How to Short the GBP? Step-by-Step Guide



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
How to Short the GBP:
- Choose a Forex broker that offers GBP trading pairs.
- Open a trading account and fund your trading account with the required initial deposit.
- Analyze the market - use technical and fundamental analysis.
- Select the GBP pair - choose a currency pair such as GBP/USD or GBP/EUR.
- Place a short trade - execute a sell order for the chosen GBP pair, indicating you expect the GBP to decrease in value.
- Set stop-loss and take-profit orders to manage your risk.
- Close the trade when your target profit is reached or market conditions change, close your position to realize your gains or limit losses.
Shorting the British pound (GBP) has gained popularity due to notable market events and success stories. A prime example is George Soros's trade on Black Wednesday in 1992. Soros made over $1 billion by betting against the British pound, demonstrating the significant profit potential in shorting GBP.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to shorting GBP, suitable for both beginners and experienced traders. It covers the basics of short selling, delves into the specifics of the GBP, and provides a step-by-step approach.
Step-by-step guide to shorting GBP
1. Choose a reliable broker
Regulation: Ensure the broker is regulated by reputable authorities such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK.
Fees: Evaluate the broker’s fee structure, including spreads, commissions, and overnight financing costs.
Trading platforms: Opt for brokers offering robust trading platforms equipped with technical analysis tools and real-time market data specific to GBP.
To help you choose better, we have prepared a comparison table of the top brokers that enable shorting the GBP:
| Plus500 | Pepperstone | OANDA | FOREX.com | Interactive Brokers | IG Markets | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Min. deposit, $ |
100 | No | No | 100 | No | 1 |
|
Currency pairs, number |
60 | 90 | 68 | 80 | 100 | 80 |
|
Max. leverage |
1:300 | 1:500 | 1:200 | 1:50 | 1:30 | 1:200 |
|
Min Spread GBP/USD, pips |
0,5 | 0,4 | 0,1 | 0,9 | 0,5 | 0,6 |
|
MAX Spread GBP/USD, pips |
1,0 | 1,4 | 0,5 | 1,4 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
|
Fixed spread GBP/USD |
No | No | No | No | No | No |
|
ECN Spread GBP/USD, avg, pips |
No | 0,15 | 0,2 | 0,4 | 0,3 | 1 |
|
Open account |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Study review | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Study review |
2. Analyze market conditions
Technical analysis: Use indicators such as moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to identify potential entry and exit points.
Fundamental analysis: Focus on the Bank of England's interest rate decisions, inflation reports, and key economic data releases like GDP growth and employment figures.
Geopolitical events: Monitor geopolitical developments, especially those related to the political and financial situation in Europe, particularly conflicts within the EU and the actions of the ECB, , as they significantly impact GBP's value.
3. Place a short order
Access trading platform: Use the broker’s platform to enter trade details, including the amount of GBP to short and the desired entry price.
Confirm trade: Select the "Sell" option to execute the trade. Ensure there is sufficient margin in the account to cover the position and potential price fluctuations.
Automation options: Many brokers offer the ability to set limit or stop orders to automate the process when specific price levels are reached.
4. Manage risk
Stop-loss orders: Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses if the trade moves unfavorably. For example, shorting GBP at $1.40 might involve setting a stop-loss order at $1.45.
Leverage management: Use leverage cautiously, as it can amplify both profits and risks. Understand the broker’s margin requirements to manage leverage effectively.
5. Monitor and adjust
Continuous monitoring: Regularly track GBP’s performance against relevant economic indicators and news events.
Strategy adjustments: Be prepared to adjust the strategy based on market movements. For instance, if new economic data indicates a stronger-than-expected UK economy, consider exiting the short position early to mitigate losses.
Best strategies to short GBP
1. Trend following
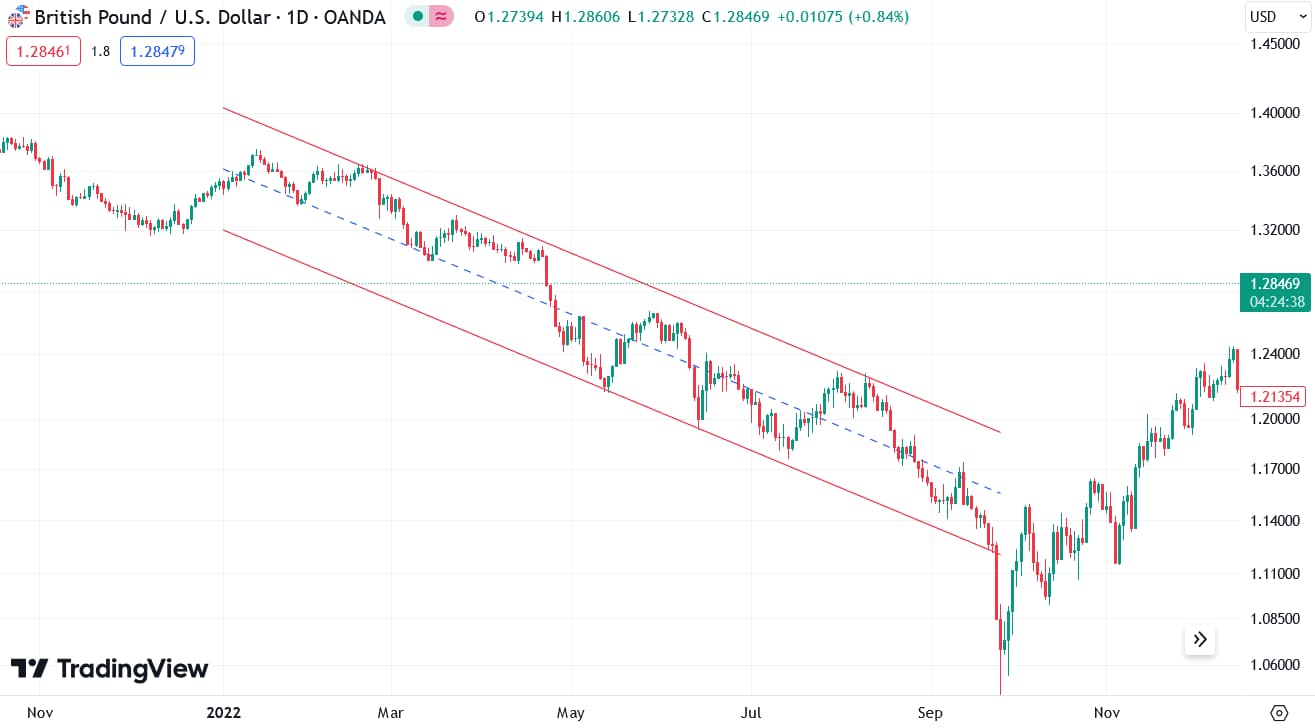
Trend following involves identifying and trading in the direction of the current market trend. When shorting GBP, traders look for established downward trends. Following a downward channel is one of the most common trend-following strategies, where traders identify a strong downward channel and remain short till the channel is broken.
2. Breakout trading
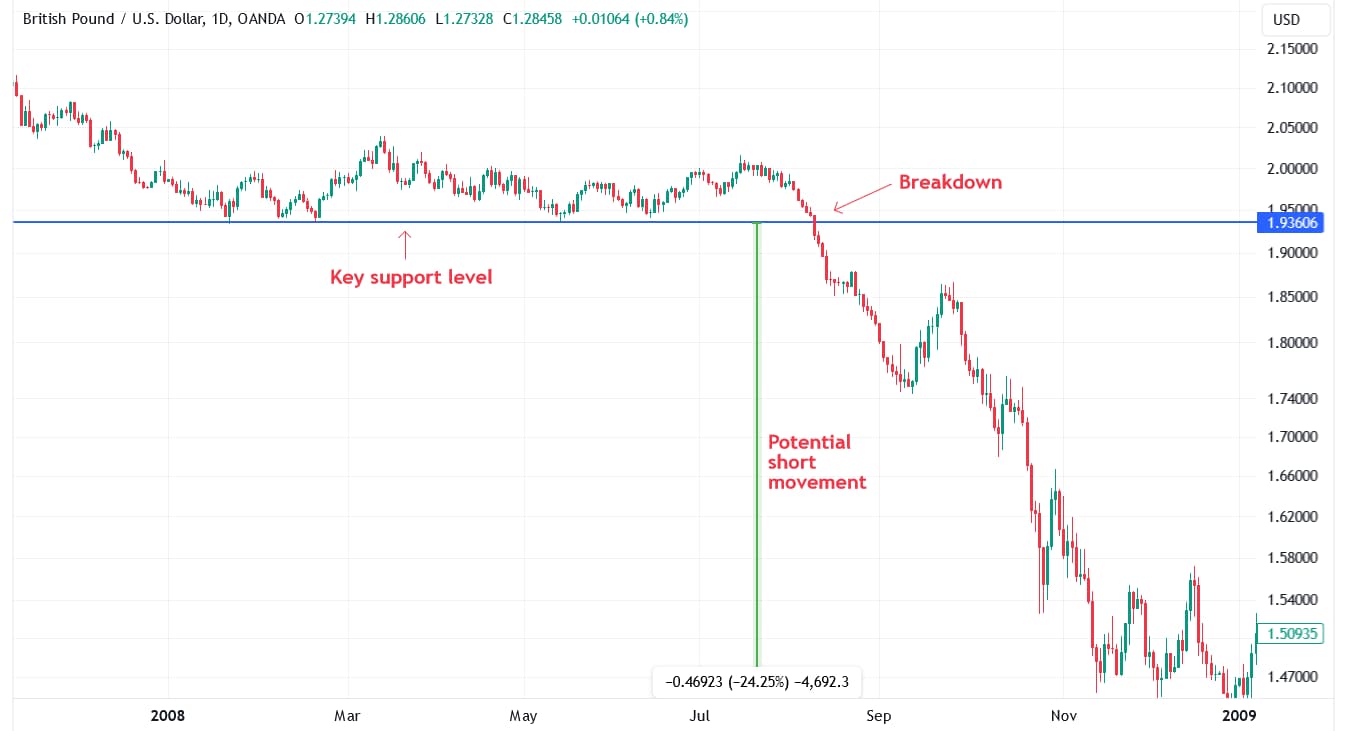
Breakout trading involves entering a trade when the price breaks through a key support level. For shorting GBP, traders watch for GBP/USD or GBP/EUR to fall below significant support levels on their charts. Support levels can be identified using historical price data or technical indicators like Fibonacci retracement levels. Once the price breaks below these levels, it often continues to move in the direction of the breakout.
3. Relative strength index (RSI) overbought conditions
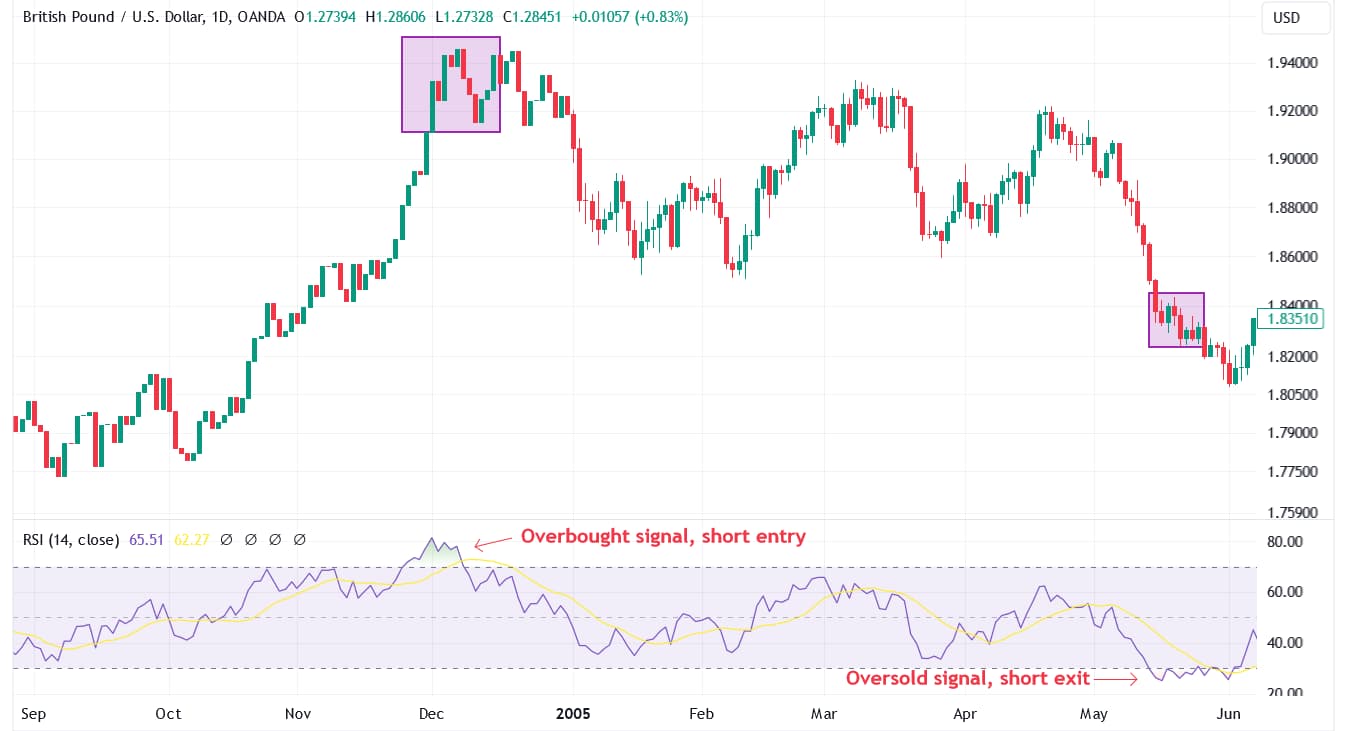
The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. An RSI above 70 typically indicates that a currency is overbought, suggesting a potential price decline. When shorting GBP, traders look for the RSI to cross below the overbought threshold of 70, indicating a possible reversal. This strategy can be combined with other indicators like the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to confirm the signal.
Understanding GBP: main facts and features
The British pound (GBP) is one of the most traded currencies globally, known for its volatility and significant impact on the forex market. Here are the key facts and features that traders should be aware of when dealing with GBP:
Historical performance: The GBP has a long history as a major global currency. Its value has fluctuated significantly over the years due to various economic and political events. Notably, the pound experienced sharp declines during the 2008 financial crisis and following the Brexit referendum in 2016.
Economic indicators: Several economic indicators play a crucial role in determining the value of GBP. These include:
Interest rates: Set by the Bank of England, changes in interest rates can attract or deter foreign investment.
Inflation rates: Higher inflation can decrease the value of GBP as it erodes purchasing power.
GDP growth: A strong economy boosts investor confidence, positively impacting the pound's value.
Market volatility: GBP is known for its volatility, making it both a risk and an opportunity for traders. Rapid price changes can lead to significant gains or losses, depending on market conditions and trader strategies.
Shorting GBP for beginners: additional tips
Beginners can shorten their learning curve in shorting GBP through these tips:
Understand market sentiment: Positive economic news can strengthen GBP, while negative news can weaken it. Staying updated with the latest economic indicators and news events impacting the UK economy is essential.
Use demo accounts: Practicing on a demo account allows traders to understand the mechanics of shorting without risking real money. Most reputable brokers offer demo accounts where users can simulate trades in real market conditions. This helps build confidence and develop strategies before trading with actual funds.
Start with small trades: By trading small amounts, beginners can minimize potential losses while learning the market dynamics. As confidence and experience grow, gradually increasing trade sizes can be considered.
Implement risk management strategies: Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and avoid using excessive leverage. A well-thought-out risk management plan can help mitigate the inherent risks of shorting.
Key lessons I’ve learned while shorting GBP
Shorting GBP has been a significant part of my trading strategy, and I've learned a few key lessons along the way:
Keeping up with economic indicators like the Bank of England’s interest rate decisions, inflation reports, and geopolitical events such as Brexit is very helpful. These factors can dramatically affect GBP’s value. Regularly checking sources like Bloomberg and Reuters helps in anticipating market moves.
The Forex market is highly volatile, and it’s easy to get caught off guard. Setting strict stop-loss orders has saved me from significant losses many times.
Before committing real money, I always practice new strategies on a demo account. In live trading, I start with small positions. This approach helps in managing risk and allows for gradual scaling as confidence and experience grow. It’s a safer way to enter the market and learn its ropes.
Conclusion
Shorting GBP can be a profitable but complex trading strategy, requiring careful planning and informed decision-making. Key aspects include choosing a reliable broker, analyzing specific market conditions, and implementing robust risk management strategies. Understanding the unique features of GBP, such as its volatility and sensitivity to economic indicators like interest rates and inflation, is crucial. Historical examples, like George Soros's legendary Black Wednesday trade, illustrate the significant profit potential when shorting GBP.
FAQs
What is the best time to short GBP?
The best time depends on market conditions, economic indicators, and geopolitical events. Monitoring these factors can help identify optimal shorting opportunities.
Can beginners short GBP?
Yes, but they should start with a strong understanding of the basics, practice with demo accounts, and manage risk carefully.
What tools are useful for shorting GBP?
Technical analysis tools, economic calendars, and news feeds are essential for tracking market trends and making informed decisions.
How does leverage affect shorting GBP?
Leverage can amplify both gains and losses, making it a powerful but risky tool. Using leverage requires careful risk management and a solid trading strategy.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.

Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Index in trading is the measure of the performance of a group of stocks, which can include the assets and securities in it.
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is the practice of buying and selling currencies in the global foreign exchange market with the aim of profiting from fluctuations in exchange rates. Traders speculate on whether one currency will rise or fall in value relative to another currency and make trading decisions accordingly. However, beware that trading carries risks, and you can lose your whole capital.
Economic indicators — a tool of fundamental analysis that allows to assess the state of an economic entity or the economy as a whole, as well as to make a forecast. These include: GDP, discount rates, inflation data, unemployment statistics, industrial production data, consumer price indices, etc.
Risk management is a risk management model that involves controlling potential losses while maximizing profits. The main risk management tools are stop loss, take profit, calculation of position volume taking into account leverage and pip value.
An ECN, or Electronic Communication Network, is a technology that connects traders directly to market participants, facilitating transparent and direct access to financial markets.






























































































































