Understanding algorithmic trading: An overview for beginners
Algorithmic trading involves a process where each trade order is executed through automated, pre-programmed instructions. This method aims to get the most out of the market by accounting for price, timing, and volume through the algorithm. Each algorithm consists of predefined criterias, based on market data and statistical analysis.
Algorithmic trading refers to the use of advanced mathematical models and computer programs to automate trading decisions. It has emerged as a pivotal tool for individual traders and institutions alike. This beginner's guide will provide an overview of algorithmic trading, how it works, its benefits, and the different types of algorithmic trading systems. We'll also look at some examples and real-world applications. Whether you're new to automated trading strategies or looking to learn more, this article will help explain the basics of this innovative trading approach.
Do you want to start trading Forex? Open an account on RoboForex!Algorithmic trading explained
Algorithmic trading is an advanced method that relies on advanced coding and formulas based on a mathematical model. However, compared to traditional trading methods, the process differs by being automated.
Moreover, no human emotions are involved that would otherwise compromise the potential outcome. Investors will typically utilize this strategy when attempting to sell or buy assets rapidly to earn from short-term price movements.
Consequently, each trader can participate in multiple trades within a 24-hour interval and capitalize on even the smallest increments in value. Aside from the stock market, the algorithmic trading approach is used in many other industries, the most notable being Forex and crypto.
Related terms for beginners
There are key terms that each beginner will come across when entering the algorithmic trading space, and these include black box, dark pool, back-testing, and optimization.
-
Black Box - refers to a trading strategy where a computer program monitors the market. Its objective is to spot signals for trading and initiate buy/sell orders. The underlying algorithms and logic are generally not disclosed or revealed to investors/traders, hence the term "black box"
-
Dark Pool - refers to a privately organized exchange for trading securities that would not be accessible by the investing public. They are intended to enable institutional investors to trade without exposure until after the trade has been executed and then reported
-
Back-Testing - the performance of a trading strategy can be evaluated through simulations. As a result, investors can expose their strategy algorithm to a stream of historical data. This enables investors the opportunity to measure various performance metrics. These include risk-adjusted returns, win rates, maximum drawdown, and profit and loss
-
Optimization - the process of improving a portfolio, algorithm, or trading system. The objective is to reduce costs while also increasing its efficiency. Any portfolio can be optimized through the reduction of risks and the increase of expected returns or the change in the frequency of rebalancing
How does algorithmic trading work?
To truly understand how algorithmic trading works, it's first essential to understand the economic theories on which it is based.
The usage of algorithms within financial markets originated back in the 1970s. They initially had simple rule-based systems, which were utilized to execute trades based on stock exchanges. These were basic but used for executing trades at the best available prices.
Let’s explore the mechanics of algorithmic trading and see why it's a topic of interest among traders.
Trading algorithms that are well-programmed can run on their own. Some human oversight will always be recommended. However, they are designed to operate as efficiently as possible. Typically, what will be required from trades is to pick a time frame and trade frequency that they can monitor. Financial constraints will need to be implemented for an algorithm to be used as efficiently as possible. Then, investors will need to create or fine-tune a strategy.
As the technology evolved, they have become far more sophisticated and now utilize artificial intelligence (AI) elements like machine learning and deep learning. Some even use large language models and analyze financial news and social media.
Example of algorithmic trading
Please, be aware that this example is for demonstration purposes only and cannot be used for taking your trading decisions.
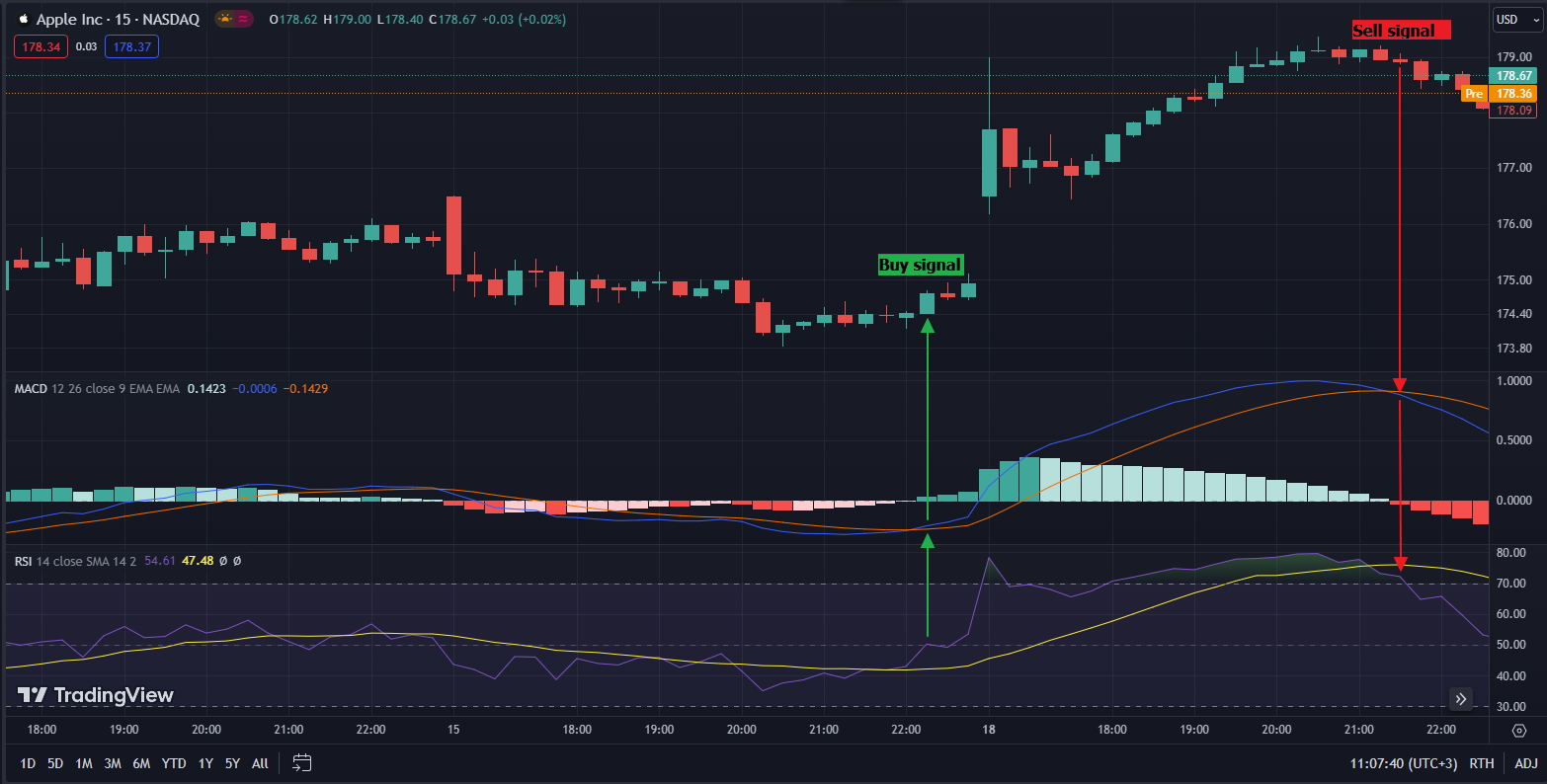
Here's an example of a very simple algorithmic trading strategy based on two very popular technical indicators - Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) and Relative Strength Index (RSI).
Let’s define that a Buy signal is generated when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, and the RSI value is above 50, indicating a potential increase of the asset price. The algorithm will monitor the chart and send a buy order when conditions are met.
The signal for closing this long position would be when the MACD line crosses below the signal line and the RSI value is in the overbought zone above 70, indicating potential reversal. The sell order would be sent, thus exiting the trade.
In the following example of the AAPL chart we can see what the trade would look like.
Benefits and challenges of algorithmic trading
Numerous benefits make algorithmic trading superior to manual trading. For example, each investor can automate their trading methods while eliminating human error. In addition, it offers much better speed and efficiency. Computer programs can analyze vast amounts of market data in real-time, benefiting those with high-frequency trading.
Algorithmic trading is also superior in terms of its objectivity. The programs are based on rules and strategies that have been defined upfront. As a result, they can eliminate the emotional biases that could impact human decision-making.
These algorithms can also benefit those who want to implement complicated strategies involving many different asset classes or advanced risk management techniques.
Some risks associated with algorithmic trading include system failures or technical risks. In addition, there can potentially be more significant losses compared to manual trading.
Also, expert advisors can assist traders and are between fully algorithmic trading and manual trading. Investors can get in-depth data as to how they can trade and learn about the various rules of testing EAs and evaluating their effectiveness.
Best Forex brokers


Expert Opinion
Fundamentally, algorithms can make trading decisions in a more objective and efficient manner compared to humans by eliminating emotional biases. However, their performance still depends on how well the underlying models and parameters have been designed.
New traders are often too results-oriented, chasing strategies with big potential returns but high risk. With algorithmic trading, it's better to focus on consistency rather than chasing overnight winners. Sustainable, smaller wins added up over time will serve you better in the long run compared to riskier strategies with volatile returns.
When live trading, start small with micro lots only. Monitor results closely. Successful backtesting doesn't guarantee identical forward performance. Be prepared to refine the strategy as needed based on what you observe.
I'd also suggest partnering with an established algorithmic trading platform rather than trying to independently code and run complex systems. This reduces the technical learning curve and operational risks. With experience, you can gradually develop your own strategies and move to more advanced platforms.
FAQs
How is algorithmic trading different from high-frequency trading?
The critical difference between them is that algorithmic trading has been designed from the ground up to provide better efficiency during long-term trading. Moreover, high-frequency trading, or HFT for short, lets traders buy and sell far quicker. As a result, algorithmic trading refers to any strategy that utilizes automated processes. HFT is a subset that only focuses on the execution of a large number of orders, at extreme speeds. Using both methods is intended to provide better results than what's possible by humans.
Is algorithmic trading legal?
Algorithmic trading is legal. However, each of the algorithmic strategies that are utilized must first be authenticated by the exchange in question before their implementation. In other words, it must comply with the applicable regulations, such as those related to market manipulation or abuse. There must be proper protocols in place alongside monitoring.
What skills are required for algorithmic trading?
Any trader must have a few skills before engaging with algorithmic trading. They must develop knowledge in statistics, quantitative analysis, programming, and financial market knowledge.
What assets can be traded using algorithms?
There is a wide range of assets supported by algorithmic trading. These include Stocks, ETFs, futures, forex, options, and cryptocurrencies. As a result, anyone can implement this trading strategy to their portfolio. In addition, anything with liquid markets can be a potential candidate.
Glossary for novice traders
-
1
Broker
A broker is a legal entity or individual that performs as an intermediary when making trades in the financial markets. Private investors cannot trade without a broker, since only brokers can execute trades on the exchanges.
-
2
Trading
Trading involves the act of buying and selling financial assets like stocks, currencies, or commodities with the intention of profiting from market price fluctuations. Traders employ various strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management practices to make informed decisions and optimize their chances of success in the financial markets.
-
3
Algorithmic trading
Algorithmic trading is an advanced method that relies on advanced coding and formulas based on a mathematical model. However, compared to traditional trading methods, the process differs by being automated.
-
4
Investor
An investor is an individual, who invests money in an asset with the expectation that its value would appreciate in the future. The asset can be anything, including a bond, debenture, mutual fund, equity, gold, silver, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real-estate property.
-
5
CFD
CFD is a contract between an investor/trader and seller that demonstrates that the trader will need to pay the price difference between the current value of the asset and its value at the time of contract to the seller.
Team that worked on the article
Milko Trajcevski is a truly determined content writer with a passion for the crypto industry. He has a successful track record of researching and effectively writing articles about cryptocurrency, non-fungible tokens, and blockchain covering the fields of crypto-asset regulations, wallets and exchanges, liquidity, altcoins, DApps, forks, mining, laddering, security and enterprise blockchain technology.
Milko focuses on contributing fresh and interesting articles to the Traders Union website, with expertise within the crypto-writing space, and a dedication to service.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).










