Liquid Staking | Comprehensive Guide



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
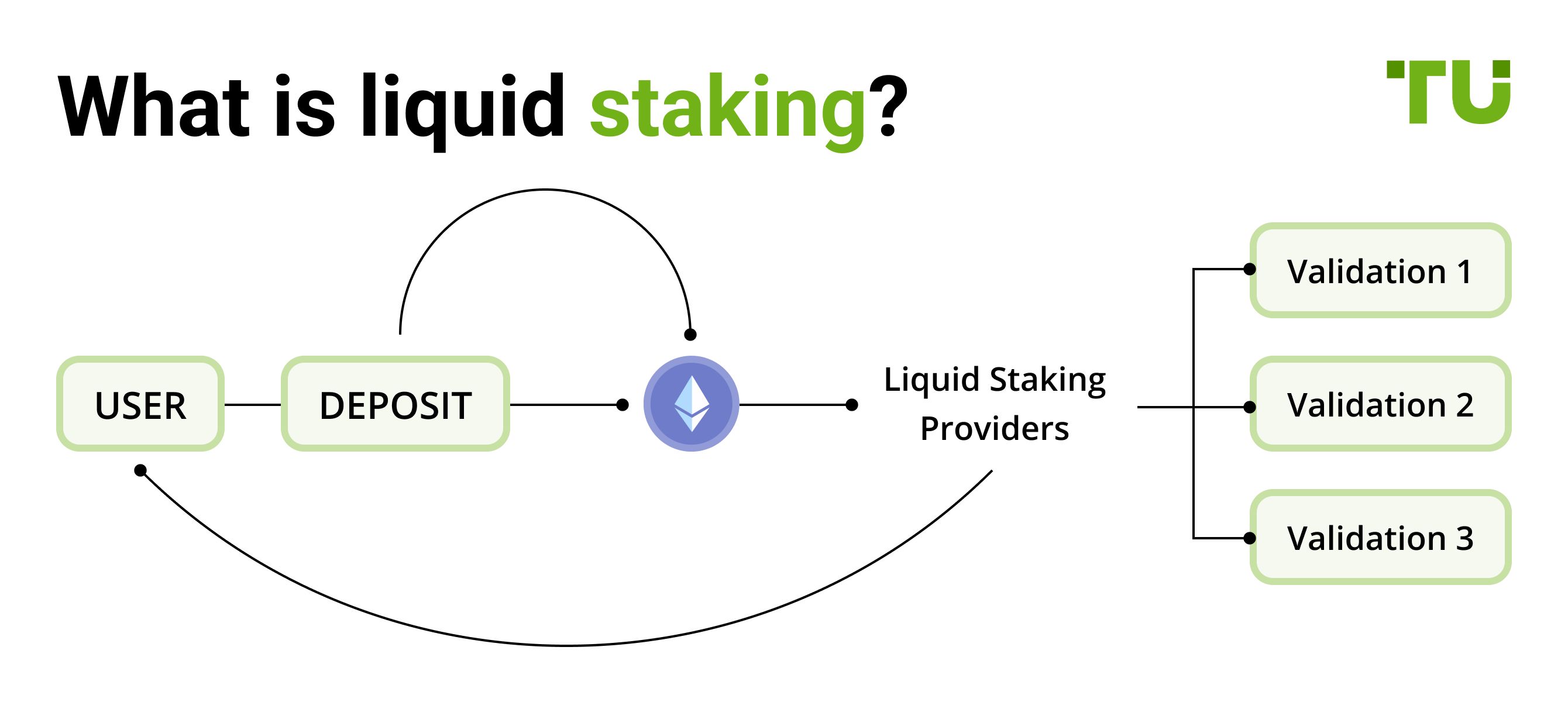
Liquid staking allows users to stake their cryptocurrency assets while still retaining liquidity, typically by receiving a token that represents the staked assets. This token can be traded, used in DeFi applications, or otherwise utilized, while the original assets continue earning staking rewards.
Staking is an essential part of many crypto networks, allowing token holders to earn rewards by contributing to network security. However, traditional staking locks up tokens, limiting their liquidity and flexibility. Enter liquid staking, a revolutionary approach that allows users to stake their assets while retaining the ability to trade or utilize them in other financial activities.
What is liquid staking?
Liquid staking transforms the way users engage with staking by providing liquidity to staked assets. Unlike traditional staking, where tokens are locked and inaccessible, liquid staking issues liquid staking tokens (LSTs) that represent the staked assets. These LSTs can be traded, lent, or used in various DeFi protocols.
Step-by-step guide to liquid staking
Choose a platform: Start by selecting a reputable liquid staking platform such as Lido, Rocket Pool, or Ankr. Research each platform's features, fees, and supported blockchains.
Connect wallet: Connect your cryptocurrency wallet to the chosen platform. This step typically involves using a browser extension or a hardware wallet.
Stake tokens: Stake your tokens on the platform. The platform will issue LSTs equivalent to your staked assets.
Utilize LSTs: Use your LSTs in various DeFi protocols to earn additional rewards, trade them, or use them as collateral.
Also we have analyzed the features of the best exchanges for staking and present a comparative table for your reference.
| Min. Deposit, $ | Coins Supported | Spot Taker fee, % | Spot Maker Fee, % | Deposit fee, % | Withdrawal fee, % | Staking | Open an account | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 329 | 0,1 | 0,08 | No | 0,0004 BTC 2,6 USDT | Yes | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 10 | 278 | 0,4 | 0,25 | No | 0,0005 BTC | Yes | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 1 | 250 | 0,5 | 0,25 | No | 0,0005 BTC | Yes | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 1 | 72 | 0,2 | 0,1 | No | 0-0,1% | Yes | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 10 | 249 | 0,5 | 0,5 | No | Fixed fee - 25 USD PayPal - 1,5% USDC - 10 USD | Yes | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Pros and cons of liquid staking
- Pros
- Cons
Accessibility: Liquid staking removes high entry barriers, making staking accessible to a broader audience. Unlike traditional staking, which might require substantial technical knowledge and a significant amount of cryptocurrency, liquid staking allows participation with smaller amounts.
Liquidity: Liquid staking provides liquidity to staked assets, allowing users to access their funds without un-staking. This means users can stake their tokens and still use them in other financial activities.
DeFi composability: LSTs can be used in DeFi applications, enhancing their utility. Users can lend, trade, or use their LSTs as collateral in various DeFi protocols.
Reduced opportunity cost: Maintaining liquidity while earning staking rewards reduces the opportunity cost. Users can still capitalize on market opportunities without waiting for the staking period to end.
Maximized utility: Liquid staking tokens (LSTs) allow users to make the most of their staked assets. These tokens can be used as collateral or in yield farming, giving users more opportunities to grow their holdings.
Slashing risk: If validators misbehave or go offline, staked tokens can be penalized. This risk is inherent to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) networks and can affect the value of your LSTs.
Centralization concerns: Large pools of staked tokens can lead to centralization, impacting network security. If a single liquid staking provider accumulates a dominant share, it may compromise the decentralization of the network.
Regulatory uncertainty: The regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies and staking is continually evolving. It's essential to stay informed about legal changes that might impact liquid staking.
Price volatility: Liquid staking tokens may not always hold a 1:1 value with the underlying staked asset, especially during periods of market volatility, leading to potential losses.
Considerations for beginners
As a beginner, one common mistake is to stake your tokens and just hold the liquid staking token (LST) without taking full advantage of its potential. Instead of letting your LST sit idle, consider putting it to work in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols like lending or liquidity pools. For example, if you stake Ethereum and receive stETH (staked Ethereum), you can use platforms like Aave or Curve to lend out stETH or provide liquidity. This way, you’re earning staking rewards and additional interest or fees from the DeFi platform, essentially allowing your assets to "double dip" for maximum returns. This dual-earning strategy offers beginners a way to increase their earnings without increasing risk too much.
Another smart move is to start with small amounts. Liquid staking can seem complex at first, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with the process in a controlled manner. Focus on understanding how the LSTs work, their use in DeFi, and how they can fluctuate in value. By starting small and diversifying where you place your staked tokens, you’ll gain confidence without risking significant losses upfront.
Considerations for advanced traders
For seasoned traders, liquid staking offers several advanced opportunities, especially around managing the peg between the liquid staking token (LST) and the underlying asset. Liquid staking tokens, such as stETH for Ethereum, are designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the original token. However, during times of market volatility or high demand for liquidity, the LST might temporarily lose this peg. By monitoring these dislocations, advanced traders can buy LSTs at a discount and sell them back or redeem them for the underlying asset once the peg returns to equilibrium. This arbitrage strategy, though risky, can lead to significant profits if timed correctly.
Another advanced tactic involves integrating liquid staking into broader trading strategies, such as using staked assets as collateral for margin trading or leveraging LSTs in derivative markets. Some liquid staking platforms even allow for staked tokens to be used in complex DeFi strategies like automated yield farming. These strategies require a strong understanding of both market trends and smart contract risks, but they offer the potential for far higher returns than simple staking or holding.
Liquid staking offers the unique advantage
For beginners getting into liquid staking, it’s smart to look for platforms that offer insurance. Some, like Lido or Ankr, have protection in place for your staked tokens if anything goes wrong with the network. This gives you peace of mind and helps you avoid the risks that come with slashing or other issues, all while still earning rewards.
Another good move is to pay attention to network upgrades or forks. When these events happen, the market can get unpredictable, and regular stakers might feel stuck because they can’t move their tokens. Liquid staking lets you stay flexible, so you can react to price changes and still earn rewards, giving you an edge over those who are locked in.
Summary
Liquid staking is a next-generation system that allows users to invest their assets and potentially see them grow. Instead of locking their funds without access, liquid staking provides users with a liquid version of their assets for use on other platforms. This feature makes staking services popular among users, as they can easily redeem their assets at any time.
While this process can be profitable, liquid staking is a complex strategy and should only be used by experienced stakers.
FAQs
What is liquid staking?
Liquid staking is a system that allows you to invest your assets in staking while providing a liquid version of those assets for use on other platforms. This means you can earn staking rewards without locking up your funds, retaining the ability to trade or utilize them elsewhere.
How does liquid staking differ from traditional staking?
Traditional staking requires locking your assets for a specified period, during which they cannot be accessed or used. Liquid staking, on the other hand, provides a liquid version of your staked assets, allowing you to maintain liquidity and use them on other platforms while still earning staking rewards.
What are the benefits of liquid staking?
The main benefits of liquid staking include the ability to earn staking rewards without locking up your assets, increased flexibility, and the opportunity to use the liquid version of your assets for other investments or transactions on different platforms.
Are there any risks associated with liquid staking?
Yes, liquid staking involves risks such as the complexity of the strategy, potential fluctuations in the value of the liquid assets, and smart contract risks. It is recommended for experienced investors who understand these risks and can manage them effectively.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Parshwa is a content expert and finance professional possessing deep knowledge of stock and options trading, technical and fundamental analysis, and equity research. As a Chartered Accountant Finalist, Parshwa also has expertise in Forex, crypto trading, and personal taxation. His experience is showcased by a prolific body of over 100 articles on Forex, crypto, equity, and personal finance, alongside personalized advisory roles in tax consultation.
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform and cryptocurrency that was proposed by Vitalik Buterin in late 2013 and development began in early 2014. It was designed as a versatile platform for creating decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts.
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.
Fundamental analysis is a method or tool that investors use that seeks to determine the intrinsic value of a security by examining economic and financial factors. It considers macroeconomic factors such as the state of the economy and industry conditions.
Options trading is a financial derivative strategy that involves the buying and selling of options contracts, which give traders the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price, known as the strike price, before or on a predetermined expiration date. There are two main types of options: call options, which allow the holder to buy the underlying asset, and put options, which allow the holder to sell the underlying asset.
Yield refers to the earnings or income derived from an investment. It mirrors the returns generated by owning assets such as stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments.