SCB | Financial Regulator of Bahamas
SCB (Securities Commission of the Bahamas) - independent regulator of the Bahamas responsible for supervising securities, investments, as well as regulating both exchange and over-the-counter (OTC) markets, which encompass Forex.. Obtaining an SCB license is mandatory to operate in the Bahamas.
A financial regulator is a government or non-government agency that supervises financial organizations for compliance with specific requirements, rules, and limits to maintain the integrity of the financial system. A regulator’s main tasks are to issue licenses that authorize entities to perform certain types of activity; ensure that licensees observe the law, standards, and norms; develop technologies that simplify communication between all market participants; consider disputes, and protect investor rights.
For a broker, holding a license means:
-
Necessity to meet the regulator’s requirements, such as maintaining capital at a specific level, segregating client accounts, disclosing financial information and billing, developing a risk management system, transparently informing traders about types of services, etc;
-
Possibility to operate in the international legal framework. Some licenses provide access to exchange markets.
On a regulator’s website, you can find its requirements for financial institutions. A license means that a broker has been checked and meets those requirements. In some cases, a license means that a trader can approach the regulator, ombudsman, and auditors to resolve disputes with the broker. Some regulators have a compensation fund in case a broker goes bankrupt.
Description and functions of the SCB
The SCB, an independent regulator of the Bahamas, is subordinate to the country’s Ministry of Finance and responsible for overseeing securities, investing, and all exchange and over-the-counter (OTC) markets, including Forex. Obtaining an SCB license is mandatory to operate in the Bahamas.
SCB’s mission and objectives in the Forex market:
-
Develop rules for the interaction between all market participants and approve standards for brokers and investment funds;
-
Promote the growth of the exchange and OTC markets. Improve the jurisdiction’s attractiveness in the international financial community;
-
Advise private investors on their rights, resources, and risks in the exchange and OTC markets;
-
Investigate breaches.
The SCB’s leverage over offenders lies in fines and the revocation of licenses.
SCB’s mission and objectives in the Forex market:
-
Possess the minimum capital of 300,000 USD and keep it at least at that level after obtaining a license;
-
Have a physical office in the Bahamas;
-
Provide a business plan and disclose the risk minimization system.
The Bahamas is an attractive jurisdiction offering optimized taxation and money flows. That is why the SCB is called an offshore regulator that makes concessions to its licensees. Entities are not required to fully disclose information, interact with self-regulatory organizations, or go through independent audits. However, the SCB aims to operate in the international financial market and therefore part of the requirements was recently toughened and brought in line with European norms. Despite its status as an offshore regulator, the Commission can be called international.
Official website and available information
The SCB website is well-structured. The section with a list of licensees and the complaint filing section are available right on the homepage. The website also features documents, laws, and norms that regulate the interaction of legal entities and private individuals. Much of the content is in pdf format.
Overview of the website:
-
Main and auxiliary menus at the top. The auxiliary menu offers links to the complaint filing section, contact details, “About Us”, and the Commission’s social media profiles.
-
Information part with the latest news and investor alerts and notices.
-
Footer with useful links to other Bahamas authorities that can help resolve disputes.



Main menu structure:
-
Home. Return to the homepage from any other page of the website.
-
The Commission. Structure, functions, and annual reports.
-
Legislative Framework. One of the subsections, “Disciplinary Decisions”, provides information about the already considered claims and decisions made.
-
Investor Centre. Here, investors can learn everything about their rights, opportunities, etc. This section partially repeats information from other sections.
-
Supervision. Securities Industry Act, Investment Funds Act, and information about financial service providers.
-
Media. News, publications, and educational content.
-
Contact Us. Address of the Commission’s head office, phone numbers, and email.
Traders are primarily interested in the section with licensees’ details and the complaint submission section. It is also worth looking through the information section sometimes, as the Commission can inform investors about possible violations by brokers or potential risks.
SCB’s mission and objectives in the Forex market:
Lists of licensees on the Commission’s website are provided in pdf format and therefore you cannot find brokers by using the search box on the homepage. General information about companies (mentions in the news or releases) cannot be accessed that way either.
The lists of licensees are divided into 4 groups:
-
Securities Industry Act, 2011;
-
Investment Funds Act, 2019;
-
Financial and Corporate Service Providers Act, 2020;
-
Digital Assets and Registered Exchanges Act, 2020.
The three letters in a broker’s license number designate the group in which the company should be searched.
To confirm a broker’s license on the SCB website, do the following:
-
1
Open the broker’s website and make sure the company has an SCB license. In most cases, such information is in the footer along with the company’s legal name. The license number can also be in “About Us”.
-
2
In the footer of the Commission’s website, select “Registrant Licensee Status Search”.
-
3
Select the group of registrants according to the license number. In this case, it is the SIA group.
-
4
On the pdf list, look for the broker by its legal name.



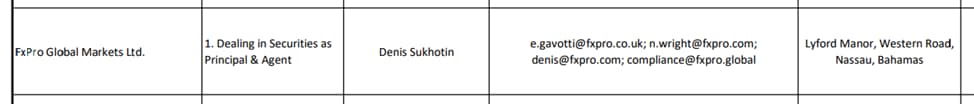
The license number is not included, but the broker’s presence on the Commission’s list confirms that the license is active. Here you can also find the company’s address, category, P.O. box, and other details.
SCB’s basic requirements for brokers
Basic requirements to obtain a license:
-
Ensure that the capital is not lower than the set level;
-
Disclose information about the strategic development plans and the risk management system.
On average, it takes the Commission 4-6 weeks to make a decision about granting a license.
Compared to European regulators, the SCB has mild requirements for license acquisition. But operation conditions have become harder. As a member of several international regulatory communities, the Commission imposes restrictions on brokers in order to fully inform investors about their rights and limit potential investor risks.
SCB license | Pros and cons
The Bahamas is interesting for brokers primarily due to the possibility of minimizing tax expenses and avoiding the disclosure of money turnover. The SCB has relatively lenient requirements for license acquisition, but at the same time, it adjusts brokers’ operations to European business standards and strictly enforces them. That is why an SCB license is trusted more than licenses from classic offshore regulators, but there is still some risk of brokers’ insecurity.
👍 Advantages of trading with an SCB-licensed broker:
• You can approach the Commission if you believe the broker has violated your rights. The SCB considers all complaints without exception;
• If the broker has problems, you will be warned about them. Based on the results of audits, the Commission’s website publishes information about breaches and possible consequences.
In the past few years, the SCB has been integrating into the global economy and going away from its offshore status. The Commission is a member of several regulatory organizations, and a trader can refer to them if it seems to him that the SCB is protracting the consideration of his complaint against a broker or defending the broker’s interests.
👎 Advantages of trading with an SCB-licensed broker:
• There is no compensation fund.
European traders should cooperate with brokers that, besides an SCB license, also have a license from an authority that covers the whole eurozone. For example, the German BaFin or the British FCA (Financial Conduct Authority).
SCB’s jurisdiction
An SCB license is only valid in the Bahamas. SCB-licensed brokers can render services to non-residents if the laws of their countries are not violated. In other countries, an SCB license is not accepted. For example, to access the U.S. exchange market, a broker has to open its representative office in this country and obtain a license from a U.S. regulator. In Forex, an SCB license is usually sufficient to conclude agreements with liquidity providers.
Submission and consideration of complaints
The SCB accepts all types of complaints. Those that are out of the Commission’s responsibility are forwarded to competent agencies. The SCB asks complainants to provide as concrete and reasoned information as possible and leave all contact details.
Basic requirements to obtain a license:
-
Possibly are committing fraud;
-
Impose services that are not authorized by their licenses;
-
Indicate license numbers that are not on the Commission’s lists of licensees;
-
Refuse to provide client account statements;
-
Disclose clients’ personal information to third parties;
-
Provide misleading information during an investingation;
-
Ignore traders’ requests to provide full information about the services and risks;
-
Groundlessly debit funds from trader accounts.
Complaint submission procedure:
-
1
You can approach the Commission if you believe the broker has violated your rights. The SCB considers all complaints without exception;
-
2
If the broker has problems, you will be warned about them. Based on the results of audits, the Commission’s website publishes information about breaches and possible consequences.

SCB-licensed brokers | How to check on a broker
Every month, TU analysts look through regulators’ websites and update information on the TU website. In this section, you can find:
-
All valid licenses held by brokers and their branch offices in different countries;
-
Types of services permitted by licenses;
-
Information about administrative penalties and warnings to brokers.
With TU, you always have the necessary information at hand!
Reviews of the SCB by complaining investors and traders
Roman, head of analytics department | St. Petersburg
I’d like to add something to the analyst’s conclusion. The SCB was and still is an offshore regulator. But unlike the agencies in Vanuatu and other offshore zones, the SCB chose to slightly adapt to some Europe standards so that both brokers and traders would trust it more.
First, ESMA (European Securities and Markets Authority) implemented new standards that significantly restricted the supply of some products in Europe. The new standards had an even bigger impact on risk reduction mechanisms, such as limits on leverage and bonuses. Before that, beginners used bonuses thoughtlessly without understanding how to repay them and increased the sizes of trades through leverage without understanding what pip value is.
ESMA reduced the risks, thereby taking away part of brokers’ competitive advantages. Most of the brokers immediately moved to the Bahamas and for good reason:
-
Offshore regulators are not trusted much. They simply don’t investigate complaints and don’t have leverage over offenders. You can’t find examples of their help;
-
The Bahamas has an effective legal system. Low taxes and strict oversight are balanced.
Tourism is the country’s primary income source. That is why both sides benefited from that situation. The Bahamas profited from the growth of online trading volume. Brokers have a regulator that is less meticulous than European agencies, but more reputable than offshore ones.
The SCB’s strength is the balance between opportunities and risks. The Commission controls brokers strictly and considers complaints. The regulatory system works leniently, but effectively. It has its pros and cons. In any case, the SCB is a good alternative to CySEC (Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission). The Bahamian regulator actually protects traders’ interests.
Igor, cryptocurrency trader | Chelyabinsk, Russia
Regulators’ websites interest me because they publish information about investigations and warn you about possible fraud. It doesn’t matter which broker it is. The very facts of violations are interesting. You can find out how brokers go around the law, what methods they use to deceive investors, how these breaches are revealed, and what fines are imposed.
Vadin, trader | Kaluga, Russia
People mistakenly think of the SCB as an offshore regulator like those in Seychelles, New Zealand, or Vanuatu. By the quality of operation and real help, I would compare it to Cyprus, Australia, and Malta.
Ruslan, trader, Ukraine
I know several types of effective regulatory systems:
-
A system of private regulators and auditors. For example, the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) and FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority) in the USA. There are several regulators and private auditors in the country, so brokers are under constant cross-control;
-
A system of the regulator’s local representatives. For example, the Investment Industry Regulatory Organization of Canada (IIROC). This regulator has agents in every province, where they supervise each company individually. Corruption there is out of the question;
-
Strict centralization. For example, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). The regulator monitors a broker’s account activity and can suspend its operation or conduct unscheduled inspections.
These options are inconvenient for brokers, as many companies won’t disclose information about themselves.
The SCB doesn’t have centralization, audits, or account segregation requirements. Unlike Seychelles or Belize, the Bahamas accept and considers your complaints. But the chances of getting real help are low.
Andrey, trader | Izhevsk, Russia
I agree with the previous comment and think that a regulatory system cannot be full-fledged without self-regulatory organizations (SROs). Regulators cannot oversee all aspects of each entity’s operation. Also, they don’t have full access to brokers’ bank accounts or internal clearing systems.
I imagine a solution like this:
-
Best brokers unite into an SRO, which obtains the right to function as a regulator;
-
If a trader has a complaint, he approaches the SRO. The brokers investigate the complaint together. The guilty broker may be expelled from the SRO;
-
If the SRO cannot resolve the issue or the trader isn’t satisfied, the complaint is filed with the jurisdiction’s regulator.
As a result, the regulator is not overloaded with traders’ problems, as the SRO deals with them. The brokers won’t violate investor rights because traders trust the SRO and will not trust the broker that got expelled. The regulator supervises the SRO.
Expert’s assessment
The SCB is a regulator that does its best to get rid of the “offshore” tag and succeeds. Initially, the Commission aimed to attract large capital to the jurisdiction and work with institutional investors. The country wanted to increase the volume of money flows. The next goal was to improve the jurisdiction’s authority in the international arena, and the Commission became stricter.
By 2021, the SCB made the following changes:
-
Imposed limits on margin trading. Brokers had to set the minimum margin at 0.5% and limit leverage to 1:200. These conditions are milder than European agencies’ requirements but harder compared to offshore regulators;
-
Banned binary options for retail traders;
-
Obliged brokers to guarantee negative balance protection – the mechanism that automatically closes trades;
-
Banned bonuses and incentives for retail clients;
-
Obliged every CFD broker to have a staff member who is responsible for the fulfillment of the Commission’s requirements.
Conclusion
The SCB can be deemed a reputable regulator that aims to meet the global standards for doing business and the protection of investor rights. But at the same time, the Bahamas remains an attractive jurisdiction in terms of taxation and lenience towards licensees. The SCB is more lenient than the SEC or MAS, but SCB-licensed brokers can be trusted.
About the author of this review
Oleg Tkachenko, author and analyst at TU
Oleg Tkachenko has been TU’s financial analyst and economic observer since 2016. During this time, he has prepared more than 100 reviews of financial companies and analytic articles on technical and fundamental analysis, as well as developed over 10 proprietary trading strategies. Oleg’s motto is to help everyone come all the way from a novice trader to a professional.
FAQs
What is the SCB?
The Securities Commission of the Bahamas (SCB) is an independent regulator of the Bahamas accountable to the country’s Ministry of Finance. The SCB fulfills the classic regulatory functions. It checks founding and financial documents of brokers before issuing licenses, oversees license holders superficially, warns investors of potential risks, and resolves disputes between market participants.
What do I get from trading with SCB-licensed Forex brokers?
-
Help in resolving disputes with brokers.
-
The SCB provides information about its licensees.
A license from the SCB means that the broker has passed initial inspection and observes Bahamian financial laws.
How to check if a broker holds an SCB license?
There are two options:
-
1
In the footer of the Commission’s website, go to “Registrant Licensee Status Search” and select one of the four groups according to the letters in the broker’s license number. Find the broker by name in the pdf file.
-
2
View the current information about the broker’s licenses in its profile on the Traders Union website.
Information about all valid licenses held by brokers is updated on TU’s website every month.
How to submit a complaint against a broker to the SCB?
-
1
In the top right corner of the SCB website, click “Complaints”. Download and complete the Complaint Submission Form and send it along with attachments to the indicated email address. The types of complaints considered by the SCB are listed in the same section (“Complaints”).
-
2
Register on the Traders Union website – it takes only 10 minutes. Verify your account within two days and become a rightful TU member. TU’s legal service is ready to help every member.
Note that registration with TU is completely free of charge.
Team that worked on the article
Oleg Tkachenko is an economic analyst and risk manager having more than 14 years of experience in working with systemically important banks, investment companies, and analytical platforms. He has been a Traders Union analyst since 2018. His primary specialties are analysis and prediction of price tendencies in the Forex, stock, commodity, and cryptocurrency markets, as well as the development of trading strategies and individual risk management systems. He also analyzes nonstandard investing markets and studies trading psychology.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).









