CySEC | Financial Regulator Of Cyprus
CySEC, the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, is a regulator for investment companies and brokers. The commission operates in partnership with the state financial and judicial authorities of Cyprus. SySEC’s objectives are to control the operation of brokers, monitor the observance of the financial laws, and consider complaints submitted by traders.
A license is an official permission from a state regulator to perform one or several types of financial activity. To obtain a license, a broker has to meet several requirements: provide information about its finances, management, and organizational structure, possess minimum registered capital, etc.
Holding a license enables a broker to:
-
Provide brokerage services legally. Without a license, a broker does not have the right to operate in jurisdictions covered by this license;
-
Be audited by independent agencies that can reveal and prevent possible problems invisible from inside the company. An audit often helps optimize internal processes;
-
Have more clients. Traders trust licensed brokers more than unlicensed ones or those holding licenses from offshore regulators.
A license allows a trader to count on the responsibility and honesty of a broker that operates in the legal framework.
In this post, TU explores CySEC’s functions, advantages, and complaint submission procedure, as well as reviews of this regulator.
Description and functions of CySEC
CySEC, the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, was established in 2001. In 2008, it got broader powers to control legal entities. In particular, CySEC can directly intervene in a company’s operation if it goes bankrupt or defaults. Licensing and control by CySEC are mandatory for investment companies (brokers in particular), their branch offices, and subsidiaries.
Tasks and purposes of CySEC in the Forex market
-
Ensures that brokers comply with the law of Cyprus and the eurozone.
-
To develop legislation and audit licensees;
-
Prevent insider trading.
-
Collect and analyze information about regulated entities.
-
Supervise brokers.
-
Receive and analyze complaints and take them into account when conducting audits.
A CySEC license means that a broker is periodically audited. Inspections may be performed by auditors of the “Big Four” accounting firms: Deloitte, Ernst &Young, KPMG, and PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC). In case a violation is found, the regulator has the right to impose a fine, revoke a license, or initiate a lawsuit.
To obtain a CySEC license, a broker has to
-
Complete an application on the regulator’s official website and pay a fee.
-
Confirm the availability of up to €1 million registered capital. The amount depends on the services provided by the broker.
-
Provide a business plan and a road map for 3 years.
-
Show the company management structure, which must include such full-time employees as a risk manager, fraud and money laundering officer, representatives of IT, financial, and accounting departments, etc. Confirmation of qualifications may be required.
-
Have documents that confirm the availability of a transaction account and segregated accounts at accredited banks.
-
Have its management team be personally present before the final approval to open an account, if requested.
Most brokers choose CySEC for several reasons that include: lower taxes, a license can be obtained in 1-3 months (the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) may review documents for up to 6 months), lower monthly fees, and fewer requirements regarding the provision of financial documentation.
Official website | Available information
Overview of the CySEC website:
-
Home. Return to the homepage from other sections.
-
The Commission. General information. Here you can find CySEC’s history, objectives, and organizational structure, read reports from previous years, view the schedule of seminars and conferences, etc.
-
Public Information. This section contains general information about the results of the regulator’s operation such as court decisions, administrative sanctions, warnings, statements, etc.
-
Regulated Entities. This section interests traders and brokers who can create their digital signatures here.
-
Regulatory Framework. Documents that regulate the interaction between all market participants.
-
Investor Protection. Client section.
Investor Protection, the main section for traders:
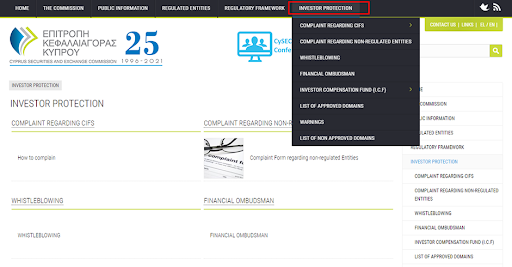
CySEC Review — Website sections
Here you can submit a complaint against a broker, apply for compensation, and contact the financial ombudsman.
How to confirm a broker’s license on the CySEC website
Brokers can be searched by name or license number. A broker’s name is a brand or a trademark that, in most cases, is not the same as the broker’s legal name. That is why searching by license number is easier.
-
1
On the broker’s website, find its license number. It can be in the homepage’s footer, FAQs, or About Us.
-
2
On the CySEC website’s homepage, enter the license number in the search box.

CySEC Review — Broker’s license number
-
3
Compare the results to information provided on the broker’s website such as registration address, company name, valid license, etc.

CySEC Review — Broker’s license search results
CySEC’s basic requirements for brokers
Basic requirements to obtain a license:
-
Up to €1 million registered capital, depending on the services provided by the broker.
-
The head office must be located in Cyprus.
-
In accordance with the principle of asset segregation, client accounts must be opened at Cyprian banks and separated from the broker’s transaction account.
-
Provide complete information about business structure. In some cases, the broker’s management team is required to be personally present when submitting an application.
The regulator can impose a fine or revoke a license. A revoked license means that the broker is forbidden from operating in Cyprus. In some cases, the regulator may initiate legal proceedings.
CySEC license | Pros and cons
CySEC is considered to be an offshore regulator that nevertheless strictly follows European rules and the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID). Brokers choose Cyprus for lower taxes compared to Europe. Registration in Cyprus automatically forces brokers to submit an application to CySEC. A CySEC license is a benefit for brokers, as this regulator is deemed to be the second strictest after the British FCA. For traders, a CySEC license is a guarantee that the broker is not a financial pyramid and is not involved in fraud.
Main advantages of trading with a CySEC-licensed broker:
👍 Main advantages of trading with a CySEC-licensed broker:
• Guarantee of the broker’s reliability. CySEC wants to uphold the reputation of the Cyprian regulatory system and its (CySEC’s) status as the golden mean between strict European and offshore regulators. Therefore, CySEC diligently controls its licensees.
• Compensation fund. The regulator cooperates with the Investor Compensation Fund of Cyprus (ICF). Also, most CySEC-licensed brokers cooperate with the independent self-regulated Financial Commission, which insures each client’s deposit for up to €20,000.
• Segregation of accounts. CySEC sees to it that traders’ money is separated from brokers’ transaction accounts. You can ask your broker’s support team which bank holds your deposit.
• Transparency. CySEC puts a stop to attempted manipulations or ambiguity in client agreements. The regulator’s purpose is to ensure maximal transparency of interaction between brokers and their clients.
A CySEC license confirms a broker’s decency and responsibility.
👎 Main disadvantages of trading with a CySEC-licensed broker:
• CySEC does not consider individual complaints. A trader can submit a complaint and thereby draw the regulator’s attention to a broker’s problems. But personal issues are only resolved through the broker’s support or an ombudsman.
• CySEC does not try to protect traders’ interests. Traders are often to blame for this because they do not read the documents that regulate cooperation. But there is also a problem with evidence: traders can only present evidence of obvious violations. Non-triggering of orders or slippage is hard to prove, and the regulator does not consider proofless complaints.
CySEC is interested in financial receipts and therefore often takes a neutral position in disputes between brokers and traders. The regulator does not hurry to resolve issues; instead, it often waits until violations or irregularities reach a “tipping point”. Sanctions applied to brokers don’t usually resolve traders’ problems.
CySEC’s jurisdiction
The regulator’s jurisdiction is Cyprus. To obtain a license, a broker has to open a branch office in Cyprus and apply for a license. Since CySEC operates in compliance with MiFID II, its license entitles brokers to operate in a number of European countries (the exceptions for each broker must be specified on its website).
Compliance with MiFID II requires that:
-
Brokers must provide extensive sets of documents every year. In addition to financial statements, brokers must provide information about their owners and management teams and confirm the absence of criminal records or open lawsuits.
-
All MiFID II entities have a single economic passport and are entitled to provide services in the eurozone.
-
The professional and financial categorization of traders determines the extent of their investor protection.
CySEC is not as meticulous as the FCA, but it also has a reputation of being a professional and trustworthy regulator.
Submission and consideration of complaints
CySEC does not consider individual complaints but promises to take them into account when conducting audits. Only collective complaints are accepted for consideration, but the website does not lay out the submission procedure or specify how many people have to submit a complaint to trigger an investigation. The regulator recommends sending copies of complaints to the website of the Cyprian ombudsman http://www.ombudsman.gov.cy/. The submission form is in pdf format.

CySEC Review — Submission and consideration of complaints
Complaint submission procedure:
-
1
On the regulator’s website, check if the broker has a valid license. If its status is Created/Modified, the license is valid and a complaint can be submitted. If the license is invalid or absent, the complaint will not be considered.
-
2
On the homepage, select “Investor Protection” and then “Complaint Regarding CIFS”.
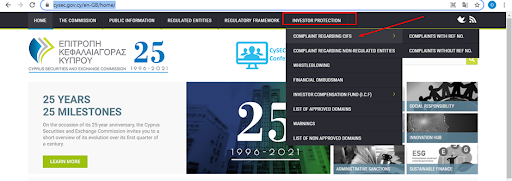
CySEC Review — Procedure for submitting a complaint to CySEC
-
3
Enter your personal details.
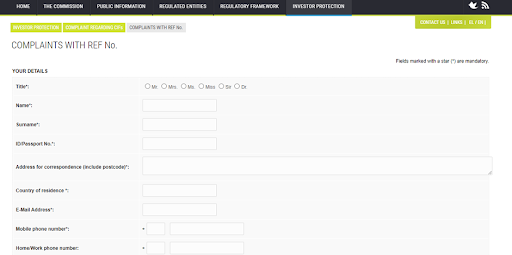
Submitting a Complaint to CySEC — Entering your personal details
-
4
To fill out the next part, you need the broker’s registration number. It’s in the broker details that can be found by the organization’s name or license number.
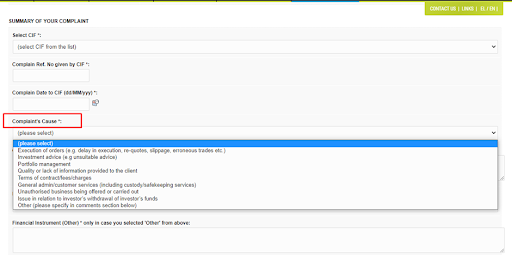
Submitting a Complaint to CySEC — Selecting a cause
-
Execution of orders. Complaints about the execution of orders, artificial slippage, etc.
-
Investment advice. Complaints about wrong recommendations from brokers. For example, a broker promised a 100% accurate trade signal. This cause occurs rarely, as brokers warn about the risks in advance.
-
Portfolio management. Complaints against investment companies. They regard brokers indirectly.
-
Quality or lack of information provided to the client. Complaints about inaccuracy or hiding of information that led to losses. For example, a broker did not warn a trader that it was mandatory to work off a bonus. Proving that a violation did take place is hard because many conditions are included in the offer and client agreement.
-
Terms of contract/fees/charges. Violations of the terms of the offer and client agreement. Financial issues such as a broker denies money withdrawals or charges unnecessary fees, money does not arrive, etc.
-
General admin/customer services. Complaints about user account settings or the blocking of a trading account or a user account.
-
Unauthorized business being offered or carried out. Complaints against a broker that violates the EU law or MiFID clauses.
-
Other.
-
5
Specify the instrument type and complaint amount.
Submitting a Complaint to CySEC — Selecting an instrument type and complaint amount
List of possible causes of complaints:
This 5th item mostly concerns Forex brokers. The other items concern stock and investment companies.
Complaint consideration time depends on the circumstances. The regulator’s representative can contact you by phone to check and clarify information in a week.
Expert’s assessment
In Europe and some Asian countries, CySEC is deemed a golden mean regulator. It offers brokers relatively simple license acquisition conditions. Unlike the FCA and BaFin (a German financial regulator), CySEC requires smaller registered capital and charges lower annual fees. But the regulator adheres to MiFID and MiFID II, which impose a number of restrictions on brokers and, respectively, on traders. For example, a limit on the maximum leverage (1:30). Practice shows, however, that this requirement is fulfilled permanently.
Although CySEC has the reputation of a European regulator, traders should not fully rely on this fact. The situation with the IronFX broker is worth mentioning as an example. At the beginning of 2015, collective complaints were being constantly lodged against the company, but CySEC ignored them for over three months. Almost a year later, when the regulator finally finished the investigation initiated by the majority of traders, the verdict was disappointing; the broker committed insignificant violations and must pay a fine of €335,000. The interests of traders were not protected and, in 2017, traders had to file a complaint with the European Commission.
Conclusion
Compared to other offshore regulators, CySEC can be called a serious organization. It responds to complaints and at least superficially controls brokers. But CySEC is not as strict as the FCA and this aspect should be taken into account when choosing a broker.
About the author of this review
Oleg Tkachenko, author and analyst at TU
Oleg Tkachenko has been TU’s financial analyst and economic observer since 2016. During this time, he has prepared more than 100 reviews of financial companies and analytic articles on technical and fundamental analysis, as well as developed over 10 trading systems. Oleg’s motto is to help everyone come all the way from a novice trader to a professional.
FAQs
What is CySEC?
CySEC, the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, is a regulator for investment companies and brokers. The commission operates in partnership with the state financial and judicial authorities of Cyprus. SySEC’s objectives are to control the operation of brokers, monitor the observance of the financial laws, and consider complaints submitted by traders. Based on the results of investigations, the regulator can impose fines and initiate legal proceedings.
What do I get from trading with CySEC-licensed Forex brokers?
-
Confidence that a broker is not a pyramid.
-
Knowledge that they operate in compliance with the financial laws of Cyprus and the eurozone, and are audited every year.
-
Access to protecting your interests through the regulator or the ombudsman.
-
Access to compensation from the insurance fund in case your broker goes bankrupt.
How to check if a broker holds a CySEC license?
-
Find the license number on the broker’s website and enter it in the search box on the regulator’s website. Check the status of the license. If there are any publications about the broker on the CySEC website (warnings, fines, etc.), you can find them under the broker’s name.
-
On Traders Union’s website, find a CySEC review that contains a regularly updated list of brokers that hold licenses from this regulator. Every month, TU’s analysts visit the regulator’s website to check every broker for a valid license, fines, or warnings.
Note that brokers may have licenses from several regulators.
How to submit a complaint against a broker to CySEC?
-
On the regulator’s website, complete a form in the section “Investor Protection/Complaint Regarding CIFS”. The regulator does not consider individual applications, but takes them into account when performing the next audit. The other option is to submit a complaint to the Cyprian ombudsman.
-
Refer your complaint to Traders Union’s legal department. Every TU client is entitled to free help in resolving disputes with brokers.
TU recommends using both options simultaneously.
Glossary for novice traders
-
1
Broker
A broker is a legal entity or individual that performs as an intermediary when making trades in the financial markets. Private investors cannot trade without a broker, since only brokers can execute trades on the exchanges.
-
2
Trading
Trading involves the act of buying and selling financial assets like stocks, currencies, or commodities with the intention of profiting from market price fluctuations. Traders employ various strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management practices to make informed decisions and optimize their chances of success in the financial markets.
-
3
Investor
An investor is an individual, who invests money in an asset with the expectation that its value would appreciate in the future. The asset can be anything, including a bond, debenture, mutual fund, equity, gold, silver, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real-estate property.
-
4
Index
Index in trading is the measure of the performance of a group of stocks, which can include the assets and securities in it.
-
5
Leverage
Forex leverage is a tool enabling traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital, amplifying potential profits and losses based on the chosen leverage ratio.
Team that worked on the article
Oleg Tkachenko is an economic analyst and risk manager having more than 14 years of experience in working with systemically important banks, investment companies, and analytical platforms. He has been a Traders Union analyst since 2018. His primary specialties are analysis and prediction of price tendencies in the Forex, stock, commodity, and cryptocurrency markets, as well as the development of trading strategies and individual risk management systems. He also analyzes nonstandard investing markets and studies trading psychology.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).





















