VFSC | Financial Regulator of Vanuatu
The VFSC is a government regulator that was created in 1993 and controlled by a separate department of the Vanuatu Ministry of Finance and Economic Management. The Commission primarily carries out executive functions and improves the population’s financial literacy.
A regulatory system is a group of government and non-government agencies that are responsible for the stability of the country’s financial system and the attractiveness of the investment climate. A regulatory system can include government regulators supervised by the Ministry of Finance or the National Bank; private regulators and auditors; self-regulatory agencies; and ombudsmen. A license from a regulator is a mandatory condition for every broker that renders services in the exchange, over-the-counter, and Forex markets.
For a broker, holding a license means:
-
Permission to render certain types of services to specific categories of clients, depending on their knowledge level, citizenship, etc.
-
Necessity to meet the regulator’s requirements and observe local and regional laws.
-
Authority in the eyes of clients.
For a trader, a license means that the broker legally exists and is supervised by third parties. The broker is not interested in deceiving traders because violations can result in fines and a bad reputation. Another benefit is that disputes with the broker can be settled through the regulator. Some regulators have compensation funds.
In this post, TU explores the VFSC’s functions, mandate, procedure for confirming licenses on the website, and the procedures for filing complaints, as well as reviews and an expert’s opinion of this regulator.
Description and functions of the VFSC
The VFSC is a government regulator that was created in 1993 and controlled by a separate department of the Vanuatu Ministry of Finance and Economic Management. The Commission primarily carries out executive functions and improves the population’s financial literacy. The monitoring of licensees is a secondary task.
The VFSC’s mission and objectives in the Forex market:
-
Grant licenses and collect charges for keeping licenses active.
-
Control licensees superficially.
-
Give advice to investors and traders.
Any license gives brokers access to international stock markets . Licensed brokers have competitive advantages because they can legally advertise their services, conclude agreements with other market participants, and render services in many countries. A license from the VFSC allows brokers to operate in most European and some Asian countries.
To obtain a VFSC license, a broker has to:
-
Register in Vanuatu, Oceania. Registration can be performed remotely from any other county.
-
Confirm that it has registered capital of about $50,000. There is no information as to whether any funds must be reserved in Vanuatu banks.
-
Provide information about the CEO. Having Vanuatu citizens on the management team is not required. The requirement for the CEO to stay in Vanuatu for at least 6 months per year is not actually overseen or fulfilled.
-
Prepare a business plan.
-
Establish Know Your Client (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) protocols, and engage with compliance officers.
-
Pay charges and fees. There is a detailed price list on the regulator’s website.
The VFSC is known for its leniency toward licensees. The Commission doesn’t have hard requirements for brokers. Yearly audits are not mandatory, there is no need to disclose the organizational structure of financial statements, and the registered capital requirements are nominal. Before issuing a license, the VFSC checks the broker’s foundation documents. The regulator’s further tasks are to inform investors about high risks.
Official website and available information
Information on the VFSC website is mostly theoretical: legislation, bylaws, and provisions for licensees.
Overview of the website:
-
The upper auxiliary menu consists of two sections. The first section features general information on what the regulator does and how to register with it, as well as contains links to the law of Vanuatu. The second section is for those who are planning to obtain a license.

VFSC Review — Section of the website
-
Main menu.
VFSC Review — Section of the website
-
Financial offers and the footer. There is not much information in the footer: only links to contacts and the site map.
VFSC Review — Section of the website
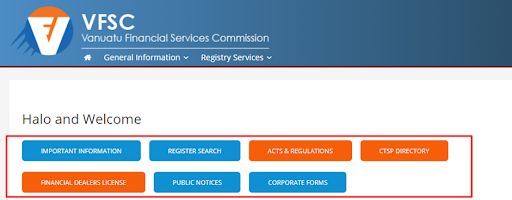
Main menu structure:
-
Important Information. The website guide.
-
Register Search. In this section, you can find any broker registered in Vanuatu or a private individual connected with it, as well as confirm the validity of a license.
-
Acts & Regulations that govern the operation and interaction in various markets.
-
CTSP Directory is a section about the licensing of companies that provide trust services.
-
Financial Dealers License is a section for companies that provide dealer services.
-
Public Notices. News and information about changes.
-
Corporate Forms. This section is interesting for those who want to obtain a license and are going to submit paper documents.
The main section for traders is “Register Search”.
How to confirm a broker’s license on the VFSC website
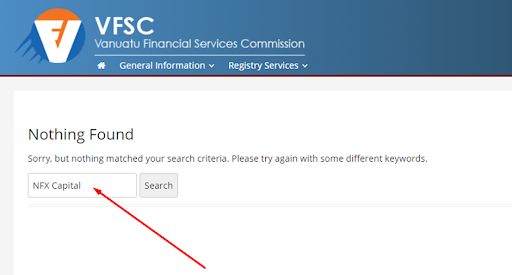
The search system on the Commission’s website is not very convenient. On the websites of most other regulators, searching on the homepage by the broker’s legal name gives you at least mentions of the company in the news and releases. On the VFSC website’s homepage, you get “Nothing Found”.
VFSC Review — Section of the website
For this reason, you shouldn’t expect the regulator to fully disclose information about brokers.
To confirm a broker’s license on the VFSC website, do the following:
-
1
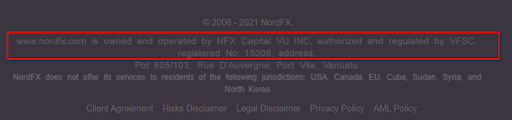
On the broker’s website, find information that the company has a VFSC license. In most cases, such information is in the footer of the broker’s website. There you can also find the broker’s legal name, which can differ from its brand name.
VFSC Review — Section of the website
-
2
On the VFSC website, open the “Register Search” section.
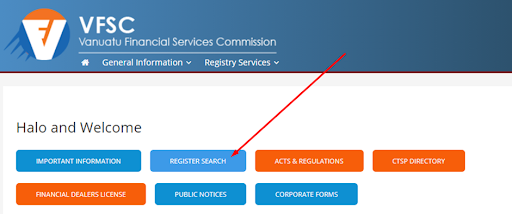
VFSC Review — Section of the website
-
3
Next, enter the broker’s name or license number. Before clicking “Search”, select “All Registers” as shown below.
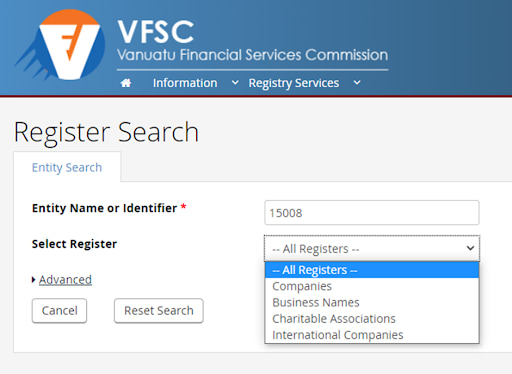
VFSC Review — Section of the website
-
4
View the results.
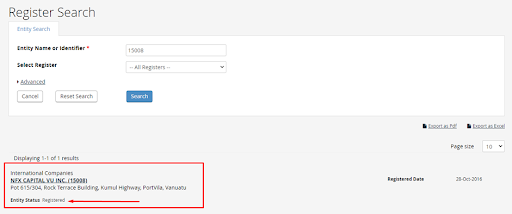
VFSC Review — Section of the website
They include general information about the license and a PDF file with a license agreement between the broker and the Commission.
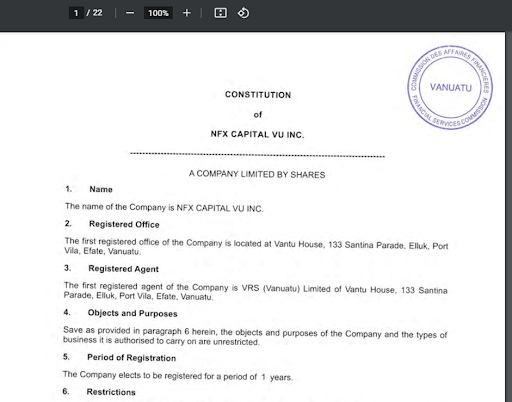
VFSC Review — Section of the website
VFSC’s basic requirements for brokers
The basic requirement to obtain a license is to provide a standard set of documents.
The VFSC is an offshore regulator that is primarily interested in the timely payment of annual contributions for license renewal. Filing a standard set of documents is more of a formality. The regulator confirms that the broker is registered, superficially checks its financial state, and then only cares about money receipts. The VFSC website even has a separate section with fees.
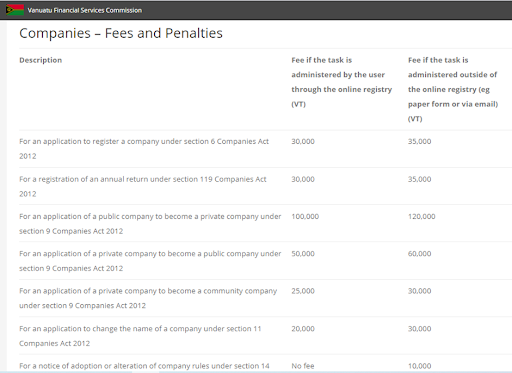
VFSC Review — Section of the website
Failure to submit a document in due time results in a fine, which adds more funds to the Commission’s budget. The prices are indicated in the local currency, which is vatu. 10,000 vatu equals approximately 90 USD. The total cost of a VFSC license is just over 10,000 USD.
VFSC license | Pros and cons
For brokers, the VFSC is one of the most favorable regulators. The jurisdiction is attractive primarily due to its concessional taxation and simple license acquisition procedure. A company meets lenient requirements for registered capital, provides a minimum set of documents, pays a relatively low contribution, and, within a month, obtains a license that permits operating in most European and Asian countries.
Advantages of trading with a VFSC-licensed broker:
-
dvantages of trading with a VFSC-licensed broker: You can be sure that the broker exists. The Commission checks if the company has a physical address and reviews its organizational structure. This reduces the chances that the company is a potential fraud.
-
The regulator’s help in disputes.
The only drawback is that a VFSC license can be ignored. It isn’t very expensive and the broker can get it again under a new legal name. In most cases, the regulator responds to violations after the fact when traders have already lost money and the revocation of a license cannot bring investments back.
Disadvantages of trading with a VFSC-licensed broker:
Additional fees are the only disadvantage. CFTC-licensed brokers incur additional expenses, such as exchange and clearing fees, that are partially passed on to traders. To recoup their time and expenses, traders have to manage capital of at least a few thousand USD.
CFTC’s jurisdiction
The VFSC is a government regulator subordinate to the Vanuatu Ministry of Finance and Economic Management. VFSC-licensed brokers can render CFD trading ervices to residents and non-residents of Vanuatu on the condition that laws of non-residents’ countries are not violated. In particular, there may be restrictions on cooperation with citizens of the USA, North Korea, and some other countries.
Submission and consideration of complaints
The VFSC website does not have a complaint submission section or a special section for investors. The “Contact Us” section includes an email address to which you can send letters or complaints, hoping that they will be considered.
What an investor should do in case of a problem with a broker such as a blocked account, denied or delayed profit payout, or other issues:
-
1
Prepare a letter of complaint that includes:
-
The broker’s accurate legal name and a link to its website.
-
Dates on which you opened an account and made the first deposit.
-
A contract, offer, or another form of agreement under which the broker renders services. You can use screenshots of documents from the broker’s website.
-
The essence of your complaint with links to the violated clauses of the agreement and the chronology of events.
-
Screenshots of your conversations with the broker’s support service.
-
-
2
Send the letter to the VFSC and other Vanuatu government authorities related to the economic sector.
-
3
Share this experience on websites of trader communities, describing your actions and the obtained result, if any. One such community is Traders Union.
VFSC-licensed brokers | How to check on a broker
This section features Forex brokers that hold, in particular, a VFSC license. Every month, TU analysts view each regulator’s website and update information about brokers on their TU pages. There, you can find the following data:
-
All valid licenses and certificates held by brokers.
-
Brokers’ membership in self-regulatory organizations, such as the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC) and the Financial Commission.
-
Types of services brokers can render in accordance with their licenses.Types of services brokers can render in accordance with their licenses.
-
Violations, comments, and guidelines. If a broker’s license is active, the regulator will publish this data on its website.
Save time by using Traders Union’s help!
Reviews of the VFSC by complaining investors and traders
Dmitry, investor | Arkhangelsk, Russia
On the internet, I couldn’t find a single clear example of how the regulator was able to prevent fraud. Or an example of the consideration of collective complaints filed by traders. If somebody finds one, please, share a link. Maybe my searches were not sufficiently thorough.
Oleg, trader, St. Petersburg
Vanuatu is a small island in the Pacific Ocean. Do you really need a license from it? Believe me, you do! I’ll explain.
Payment for a domain and the creation of a website are a matter of a few thousand bucks. If you are interested, google “HYIP”. After the website is launched, they advertise it, collect deposits, and disappear. This is a classic scheme for companies that don’t even have a registration address.
Now, about the license. Many sources say that a license from Vanuatu means nothing. Registration is cheap and the regulator doesn’t consider complaints and checks almost nothing. Maybe it’s true. But! No matter how cheap a license is, a broker still has to file entitling documents for registration. And although an office in Vanuatu is not needed, the company does have an office somewhere and it must be mentioned. If someone really needs to inspect a broker, it will be inspected. It means that even this kind of license won’t let the broker risk too much. Stealing some money from a few simpletons without making noise is not a problem. Simpletons are not likely to complain even if they know English well enough.
My point is that an offshore license is better than no license at all. If a broker is licensed, it means that it at least exists. It’s not some faceless site in the ocean of electronic data. Of course, BaFin is far more serious, but trading conditions for its brokers are less favorable. The choice is yours!
Vladimir, trader | Tomsk, Russia
I hypothetically imagined how I would file a complaint with the VFSC. No matter where you look on the regulator’s website, you see information about charges, fees, and payment for legal entity registration or license renewal – everything is about money collected from licensees. And there is nothing for traders! No black lists of brokers or information about warnings issued to somebody. One section has a few documents about canceled licenses, but they all are from 2018-2020. It seems the regulator didn’t record anything in 2021.
It gets more interesting. The website doesn’t have any sections like “For traders” or “File a complaint”. I mean you can’t find either a complaint filing form that explains how to properly prepare and file a complaint; or a section for traders at all. There are two email addresses in “Contact Us”: for registration and for “other issues”. I imagine what a mess they must have in their mail if they get spam and a lot of other letters, besides complaints, at the same address.
The cherry on top and just for the fun of it, I tried sending an email with a question about a VFSC-licensed broker because I had a problem getting verified and wanted to get more information. I sent the letter with a read notification. Alas, that was it – the letter simply wasn’t read, let alone registered, or given a number, etc. Can this license be of any use to a trader? I don’t know.
Sergey, analyst, Yalta
IA license is the last thing you should consider when choosing a broker. To hope that the regulator really checks something is to deceive yourself. Here is why:
-
If brokers submitted their annual financial statements, the regulator would publish them. It’s not a commercial secret. All stock companies at least disclose their balances to calculate multipliers. And brokers’ financial statements are only published by U.S. regulators.
-
Few people are willing to go through the ordeal of filing a complaint in accordance with all the rules and then corresponding with the regulator for a long time. However, there may be no correspondence at all because most offshore regulators only consider collective complaints by self-regulatory organizations or trader communities.
-
A license is not a panacea. First, few people pay attention to who holds the license and with whom they conclude an agreement. Sometimes, these are different legal entities. Second, even regulators don’t always give you information about the services they permit. They just indicate that a license is active, and you may not know if a broker provides access to cryptocurrency trading, for example.
Pay attention to trading conditions and remember that you can lose money anytime. Trading is always risky.
Ivan, trader | Bryansk, Russia
I personally haven’t dealt with this regulator or written complaints to it. But brokers with its license seem suspicious to me. The VFSC has an active marketing campaign, bonuses, affiliate programs, etc. But it’s just my subjective opinion.
Expert’s assessment
The VFSC is a government regulator whose essence is best described by the following facts:
-
To register, the broker only needs to provide information about its CEO, who is not required to be personally present when submitting documents. On the internet, they offer registration through intermediaries, i.e., shell companies registered in Vanuatu.
-
The company must register in Vanuatu, but it can be done remotely for an additional payment. Opening a physical office in the country is not required.
-
There are no strict requirements for registered capital. The broker has to confirm the availability of about $50,000. As a comparison, European regulators require registered capital of $0.5-1 million. The cost of obtaining a VFSC license is a little over $10,000.
-
The regulator’s basic requirement is to pay money for keeping licenses active. The website has a page with fees, but doesn’t have a complaint filing form.
There is no information about segregated accounts or an ombudsman either. A compensation fund is not provided. Which authority traders should additionally contact if they have questions is also unknown.
Conclusion
The VFSC may be the least favorable of all offshore regulators. Brokers like this jurisdiction for its lenient taxation and low cost of license renewal and because the Commission doesn’t ask too many questions. Brokers need a nominal license. It makes them look reputable in the eyes of those who are not versed in these issues and allows them to legally conclude agreements with providers of liquidity, quotations, etc. In terms of risks, a VFSC license is definitely less favorable than, for example, licenses from the half-offshore CySEC or ASIC. But even this license at least confirms that a broker exists.
About the author of this review
Oleg Tkachenko, author and analyst at TU
Oleg Tkachenko has been TU’s financial analyst and economic observer since 2016. During this time, he has prepared more than 100 reviews of financial companies and analytic articles on technical and fundamental analysis, as well as developed over 10 trading systems. Oleg’s motto is to help everyone come all the way from a novice trader to a professional.
FAQs
What is the VFSC?
The VFSC is the financial regulator of the Vanuatu government. Its tasks include enforcement of local financial laws and informing investors about their rights, resources, and risks.
What do I get from trading with VFSC-licensed Forex brokers?
Confidence that brokers exist as legal entities.
A license from the VFSC is of no practical importance to traders. The Commission does not have a complaint filing form on its website, ignores most complaints by private individuals, and does not provide a compensation fund. The only benefit is that brokers are checked by the Commission and do have legal addresses, business plans, and real teams.
How to check if a broker holds a VFSC license?
There are two options:
-
1
On the regulator’s website, go to the “Register Search” section and enter the broker’s license number or legal name.
-
2
Open the broker’s page on the Traders Union website. There, you will find information about all valid licenses and violations, if any. Information is updated every month.
How to submit a complaint against a broker to the VFSC?
-
1
Send an email to the regulator.
-
2
After registering on the TU website, refer to TU’s lawyers for free legal help.
In the first case, the chances that the regulator will read the email are low. According to traders’ reviews, the VFSC ignores complaints by private individuals. The second option is more effective because registration on TU’s website and legal support are free and TU is interested in protecting its members.
Glossary for novice traders
-
1
Broker
A broker is a legal entity or individual that performs as an intermediary when making trades in the financial markets. Private investors cannot trade without a broker, since only brokers can execute trades on the exchanges.
-
2
VFSC
VFSC is the financial regulatory authority of Vanuatu. It was created by the Vanuatu Financial Services Commission of 1993 when it assumed a part of the responsibilities of the Ministry of Finance and Economic Management. VFSC is a offshore regulator.
-
3
Trading
Trading involves the act of buying and selling financial assets like stocks, currencies, or commodities with the intention of profiting from market price fluctuations. Traders employ various strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management practices to make informed decisions and optimize their chances of success in the financial markets.
-
4
Investor
An investor is an individual, who invests money in an asset with the expectation that its value would appreciate in the future. The asset can be anything, including a bond, debenture, mutual fund, equity, gold, silver, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real-estate property.
-
5
CFD
CFD is a contract between an investor/trader and seller that demonstrates that the trader will need to pay the price difference between the current value of the asset and its value at the time of contract to the seller.
Team that worked on the article
Oleg Tkachenko is an economic analyst and risk manager having more than 14 years of experience in working with systemically important banks, investment companies, and analytical platforms. He has been a Traders Union analyst since 2018. His primary specialties are analysis and prediction of price tendencies in the Forex, stock, commodity, and cryptocurrency markets, as well as the development of trading strategies and individual risk management systems. He also analyzes nonstandard investing markets and studies trading psychology.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).









