ASIC | Financial Regulator Of Australia
ASIC is the Australian Securities and Investments Commission that, along with the Reserve Bank of Australia, performs constant supervision over licensees and their interaction with each other. One of ASIC’s tasks is to collect information from open sources about brokers, banks, and investment and insurance funds.
Every country has a financial regulator that controls the operation of licensees and their interaction with each other, helps to resolve disputes, protects the rights of private clients, participates in the development of regulatory documents, counteracts fraud, etc. A regulator's license means that a broker operates in compliance with local laws and meets all financial requirements.
For a broker, a license means the following:
-
The broker has to meet its regulator’s requirements, such as maintain its equity at a set level, observe the accounts segregation principle, and conduct its business transparently, etc;
-
It can operate legally in the countries covered by the license, promote its brand, and advertise its services. Advertising brokerage services without a license is prohibited in many countries;
-
It has to be audited periodically and follow recommendations based on the results of audits.
For a trader, a license is an assurance that a broker observes the law and is not a pyramid and that disputes can be resolved through a regulator. It, however, is not a guarantee.
Description and functions of ASIC
ASIC, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission, is the only financial regulator in the mainland. The regulator was established in 1998, but only in 2001, having partially assumed the powers of the Reserve Bank of Australia, did it start to perform its functions in full. In 2002, the regulator began controlling the banking system and, in 2009, the stock market. ASIC regulates investment, retirement, and insurance funds, banks, brokers, and participants of exchange and over-the-counter markets.
Tasks and purposes of ASIC in the Forex market
-
Issues and revokes brokerage licenses;
-
Helps to settle disputes and consider complaints and claims;
-
Counteracts fraud. Reveals manipulations and violations of financial laws;
-
Collects and analyzes information about the financial operations of licensees;
-
Performs superficial analysis of financial statements;
-
Participates in the improvement of financial laws and the development of statutory acts that regulate the interaction between all market participants.
However, compared to some European regulators, ASIC’s requirements for brokers are less strict. Minimum equity and annual fees are lower, complete in-depth management checks are not performed, and financial statements are analyzed superficially. Nevertheless, it is mandatory to go through annual audits that evaluate brokers’ solvency and help optimize internal technological processes.
Information available on the website
The ASIC’s website is complex:
-
Main menu at the top;
-
Auxiliary menu on the right;
-
Additional tabs in subsections. When you click on the links, you are redirected to separate websites that have their own sub-structure.
Overview of the ASIC website:
-
For business is a section for potential or existing licensees, where you can apply for a license, get information about the protection of brokerage business, etc.
ASIC Website Sections — For business
-
For finance professionals is an additional section for brokers, auditors, and other professional participants of financial markets.
ASIC Website Sections — For finance professionals
-
For consumers is a section for traders and private individuals connected with financial markets.
ASIC Website Sections — For consumers
-
View a list of blocked or canceled licenses;
-
Get advice on finance and investment;
-
Find information on how to work with banks and insurance companies;
-
Lodge a complaint or a claim.
For consumers is the main section for traders. Here you can:
This list only contains the main sections. You can find a full list of sections by clicking Site Map at the bottom.

Image_Title
How to confirm a broker’s license on the ASIC website
ASIC’s website structure is very complicated. The website contains a lot of information, which is not structured the best way, and most of it suggests that you open another tab to find more information or watch an educational video.
Another reason why searching for brokers can be difficult is that the primary website has numerous autonomous branches. For example, there is no guarantee that you will get a result by entering a broker’s license number in the search box on the homepage.
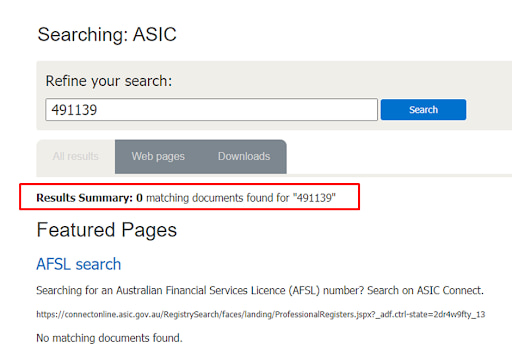
Searching for a Broker’s License on the ASIC Website — License number
Also, you cannot always find information about a broker by its name.
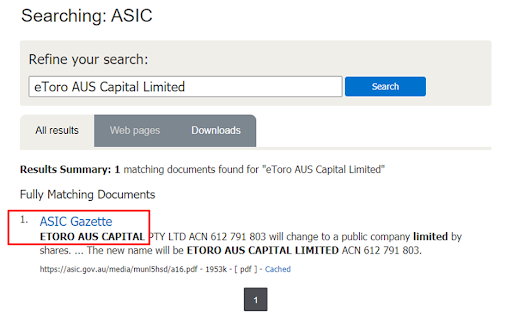
Searching for a Broker’s License on the ASIC Website — Search results
In the example above, only a mention of a broker was found in the regulator’s website content.
The following license search procedure is not the only one, but TU thinks it’s the easiest and quickest.
How to find a broker’s license on the ASIC website
-
1
On the broker’s website, find its license number or full legal name. The broker may have several branch offices registered in different jurisdictions under different names.
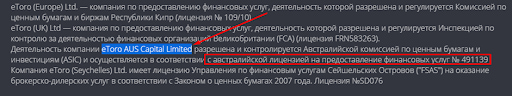
Screenshots from broker’s website.
-
2
In the Google search bar, enter the following request: “check ASIC license”.
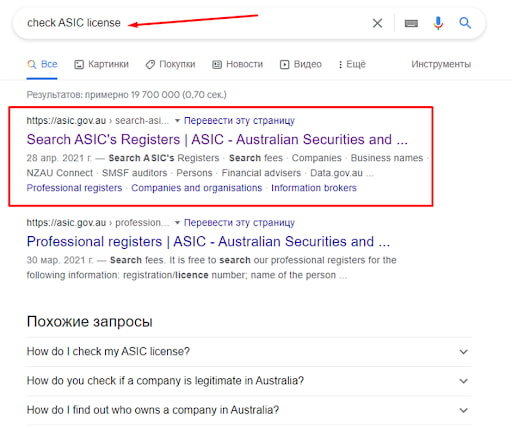
Confirmation of an ASIC License — Via Google search
-
3
Follow this link to the regulator’s website and click “Companies”.
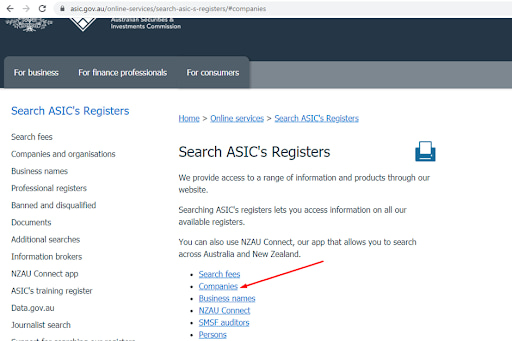
Confirmation of an ASIC License — Companies
-
4
Click “Search now on ASIC Connect”. You will be redirected to an autonomous website branch.
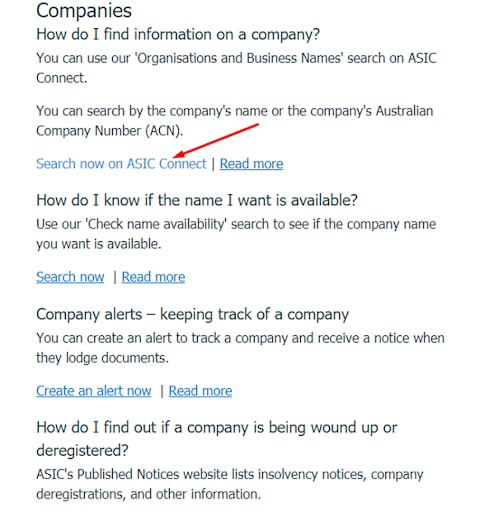
Confirmation of an ASIC License — Searching for a broker
-
5
Enter the broker’s name.
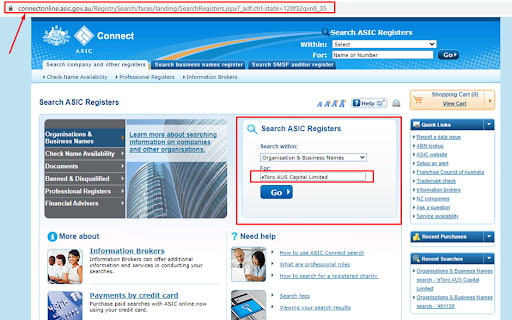
Confirmation of an ASIC License — Searching for a broker by name
-
6
View information about the broker’s license.
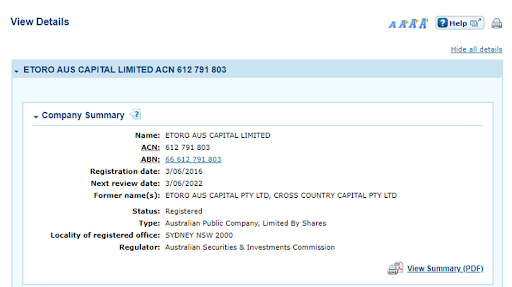
Confirmation of an ASIC License — Broker’s license information
Using this method, anyone can review basic details of a brokerage license: its Australian Company Number (ACN), Australian Business Number (ABN), date of registration and renewal date, status, as well as the full name of the company that holds this license.
ASIC’s basic requirements for brokers
Basic requirements to obtain a license:
-
Minimum equity of 0.5-1 million AUD. The amount depends on the brokerage services offered.
-
Provide information about owners and the management team.
-
Pay annual fees.
ASIC cooperates with other narrowly-focus controlling bodies such as the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC), the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA), etc. Such an approach enables ASIC to control various aspects of a broker’s activities.
ASIC license | Pros and cons
ASIC is a relatively reputable regulator whose control and requirements are less strict than those of some regulators in the U.S. and Europe. The key conditions a broker must fulfill are to have an office in Australia or New Zealand, possess the equity required, and provide information about the management team.
👍 Main advantages of trading with an ASIC-licensed broker
• Protection of traders’ interests. Unlike many other regulators, ASIC considers traders’ complaints without redirecting them to the ombudsman or other authorities. If necessary, the regulator can engage the Australian Federal Police or the Reserve Bank;
• Guarantee of brokers’ reliability. Traders can be sure that brokers will not use their money for their own purposes;
• The regulator considers individual complaints if a trader provides sufficient evidence.
An ASIC license confirms a broker’s decency and responsibility. To control brokers, the regulator uses Iress [Integrated Real-time Equity (Software) System], a secure tool that automatically aggregates and ranks information about licensees from open online sources.
👎 Main disadvantages of trading with an ASIC-licensed broker
• ASIC does not control its licensees as strictly as some European regulators. The regulator analyzes statements superficially, monitors new negative online comments, and considers complaints. ASIC disregards the trading conditions of high-risk brokers and does not conduct in-depth audits of their operations. ASIC does not try to prevent fraud and mostly reacts to already committed violations;
• No information about the protection of traders’ interests. No information on how brokers (should) observe the account segregation rule. No information about an insurance fund (it is most likely unavailable);
• Paid access to some information.
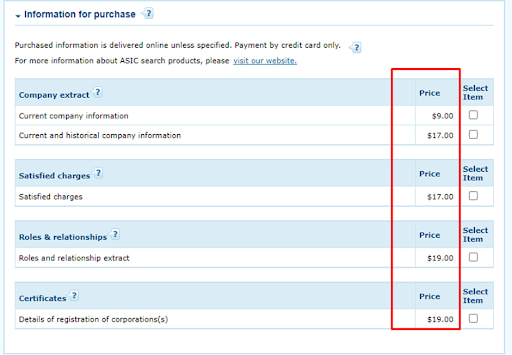
Reviewing ASIC Licenses — Paid access
ASIC is lenient with brokers, which is not very good for traders. Absence of an insurance fund is another downside for traders and a benefit for brokers that don’t have to pay fees. Nevertheless, unlike most offshore regulators, ASIC tries to control its licensees, thereby guaranteeing brokers’ reliability.
ASIC’s jurisdiction
ASIC’s jurisdiction is Australia and New Zealand. To obtain a license, a broker has to register an office in one of these countries. Since Australia is not related to Europe or Asia, the regulator’s licenses are only valid within its jurisdiction.
Submission and consideration of complaints
ASIC considers individual complaints irrespective of the amount of each claim or the amount of the deposit. The regulator does not engage ombudsmen; it tries to fix problems itself.
Complaint submission procedure:
-
1
On the ASIC website’s homepage, open the “For consumers” tab and select “How to complain”.
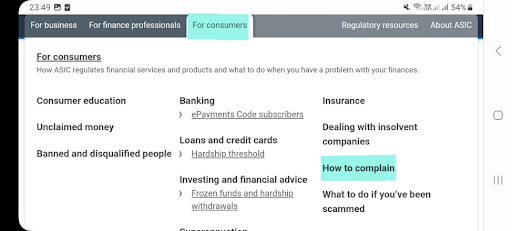
ASIC Review — Submission and consideration of complaints
-
2
Follow the “How to complain” link.
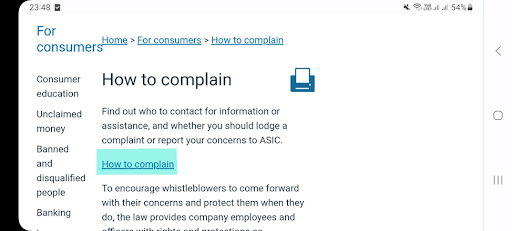
ASIC Review — Submission and consideration of complaints
-
3
Study all the available information. There is no application form, but this section explains in detail what types of complaints and to which instances traders can submit.
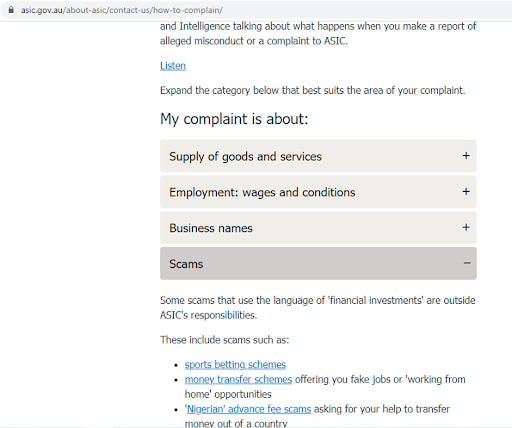
ASIC Review — How to complain
-
4
Write a letter of complaint in accordance with the rules included and send it by email.
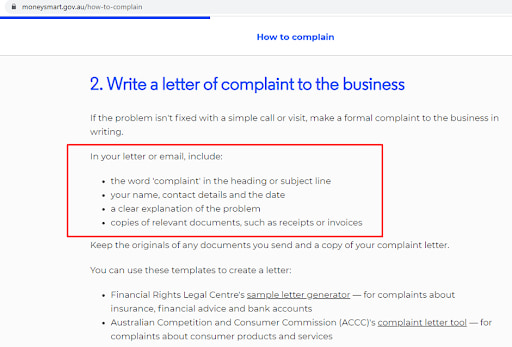
ASIC Review — Preparation and submission of complaints
The term in which your complaint will be considered depends on many factors, including the set of documents submitted. Complaints may be considered in 2-4 weeks.
Expert’s assessment
-
U.S. regulators. This jurisdiction has its own closed world with its own rules.
-
First-level regulators, such as the British FCA or the German BaFin. They are distinguished by strict supervision and deemed to be the most reputable.
-
Offshore regulators, such as IFSC (Belize) or FSC BVI (British Virgin Islands). They have lenient terms of registration and control their licensees superficially.
-
ASIC. The Australian regulator does not belong to any of these groups. It’s not a first-level authority as it does not perform an in-depth analysis of its licensees’ operations and does not have hard requirements for brokers’ organizational structure or operating principles. ASIC cannot be placed among offshore regulators, either. It works closely with the Reserve Bank of Australia, and an ASIC license means that if a broker commits an obvious violation, the Reserve Bank may intervene in its operation.
ASIC is more like an observer or arbiter than a legitimate controlling body. The conditions for obtaining a license are relatively lenient and there is no total control like with the FCA. Counteraction against fraud consists in responding to complaints and considering disputes. The regulator does not operate through ombudsmen and deals with issues itself. There were cases when ASIC helped to correct trading mistakes that could have radically changed the quotes of some companies.
Conclusion
Brokers mostly acquire an ASIC license as an additional assurance to traders. The primary benefit for brokers is that ASIC considers complaints itself, without unnecessary bureaucracy. But traders should not rely too much on the regulator in disputes with brokers.
FAQs
What is ASIC?
ASIC is the Australian Securities and Investments Commission that, along with the Reserve Bank of Australia, performs constant supervision over licensees and their interaction with each other. One of ASIC’s tasks is to collect information from open sources about brokers, banks, and investment and insurance funds. The regulator pays special attention to complaints and negative reviews. ASIC also controls payments between market participants, serves as an arbiter during controversies, conducts audits of brokers, and develops requirements and recommendations.
What do I get from trading with ASIC-licensed Forex brokers?
-
You can directly address the regulator in case a broker violates your client agreement or acts against your interests.
-
The assurance that a broker operates within the legal framework of its jurisdiction.
How to check if a broker holds an ASIC license?
-
In the Google search bar, enter the request: “check ASIC license”.
-
On the ASIC website, go to “Companies Search now on ASIC Connect” to search for a license by its number or the broker’s legal name.
Another option is to visit the Traders Union website, which features monthly updated information on every broker and its licenses.
How to submit a complaint against a broker to ASIC?
-
On ASIC’s website, open the “For consumers” tab and select “How to complain”.
-
Find the needed type of complaint and follow the instructions.
-
Prepare a letter of complaint and send it by email.
ASIC’s website is overloaded with additional information and has a complicated structure. Even if there is a complaint submission form on the website, you cannot find it quickly. But there is information that complaints can be lodged via email.
Use this simpler alternative. Contact TU’s legal department. Every TU member is entitled to free legal help in resolving disputes. TU’s lawyers are always ready to help you complete a complaint on the ASIC website.
Team that worked on the article
Oleg Tkachenko is an economic analyst and risk manager having more than 14 years of experience in working with systemically important banks, investment companies, and analytical platforms. He has been a Traders Union analyst since 2018. His primary specialties are analysis and prediction of price tendencies in the Forex, stock, commodity, and cryptocurrency markets, as well as the development of trading strategies and individual risk management systems. He also analyzes nonstandard investing markets and studies trading psychology.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
The topics he covers include trading signals, cryptocurrencies, Forex brokers, stock brokers, expert advisors, binary options. He has also worked on the ratings of brokers and many other materials.
Dr. BJ Johnson’s motto: It always seems impossible until it’s done. You can do it.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO). Mirjan is a cryptocurrency and stock trader. This deep understanding of the finance sector allows her to create informative and engaging content that helps readers easily navigate the complexities of the crypto world.





















