money in an asset with the expectation that its value would appreciate in the future. The asset can be anything, including a bond, debenture, mutual fund, equity, gold, silver, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real-estate property.





























































































































