Thematic Investing: A Full Guide To Trend-Based Investing



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
Thematic investing is all about focusing on long-term trends that span multiple industries, rather than limiting yourself to specific sectors. This strategy lets you tap into big-picture changes like electric vehicles or cybersecurity, which can affect a wide range of companies. And remember, it’s not a "set it and forget it" approach — you’ll need to keep an eye on your investments and make adjustments as trends evolve to keep your portfolio on track for future growth.
Unlike traditional investing that might keep you in a sector like energy or healthcare, thematic investing follows broader shifts in the world. The key is not just spotting these trends but also digging deep into their growth potential and risks. In this article, we will understand how to approach thematic investing, compare it with traditional investing and see historical returns generated by thematic investing.
What is a thematic investing?
Thematic investing is an investment strategy that focuses on identifying and capitalizing on long-term trends or themes, rather than on specific companies, sectors, or regions. These themes typically revolve around large-scale societal, economic, or technological shifts, such as environmental sustainability, demographic changes, technological innovation, or healthcare advancements.
Investors in thematic investing select assets based on their alignment with these trends, believing that companies and industries tied to these themes will experience growth as the themes become more prevalent. Popular themes include renewable energy, artificial intelligence, electric vehicles, aging populations, and digitalization.
Thematic investing vs. traditional investing
Traditional investing typically involves selecting stocks or funds based on their performance within specific sectors, like healthcare or energy. In contrast, thematic investing looks beyond sector boundaries, focusing on the larger macroeconomic and societal trends that drive long-term growth across various industries. This approach can provide broader exposure and potentially higher returns, as it allows investors to capitalize on the interconnectedness of global markets.
 Comparison of Thematic Investing vs. Traditional Investing, source: Morningstar
Comparison of Thematic Investing vs. Traditional Investing, source: MorningstarHow to get started with thematic investing
Step 1: Identify trends
The first step in thematic investing is identifying the trends that have the potential to drive long-term growth. This involves looking at macroeconomic factors, technological advancements, and societal changes that are shaping the future. Tools like Google Trends, financial news platforms, and specialized thematic research services can help you spot emerging trends. For example, the rise of electric vehicles or the increasing focus on cybersecurity are trends that could form the basis of a thematic investment strategy.
Step 2: Analyze the theme
Once you've identified a trend, the next step is to analyze its potential as an investment theme. This involves evaluating the theme's growth prospects, market impact, and associated risks. Look for data points like revenue growth, market penetration, and regulatory developments that could affect the theme's performance. For instance, when analyzing the theme of renewable energy, consider factors like government policies, technological advancements, and consumer adoption rates.
Step 3: Select the right investment products
After analyzing the theme, you'll need to select the investment products that best capture its potential. These could include thematic ETFs, mutual funds, or individual stocks that align with your chosen theme. When choosing a product, consider factors like fund performance, expense ratios, and the underlying holdings. For example, if you're interested in the artificial intelligence theme, you might look for an ETF that includes a diverse range of AI-focused companies across different sectors.
To invest, you will also need to choose a reliable broker. We have studied the conditions of the best brokers and offer you to read the comparison table.
| Demo | Min. deposit, $ | ETFs | Stocks | Investor protection | Open account | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | 50 | Yes | Yes | €20,000 £85,000 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| Yes | 5 | Yes | Yes | €20,000 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| Yes | 10 | Yes | Yes | No | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| Yes | 50 | Yes | Yes | £85,000 €20,000 | Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
|
| Yes | 100 | Yes | Yes | No | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Step 4: Monitor and adjust
Thematic investing is not a "set it and forget it" strategy. It's essential to continuously monitor your investments and be ready to adjust your portfolio as the theme evolves. This could involve rotating out of themes that have reached maturity and reallocating capital to emerging trends. Tools like portfolio management software or thematic investment platforms can help you keep track of your themes and make informed decisions.
Key themes in thematic investing
Technology stocks
The pace of innovation in the technology sector is staggering, with new technologies like AI, blockchain, and quantum computing transforming industries at a breakneck speed. Investing in technology stocks offers the opportunity to ride the wave of this innovation, capturing the growth of companies at the forefront of these changes.
For instance, AI is revolutionizing not just the tech sector but also healthcare, finance, and even retail. Companies like Microsoft, with its Azure AI services, or Amazon, with its AI-driven e-commerce platform, are prime examples of how technology stocks can offer exposure to this powerful theme. However, it’s also important to consider the risks — such as the potential for overvaluation and the rapid pace of technological obsolescence.
 Historical Performance of Technology ETF (XLK), Source: Yahoo Finance
Historical Performance of Technology ETF (XLK), Source: Yahoo FinanceHealthcare investing
The healthcare sector is undergoing a transformation, driven by innovations in biotechnology, precision medicine, and health technology. These advancements offer investors the opportunity to tap into a sector that is not only essential but also poised for significant growth. The aging global population and the increasing demand for personalized medicine are key drivers of this theme.
Investing in healthcare might involve focusing on biotech firms developing cutting-edge treatments, or companies like Medtronic, which are leading the way in medical device innovation. However, healthcare investing also comes with its own set of challenges, including regulatory risks and ethical considerations, particularly when it comes to areas like genetic modification and drug pricing.
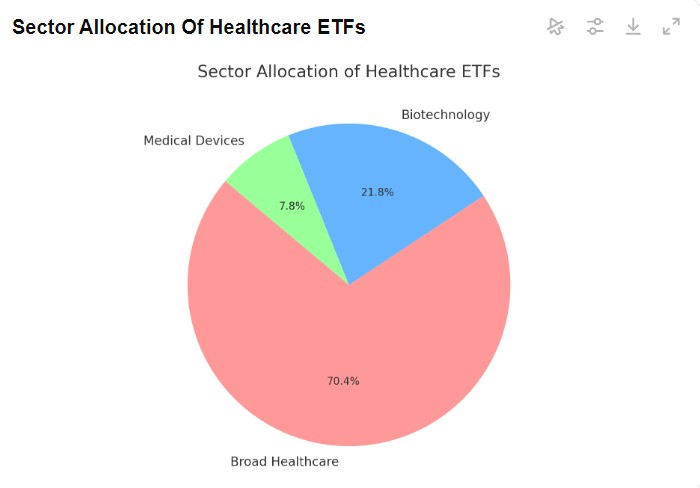 Sector Allocation of Healthcare ETFs, Source: etf.com
Sector Allocation of Healthcare ETFs, Source: etf.comRenewable energy
Investing in renewable energy involves looking at companies that are leading the transition to a low-carbon economy. This includes firms like Tesla, which is at the forefront of the electric vehicle revolution, and NextEra Energy, a major player in the renewable energy sector. While the potential for growth in this theme is significant, investors must also be mindful of the risks, such as changes in government policies and the technological challenges associated with energy storage.
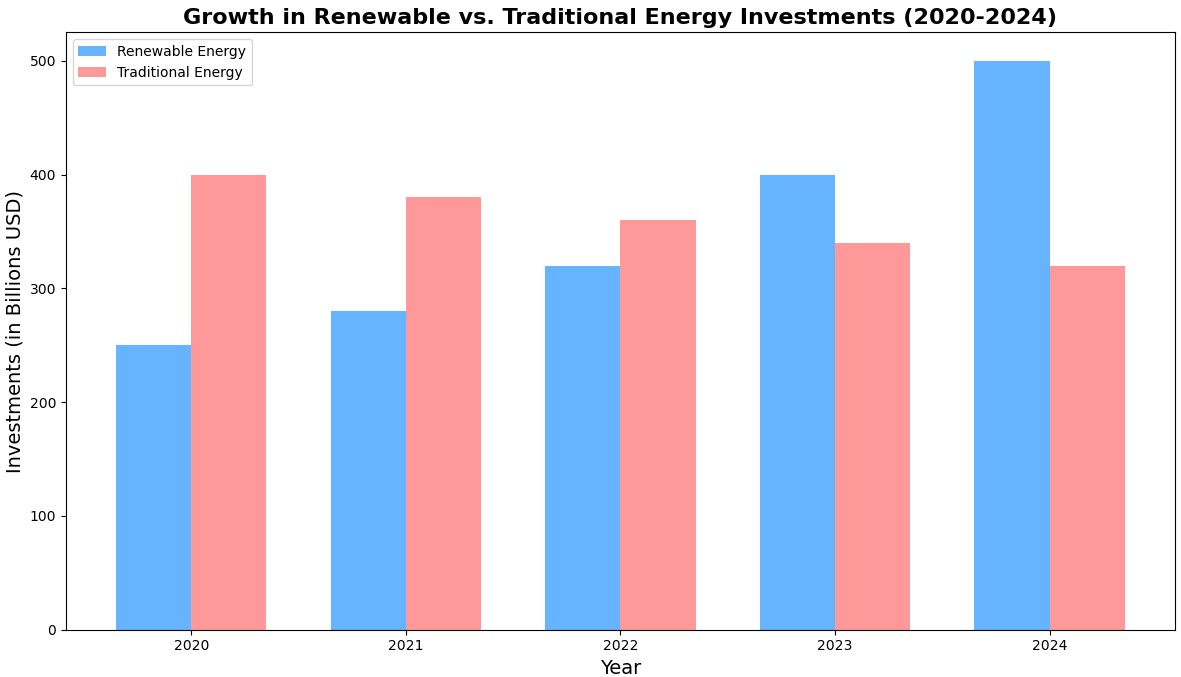 Growth in Renewable vs. Traditional Energy Investments (2020-2024), source: International Energy Agency (IEA)
Growth in Renewable vs. Traditional Energy Investments (2020-2024), source: International Energy Agency (IEA)Other emerging themes
Beyond the major themes of technology, healthcare, and renewable energy, there are several emerging themes that offer unique opportunities for growth. These include demographic shifts, such as the rise of the middle class in emerging markets, and the future of mobility, encompassing electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and smart cities.
For example, the theme of demographic change might lead you to invest in companies that cater to the aging population, such as those in the healthcare and financial services sectors. Similarly, the future of mobility theme could involve investments in companies developing autonomous vehicle technology or smart infrastructure.
Pros and cons of thematic investing
- Pros
- Cons
- Access to high-growth opportunities. Thematic investing lets you capitalize on emerging trends like AI and renewable energy, offering the potential for significant returns.
- Portfolio diversification beyond traditional sectors. Investing across multiple sectors through themes like digital transformation or sustainability can provide broader diversification.
- Alignment with personal values. You can align your investments with your values, such as supporting environmental sustainability through renewable energy or ESG practices.
- Forward-looking investment strategy. Focuses on future trends, positioning your portfolio to benefit from long-term megatrends like electric vehicles and smart cities.
- Hard to know if you're overpaying. When you're investing in trendy sectors, it's tough to tell if you're paying a fair price for stocks, especially if those companies aren’t making profits yet.
- No clear track record to rely on. Since many themes are based on newer industries, you don’t have much historical data to show how they might perform when the market takes a hit.
- Expensive to get in. Thematic funds often come with higher fees, which can quietly chip away at your profits over time.
Risks and warnings
Market volatility
Thematic investments can be highly volatile, as they are often tied to emerging trends and sectors that may experience rapid changes. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the technology sector saw explosive growth, with companies like Zoom and Peloton surging in value. However, as the pandemic subsided and market conditions normalized, these stocks experienced significant corrections, demonstrating the volatility associated with thematic investing.
Concentration risk
Thematic ETFs and funds are typically focused on specific sectors or themes, leading to less diversification compared to broader market funds. For instance, the ARK Innovation ETF (ARKK) heavily concentrates on disruptive technology companies. When these high-growth stocks faced a downturn in 2022 due to rising interest rates and economic uncertainty, ARKK's performance was significantly impacted, highlighting the risks of concentration in a single theme.
Regulatory risks
Changes in government policies and regulations can significantly affect certain themes, especially in sectors like technology, energy, and healthcare. For example, in 2021, the Chinese government implemented strict regulations on its technology sector, impacting companies like Alibaba and Tencent. Investors in thematic funds focused on Chinese tech stocks experienced sharp declines as a result of these regulatory changes.
Look for themes with a broader impact
When choosing a theme for your investments, don’t just stick to broad ideas like technology or renewable energy because they’re trendy. Instead, look for deeper changes in how people live and work. For example, instead of just jumping on electric vehicles, think about how that trend affects other areas, like companies making batteries, building charging stations, or mining materials like lithium. You want to find themes that touch multiple areas and offer more than one way to grow your money.
Another thing to keep in mind is how global politics and laws will affect the theme you're interested in. A lot of new trends, like AI or biotech, depend heavily on what governments decide to regulate or support. If you're looking at green energy, think about how climate rules in big countries like the U.S. or China will impact the market. The smartest investments aren't just in the hottest sectors but in ones that can survive and grow under future regulations.
Conclusion
Thematic investing is all about spotting big trends that are shaping the world and putting your money where the future is headed. Instead of sticking to the usual sectors like tech or healthcare, thematic investing looks at the bigger picture, connecting different industries through common themes like renewable energy, AI, or healthcare innovation. It’s a way to align your investments with your beliefs, whether that’s supporting clean energy or backing the latest tech innovations.
FAQs
Are there any tax implications specific to thematic investing?
Yes, like all investments, thematic investing can have tax implications. Capital gains taxes may apply when you sell your investments for a profit. It’s essential to consult with a tax advisor to understand the specific tax obligations related to your thematic investments.
Can I lose money with thematic investing even if the theme is growing?
Yes, it’s possible to lose money if the specific companies or funds you’ve invested in underperform, even if the broader theme is growing. Market timing, management fees, and stock selection within the theme can all impact your returns.
Is thematic investing suitable for retirement portfolios?
Thematic investing can be suitable for retirement portfolios, especially if you have a long-term investment horizon. However, it’s important to balance thematic investments with more stable, income-generating assets to manage risk.
How do I know if a theme is just a short-term fad?
Try analyzing the underlying drivers of the theme. Look for structural trends backed by strong macroeconomic factors, technological advancements, and widespread adoption rather than hype-driven themes.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Oleg Tkachenko is an economic analyst and risk manager having more than 14 years of experience in working with systemically important banks, investment companies, and analytical platforms. He has been a Traders Union analyst since 2018. His primary specialties are analysis and prediction of price tendencies in the Forex, stock, commodity, and cryptocurrency markets, as well as the development of trading strategies and individual risk management systems. He also analyzes nonstandard investing markets and studies trading psychology.
Also, Oleg became a member of the National Union of Journalists of Ukraine (membership card No. 4575, international certificate UKR4494).
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.
Diversification is an investment strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce overall risk.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that relies on cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology.
Risk management is a risk management model that involves controlling potential losses while maximizing profits. The main risk management tools are stop loss, take profit, calculation of position volume taking into account leverage and pip value.
An investor is an individual, who invests money in an asset with the expectation that its value would appreciate in the future. The asset can be anything, including a bond, debenture, mutual fund, equity, gold, silver, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real-estate property.






























































































































