Yield Explained: Types, Calculations, And Examples



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
Yield is one of the key indicators of investment returns. In general terms, yield is a measure that expresses the income generated from an investment relative to its cost. Different types of yield include:
- Bond yield - is the interest income an investor earns on a bond investment
- Dividend yield - is a financial metric that reflects the ratio of a company's annual dividend payments to its current market price per share
- Real estate yield - is a financial metric that reflects the income generated from real estate investments
- Yield in crypto refers to the returns or earnings generated from holding, staking, lending, or participating in various blockchain-based activities
Maximizing investment returns is the key goal of every investor. To achieve this goal, it is important to understand the basic principles of asset management and apply effective strategies. A key part of your investment returns would be the yield generated by your portfolio. In this article, we discuss the different types of yield and their calculation.
Main types of yield
In general terms, yield is a measure that expresses the income generated from an investment relative to its cost . It is calculated as the percentage ratio of the profit earned from investments to their cost. Yield can be measured for various financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and other assets.
For investors, the yield of the portfolio helps evaluate the efficiency and profitability of the investments made. Key aspects of the importance of yield include:
Comparison of investment opportunities . Yield allows investors to compare different investment instruments and decide where to allocate their funds. For example, a higher yield may indicate a more attractive investment;
Risk assessment . Often, yield has an inverse relationship with risk. Instruments with high yield may carry greater risk than those offering lower yield. Investors should consider this relationship when forming their portfolios;
Income forecasting . Yield allows investors to forecast future income from their investments. This is particularly important for those relying on regular payments, such as dividends from stocks or coupons from bonds;
Financial planning . Understanding current and expected yields helps investors build long-term financial plans, including retirement savings and other long-term goals.
Bond yield
Bond yield is the interest income an investor earns on a bond investment. It reflects the return that can be expected if you hold a bond to maturity.
Types of bond yield: current yield, yield to maturity (YTM)
The current yield is the ratio of the annual coupon payments to the current market price of the bond;
Yield to Maturity (YTM) is the total yield that an investor will receive if he or she holds the bond to maturity, taking into account all coupon payments and the difference between the purchase price and par value.
How Bond Yield is Calculated
Current yield is calculated as the annual coupon income divided by the current market price of the bond:

Yield to Maturity (YTM) is more complex and requires considering all future coupon payments, the current price, and the nominal value of the bond. The formula for YTM does not have a simple analytical expression and is usually solved numerically, but the basic equation looks like this:
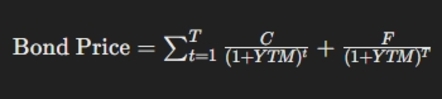
where:
C is the annual coupon payment,
F is the face value of the bond,
T is the number of years until maturity,
YTM is the yield to maturity.
Examples of bond yield calculation
If a bond with a face value of $1,000 has a coupon rate of 5% and a current market price of $950, the current yield will be 5.26% (50/950*100). To calculate the YTM, you need to use special formulas or a financial calculator that takes into account discounting all future payments.
Dividend yield
Dividend yield is a financial metric that reflects the ratio of a company's annual dividend payments to its current market price per share. This indicator helps investors assess the income they can receive from investing in stocks through dividends.
How Dividend Yield is Calculated
Dividend yield is calculated as the annual dividend paid per share divided by the current market price per share, multiplied by 100 to get a percentage:

Examples of Dividend Yield Calculation
If a company pays an annual dividend of $5 per share and the current market price of the stock is $100, the dividend yield would be 5%:

If the stock price drops to $80 while the dividend payments remain the same, the dividend yield would increase to 6.25%:

Note : High dividends are not always considered a positive indicator.It could be :
Unsustainable business: when paying high dividends, the company may face financial difficulties and may not be able to sustain stable growth .
HYIP: an attempt to attract investors to a financial pyramid scheme .
Tax manipulation: in some countries dividends are not taxed as investment income .
Optimal choice: study the dividend statistics of similar companies and choose the option with dividends at or slightly above the average.
Real estate yield
Real estate yield is a financial metric that reflects the income generated from real estate investments. This indicator helps investors assess how effectively their real estate investments generate income.
How Real Estate Yield is Calculated
Real estate yield is calculated as the ratio of annual net operating income (NOI) to the current market value of the property, expressed as a percentage:
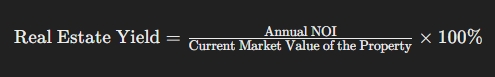
Annual NOI is calculated by subtracting all operating expenses (management, taxes, insurance, etc.) from the gross rental income.
Examples of Real Estate Yield Calculation
Suppose an investment property generates an annual rental income of $100,000, and the operating expenses are $30,000. Therefore, the annual NOI is $70,000. If the current market value of the property is $1,000,000, the real estate yield would be 7%:
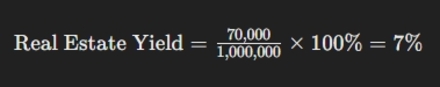
If the market value of the property increases to $1,200,000 with the same NOI, the yield would decrease to 5.83%:

Why Real Estate Yield is Important to Investors
Real estate yield is a key metric for investors because it helps evaluate the profitability of their real estate investments . A high yield can indicate more favorable investment opportunities, while a low yield may signal the need to review the investment strategy or look for more profitable properties. Additionally, real estate yield helps investors compare different properties and choose those that offer the highest returns with minimal risks.
To help you test your strategies and choose the most effective ones in terms of profitability, we have compared a number of brokers who offer a wide range of assets that will satisfy the most trading strategies, including those requiring stocks, bonds and currency pairs.
| Plus500 | Pepperstone | OANDA | FOREX.com | Interactive Brokers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Min. deposit, $ |
100 | No | No | 100 | No |
|
Spread |
From 0.8 pips | from 0.0 pips | From 0 p for currency pairs | From 0.2 pips | From 0 pips |
|
Max. leverage |
1:300 | 1:500 | 1:200 | 1:50 | 1:30 |
|
Stocks |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Bonds |
No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
ETFs |
Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
|
Crypto |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Options |
Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes |
|
Regulation |
FCA, CySEC, MAS, ASIC, FMA, FSA (Seychelles) | ASIC, FCA, DFSA, BaFin, CMA, SCB, CySec | FSC (BVI), ASIC, IIROC, FCA, CFTC, NFA | CIMA, FCA, FSA (Japan), NFA, IIROC, ASIC, CFTC | SEC, FINRA, SIPC, FCA, NSE, BSE, SEBI, SEHK, HKFE, IIROC, ASIC, CFTC, NFA |
|
Open account |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Study review | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Yield in crypto
Yield in crypto refers to the returns or earnings generated from holding, staking, lending, or participating in various blockchain-based activities. This concept is similar to earning interest or dividends in traditional finance but is typically realized through decentralized financial (DeFi) protocols and crypto-specific mechanisms. Here are the main ways to earn yield in crypto:
Staking yield - earned by participating in a proof-of-stake (PoS) or delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) blockchain network. Users lock up their cryptocurrencies to help validate transactions and secure the network, receiving rewards in return.
Yield farming - a DeFi strategy where users provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges or lending platforms and earn rewards, often in the form of additional tokens.
Mining yield - rewards earned from mining cryptocurrencies, involving the use of computational power to solve complex mathematical problems and validate transactions on a proof-of-work (PoW) network.
Airdrop yield - free distribution of new tokens to holders of an existing cryptocurrency, often as part of a promotional strategy or community-building effort.
Dividend yield - some blockchain projects distribute a portion of their profits to token holders in the form of dividends, akin to traditional stock dividends.
Here's a comparison table of some of the cryptocurrency exchanges based on various factors such as fees, supported currencies, security and user experience:
| Exchange | Trading fees | Supported currencies | Security features | User experience | Open an account |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | 0.10% per trade | 500+ | Two-factor authentication, cold storage | Advanced, feature-rich | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
| Coinbase | 0.50% per trade | 100+ | Two-factor authentication, insurance | User-friendly, intuitive | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
| Kraken | 0.16% maker, 0.26% taker | 50+ | Two-factor authentication, cold storage | Reliable, advanced tools | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
| Bitfinex | 0.10% maker, 0.20% taker | 100+ | Two-factor authentication, cold storage | Advanced features | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
To increase profitability, distribute capital between different assets and follow market trends
Based on my experience, maximizing investment returns requires understanding of key principles and strategies such as diversification and regular portfolio review.
Thus, the distribution of capital between stocks, bonds and real estate reduces risks and increases profitability. All these investments carry different types of yields.
Market conditions are constantly changing, so assets that have been profitable in the past may lose their attractiveness. In such cases, portfolio analysis and adjustments help maintain high returns.
To further increase your returns, use profits to purchase additional assets, which contributes to capital growth and long-term returns. Finally, invest in assets with high growth potential and stable returns by analyzing financial performance and market trends.
Conclusion
Yield is a key indicator of investment returns , showing the income generated from an investment relative to its cost. There are different types of yield, including bond yield, dividend yield, and real estate yield. Bond yield includes current yield and yield to maturity (YTM), dividend yield is the annual dividend payments relative to the stock price, and real estate yield is the net income relative to the property value. Yield helps investors compare opportunities, assess risks, forecast income, and plan financially. Higher yields may come with higher risks , so investors use yield to compare different investment options and build balanced portfolios.
Maximizing investment returns is based on competent asset management and understanding key strategies. Portfolio diversification, distributing capital among various asset classes, and regularly reviewing the investment portfolio help reduce risks and adapt to market changes. For long-term yield enhancement, it is crucial not only to retain profits but also to reinvest them in purchasing additional assets. This fosters capital growth and increases overall returns.
FAQs
Why is diversification important for maximizing investment returns?
Diversification helps reduce risks by spreading investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. This minimizes the impact of losses from one asset on the overall portfolio, leading to more stable income and long-term growth.
How often should the investment portfolio be reviewed?
It is recommended to review the investment portfolio at least once a year. However, significant changes in market conditions or an investor's personal circumstances may require more frequent analysis and adjustments.
What key principles help increase investment yield?
To increase investment yield, it is important to follow principles of diversification, regular portfolio review, and reinvesting income. Selecting quality assets with high growth potential and stable returns also plays a crucial role in achieving maximum profitability.
What role does reinvesting income play in maximizing returns?
Reinvesting income allows using the earned profits to purchase additional assets, contributing to the growth of overall capital and long-term yield. This creates a compounding effect, where returns accumulate and multiply over time.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.

Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Diversification is an investment strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce overall risk.
Forex leverage is a tool enabling traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital, amplifying potential profits and losses based on the chosen leverage ratio.
Yield refers to the earnings or income derived from an investment. It mirrors the returns generated by owning assets such as stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments.
An investor is an individual, who invests money in an asset with the expectation that its value would appreciate in the future. The asset can be anything, including a bond, debenture, mutual fund, equity, gold, silver, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real-estate property.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that relies on cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology.






























































































































