Main Types Of Currency Pairs In Forex Trading



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
Forex pairs are categorized into three main types:
As of 2024, the Forex market is the most liquid financial market, with a daily trading volume exceeding $7.5 trillion. Currency pairs are the foundation of Forex trading, indicating the comparative worth of one currency in relation to another and effective trading is impossible without understanding the different types of currency pairs. This article discusses the main types of currency pairs, offering insights beneficial for both beginner and advanced traders.
What are the main types of currency pairs?
In Forex trading, currency pair is one of the most basic concepts, representing the exchange rate between two different currencies. A pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency. For instance, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro is the base currency, and the US dollar is the quote currency. Traders in the Forex market buy one currency while simultaneously selling another, aiming to profit from changes in the currency's value.
| Category | Example Pairs | Characteristics | Average Daily Volume (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
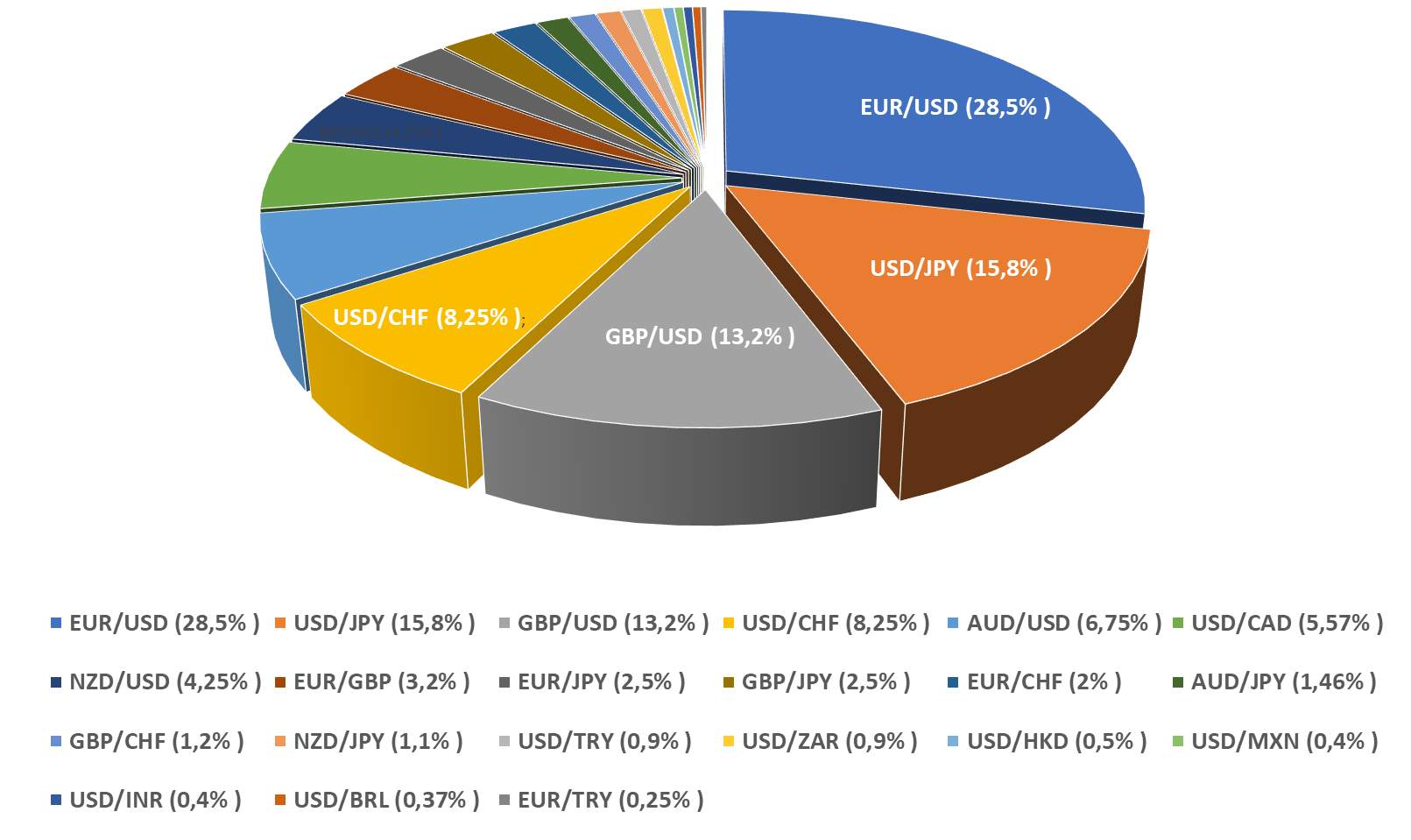
Major | EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, USD/CAD, AUD/USD, NZD/USD | High liquidity, tight spreads, low volatility | EUR/USD: $1.1 trillion; USD/JPY: $900 billion |
Minor | EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD, GBP/JPY | Moderate liquidity, wider spreads than majors | EUR/GBP: $300 billion; AUD/NZD: $200 billion |
Exotic | USD/TRY, USD/ZAR, EUR/TRY | Low liquidity, high volatility, wider spreads | USD/TRY: $50 billion; USD/ZAR: $40 billion |
Major currency pairs
Major currency pairs feature the most widely traded currencies in the Forex market. These pairs are characterized by their high liquidity and tight spreads, making them highly attractive for traders. The primary examples include:
EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar): This is the most traded currency pair, accounting for approximately 24% of daily Forex trading volume. Its popularity stems from the economic stability of the Eurozone and the United States.
USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen): Known for its liquidity and tight spreads, this pair is heavily influenced by the economic policies of the US Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan, as well as geopolitical events in the Asia-Pacific region.
GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar): Commonly referred to as "Cable," this pair is known for its volatility, influenced by economic data and political developments in the UK and the US.
USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc): Often considered a safe haven pair, it is influenced by the stability of the Swiss economy and the policies of the Swiss National Bank.
USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar): This pair is often referred to as the "Loonie" and is heavily influenced by the price of crude oil, as Canada is one of the world's largest oil producers. Economic data from both the US and Canada, as well as trade policies, play significant roles in its movement.
AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar): Known as the "Aussie," this pair is influenced by commodity prices, particularly gold and iron ore, which are major exports of Australia. It is also affected by the interest rate differentials between the Reserve Bank of Australia and the US Federal Reserve.
NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar/US Dollar): Often called the "Kiwi," this pair is driven by the performance of the New Zealand economy, agricultural exports, and interest rate policies of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand. Global risk sentiment and commodity prices also impact its movements.
Key characteristics of major currency pairs:
High liquidity: Major pairs are highly liquid, meaning they can be bought and sold in large quantities without significantly affecting the exchange rate.
Tight spreads: Due to their high trading volume, these pairs have tight bid-ask spreads, reducing trading costs.
Economic and geopolitical influence: These pairs are significantly impacted by economic indicators (such as GDP, employment rates, and inflation) and geopolitical events.
Political events influencing major pairs:
Elections: National elections can lead to significant currency fluctuations due to changes in government policies.
Trade agreements: Announcements or changes in trade agreements can impact currencies by affecting trade balances and economic outlooks.
Central bank policies: Decisions on interest rates and monetary policies by central banks like the Federal Reserve, ECB, BoJ, RBA and SNB.
Geopolitical tensions: Significant events and geopolitical conflicts can cause market volatility.
Minor currency pairs
Minor currency pairs (cross-currency pairs), do not include the US dollar but consist of other major currencies. These pairs provide additional trading opportunities and can offer unique advantages and challenges. The most liquid cross pairs at the moment are considered:
EUR/GBP (Euro/British Pound): This pair is influenced by the economic relationship between the Eurozone and the UK, as well as political events such as Brexit.
AUD/NZD (Australian Dollar/New Zealand Dollar): Reflecting the close economic ties between Australia and New Zealand, this pair is impacted by commodity prices and regional economic data.
GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen): Known for its volatility, this pair is influenced by economic indicators from the UK and Japan, as well as broader market risk sentiment.
Key characteristics:
Moderate liquidity: Minor pairs have lower trading volumes compared to major pairs but still offer substantial liquidity.
Wider spreads: Due to lower liquidity, minor pairs typically have wider bid-ask spreads, leading to higher trading costs.
Economic and political influence: These pairs are influenced by economic data, central bank policies, and political events from the involved countries.
Political events influencing minor pairs:
Regional elections: Elections in the countries involved can cause significant currency fluctuations.
Economic policies: Changes in economic policies or trade relations between the countries involved.
Geopolitical events: Regional geopolitical developments and trade agreements.
Exotic currency pairs
Exotic currency pairs consist of major currency paired with a currency from an emerging or smaller economy. Examples include USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira) and EUR/TRY (Euro/Turkish Lira). These pairs are characterized by their lower liquidity and higher volatility, which presents both higher risks and potential rewards for traders.
Key characteristics:
Low liquidity: Exotic pairs have significantly lower trading volumes compared to major and minor pairs, leading to less favorable trading conditions.
High volatility: Due to their lower liquidity, exotic pairs can exhibit significant price swings, which can be both an opportunity and a risk.
Economic and political influence: These pairs are highly influenced by the economic conditions and political stability of the emerging market involved.
Political events influencing exotic pairs:
Political instability: Changes in government, political unrest, or instability in the emerging market can cause significant currency fluctuations.
Economic reforms: Structural economic reforms or changes in monetary policy in the emerging market can impact the currency pair.
Geopolitical tensions: Regional conflicts or tensions can lead to increased volatility in exotic currency pairs.
How to choose a type of currency pair?
Choosing the right type of currency pair to trade depends on several factors, including your trading goals, risk tolerance, experience level, and the market conditions. Here are some key considerations and steps to help choose a type of currency pair:
Assess your experience level - for beginners it’s often recommended to start with major currency pairs (like EUR/USD, USD/JPY) due to their high liquidity and lower spreads. Experienced traders may venture into minor or exotic pairs to capitalize on higher volatility and potentially larger price movements.
Analyze market conditions. Major pairs are generally less volatile and are influenced by the economic stability of the countries involved. Consider how political events may impact currency pairs, especially exotics which can be highly volatile during political instability.
Consider liquidity and spread. High liquidity pairs (majors) are easier to trade and typically have tighter spreads. Lower spreads reduce trading costs, which is crucial for high-frequency traders.
Evaluate economic indicators. Currencies from countries with higher interest rates often attract more investors, affecting their value. Strong economic performance usually strengthens a country’s currency. High inflation can weaken a currency.
Use technical and fundamental analysis.Look for currency pairs that exhibit clear trends or patterns that you are comfortable trading. Choose pairs based on underlying economic fundamentals and news events.
How to trade currency pairs: practical steps
Choose a reputable Forex broker: It is essential to ensure that the broker is well-regulated, offers competitive spreads, reliable trade execution, and robust customer support.
Below is a table of top-5 Forex brokers according to Traders Union
| Currency pairs | Min. deposit, $ | Max. leverage | Min Spread EUR/USD, pips | Max Spread EUR/USD, pips | Min Spread GBP/USD, pips | MAX Spread GBP/USD, pips | Open account | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 100 | 1:300 | 0,5 | 0,9 | 0,5 | 1,0 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 90 | No | 1:500 | 0,5 | 1,5 | 0,4 | 1,4 | Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
|
| 68 | No | 1:200 | 0,1 | 0,5 | 0,1 | 0,5 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
|
| 80 | 100 | 1:50 | 0,7 | 1,2 | 0,9 | 1,4 | Study review | |
| 100 | No | 1:30 | 0,2 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 1,5 | Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open a trading account: Traders should select a trading platform and register for an account to gain access to the Forex market.
Develop a trading strategy: Creating a detailed plan, including entry and exit points, risk management, and preferred currency pairs, is crucial for consistent trading.
Use demo accounts for practice: Utilizing demo accounts allows traders to simulate trading without financial risk, helping to refine strategies and build confidence.
Implement risk management techniques: Employing tools like stop-loss orders and appropriate position sizing can help manage potential losses and protect capital.
Monitor and analyze market trends: Staying informed about economic indicators, political events, and market news is vital for making well-informed trading decisions.
Understanding the economic and geopolitical factors that influence currency pairs
As an experienced Forex trader, I stress the importance of understanding the unique economic and geopolitical factors that influence currency pairs. Traders must focus on regulatory compliance and select reputable brokers to ensure a secure trading environment. Personally, practicing with demo accounts to develop effective strategies and build confidence has been a game-changer for me. I also advise traders to stay updated on global economic events and political developments, as these can significantly impact currency values. Also remember that diversifying your portfolio and using risk management techniques are crucial to mitigating potential losses and maximizing trading success.
Finally, when selecting a currency pair, traders should consider factors such as economic stability, political environment, market volatility, and trading volume.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of currency pairs is foundational for successful Forex trading. This article explored the characteristics and trading dynamics of major, minor, and exotic currency pairs, which are central to the Forex market. Major pairs, like EUR/USD and USD/JPY, offer high liquidity and tight spreads, making them ideal for most traders. Minor pairs, such as EUR/GBP and AUD/NZD, provide diversification but come with wider spreads. Exotic pairs, like USD/TRY, present high-risk, high-reward opportunities due to their volatility and low liquidity. Mastering these categories allows traders to navigate the Forex market with greater confidence and precision.
FAQs
What is the most traded currency pair?
The EUR/USD pair is the most traded currency pair, accounting for about 24% of daily Forex trading volume.
Why are major currency pairs recommended for beginners?
Major pairs are recommended due to their high liquidity and lower volatility, making them more stable and less risky for beginners.
What are exotic currency pairs?
Exotic pairs involve one major currency and one from an emerging or smaller economy, offering high-risk, high-reward opportunities.
How can traders manage risks in Forex trading?
Traders can manage risks by using stop-loss orders, limiting leverage, and staying informed about market news and economic indicators.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Parshwa is a content expert and finance professional possessing deep knowledge of stock and options trading, technical and fundamental analysis, and equity research. As a Chartered Accountant Finalist, Parshwa also has expertise in Forex, crypto trading, and personal taxation. His experience is showcased by a prolific body of over 100 articles on Forex, crypto, equity, and personal finance, alongside personalized advisory roles in tax consultation.
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Risk management is a risk management model that involves controlling potential losses while maximizing profits. The main risk management tools are stop loss, take profit, calculation of position volume taking into account leverage and pip value.
Risk management in Forex involves strategies and techniques used by traders to minimize potential losses while trading currencies, such as setting stop-loss orders and position sizing, to protect their capital from adverse market movements.
Diversification is an investment strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce overall risk.
Fundamental analysis is a method or tool that investors use that seeks to determine the intrinsic value of a security by examining economic and financial factors. It considers macroeconomic factors such as the state of the economy and industry conditions.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that relies on cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology.






























































































































