How to Read Forex Charts: A Beginner's Guide
Chart reading involves the ability to extract from a sequence of price bars the story of successes and defeats in the battle between buyers and sellers. To do this:
-
study chart patterns and candlestick patterns;
-
study indicators, with a preference for volume indicators;
-
research market psychology.
Ultimately, you should gain an understanding of how the balance of supply and demand is shifting and who is currently losing money: buyers or sellers.
Understanding Forex charts is a critical element for successful currency trading. This tutorial for beginners aims to equip you with the fundamental skills required to interpret these charts effectively.
We will explore the fundamentals of reading trading charts, applying technical analysis, and utilizing various indicators. This guide is designed to simplify complex concepts, turning beginner traders into knowledgeable market participants.
-
How do I learn to read Forex charts?
Start by familiarizing yourself with the different chart types, such as bar, candlestick, and line charts. Then, study key components like price and volume movements, trends, and timeframes, and practice interpreting these elements through online resources, trading courses, or Forex simulators to gain hands-on experience.
How do you read a trading chart?
Reading a trading chart is akin to understanding a unique language spoken by the currency markets. It begins with recognizing the types of charts available and their distinct features.
Forex charts typically come in three forms:
-
Bar charts are simple yet informative, representing the opening, high, low, and closing prices (OHLC) of a currency pair within a specific timeframe.
-
Candlestick charts, originating from Japan, offer a more detailed view, with each 'candle' depicting the same OHLC information but in a visually intuitive manner.
-
Professional footprint charts, commonly used in futures markets, provide an even deeper analysis, showing detailed price and volume data at each price point.
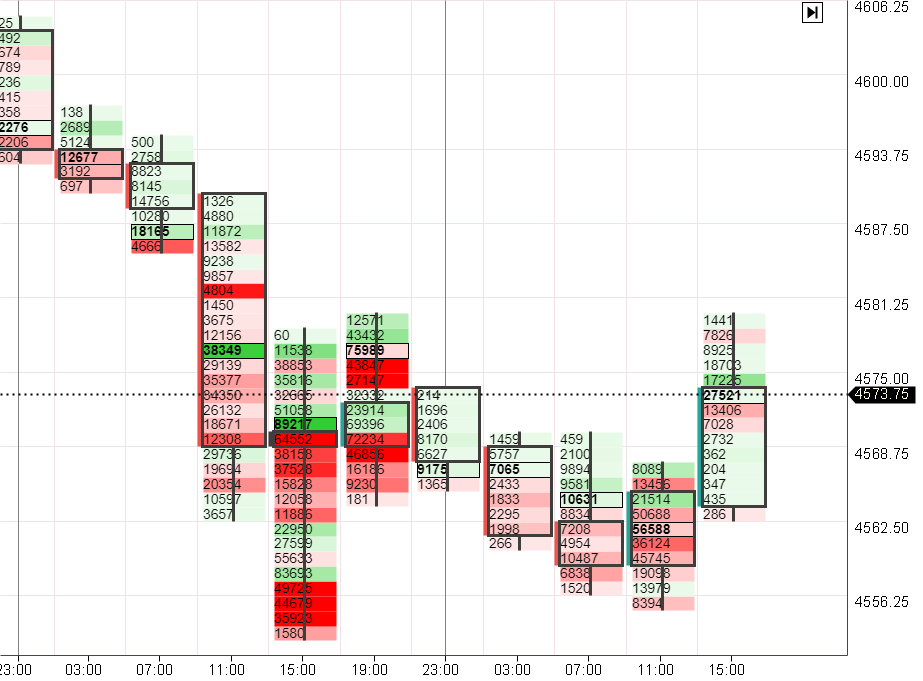
Footprints allow you to "see the contents" of classic candlestick charts
Key elements such as the OHLC are crucial in understanding market dynamics. The 'Open' denotes the price at the beginning of the trading period, 'High' indicates the highest price reached, 'Low' is the lowest price, and 'Close' is the price at the end of the period. This data, combined with the volume indicator, which shows the trading activity during a period, gives traders insights into market sentiment.
Timeframes are another essential component. These charts can range from very short (like 1-minute charts) to much longer (like daily, weekly, or monthly charts). Selecting the right timeframe depends on a trader's strategy, whether they are a day trader, swing trader, or long-term investor.
In addition to understanding the structure of charts, recognizing trends is vital. Trends in Forex charts are generally categorized into three types:
-
Uptrend - where the market consistently creates higher highs and higher lows
-
Downtrend - characterized by lower highs and lower lows
-
Sideways trend - where the market is relatively flat, indicating indecision among traders
Understanding these trends is critical as they provide a snapshot of market sentiment and potential future price movements. This knowledge, combined with the chart types and key elements mentioned above, forms the foundation of reading and interpreting Forex charts.
Using technical analysis to read Forex charts
Technical analysis is an indispensable tool for interpreting Forex charts. This method relies on historical price data and statistical trends to forecast likely future market behavior. It helps traders identify potential turning points in the market, empowering them with the foresight needed for strategic trading decisions.
Key concepts of technical analysis include:
-
Trendlines are straight lines drawn on charts that connect a series of prices. They help visualize and define the direction of a trend. An upward trendline connects the lows in an uptrend, while a downward trendline connects the highs in a downtrend. These trendlines can act as indicators for potential market reversals.
-
Support and resistance levels are another critical aspect. 'Support' refers to a price level where a downtrend can be expected to pause due to a concentration of demand. In contrast, 'Resistance' is a price level where a trend can stall temporarily due to a concentration of selling interest. Understanding these levels helps traders anticipate where prices might reverse or continue their trend.
-
Candlestick patterns are specific formations created by the movement of prices on a candlestick chart, which can signal potential market movements. Some common patterns include 'Doji,' 'Hammer,' and 'Engulfing' patterns, each indicating different market sentiments and potential price movements.
Using indicators to read Forex charts
Indicators are mathematical calculations based on a currency pair's rate, volume, or open interest and are used to forecast future price movements. These tools are essential for traders as they can provide insights into market trends, momentum, volatility, and market strength.
The number of classic indicators of technical analysis is measured in many dozens. Among the most popular are:
-
Moving Averages smooth out price data to create a single flowing line, making it easier to identify the direction of the trend.
-
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions in the price of a currency pair.
-
The MACD is used to spot changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a currency's price.
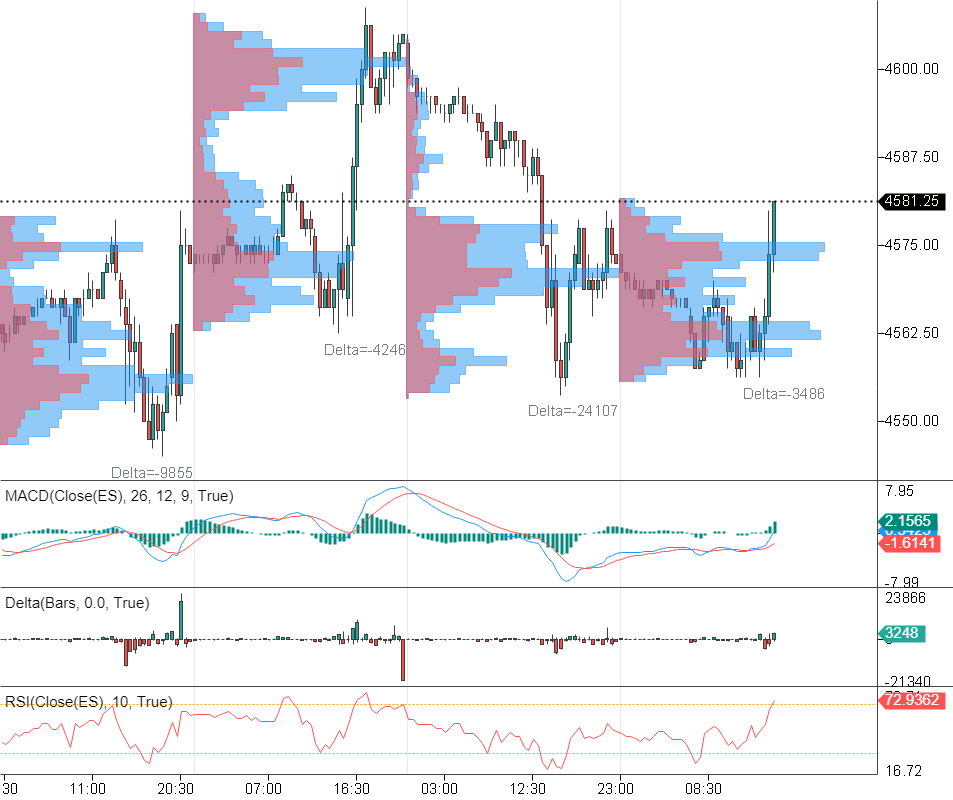
The following indicators have been added to the chart: MACD, RSI, Delta, Volume Profile
Modern advanced indicators, such as Delta and Market Profile indicators, offer more advanced insights. Delta refers to the difference in the volume of trades executed at bid and ask prices and can provide an understanding of market direction. Profile indicators, like Market Profile or Volume Profile, provide a visual representation of trading activity over a specific time period at certain price levels, highlighting areas of high and low trading activity.
Read our guide on How To Use Technical Indicators To Analyze Forex Charts to learn valuable tips on how to use indicators.
Best Forex brokers


Tips for reading the Forex charts
Mastering the art of reading Forex charts is a blend of science and intuition, demanding both technical skills and a keen market sense. Here are some invaluable tips for beginners to navigate through the intricate world of Forex charts:
-
Use multiple timeframes: Analyzing a currency pair across different timeframes offers a more comprehensive view of the market. For example, while a daily chart may show a long-term trend, a 1-hour chart can provide insights into the intraday market dynamics. This multi-timeframe approach helps in making more balanced and informed trading decisions.
-
Analyze market reactions to news: Forex markets are highly sensitive to global events and economic news. Understanding how prices react to positive or negative news can offer clues about market sentiment and potential future movements. This analysis can help traders anticipate volatile market conditions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
-
Backtest your strategies: Before applying any trading strategy in live markets, it’s crucial to backtest it using historical data. This practice helps in understanding the effectiveness of the strategy and in identifying any potential flaws or improvements.
-
Use simulators for training: Practicing with Forex simulators is a great way to gain experience without risking real money. Simulators offer a realistic trading environment, enabling beginners to hone their chart reading skills and test trading strategies in real-time market conditions.
-
Stay informed and keep learning: The Forex market is dynamic, and continuous learning is key. Stay updated with the latest market trends, economic news, and technical analysis methods. Regularly revisiting and refining your trading strategies based on new knowledge and market conditions is crucial for long-term success.
You’d do well to remember that there is never a 100% guarantee when Forex trading, and you must always keep the risks in mind. With that said, our list of tips should serve as a good starting point and increase the likelihood of your success in Forex markets.
Summary
Reading Forex charts is a fundamental skill for any currency trader, forming the backbone of successful trading strategies. While it may appear daunting at first, with practice and the right approach, it becomes an invaluable tool in navigating the Forex market.
This guide has walked you through the essentials of understanding Forex charts, from the basics of chart types and trends to the complexities of technical analysis and indicators. By applying the tips provided, you can enhance your ability to read and interpret these charts, paving the way for more informed and strategic trading decisions.
Glossary for novice traders
-
1
Broker
A broker is a legal entity or individual that performs as an intermediary when making trades in the financial markets. Private investors cannot trade without a broker, since only brokers can execute trades on the exchanges.
-
2
Trading
Trading involves the act of buying and selling financial assets like stocks, currencies, or commodities with the intention of profiting from market price fluctuations. Traders employ various strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management practices to make informed decisions and optimize their chances of success in the financial markets.
-
3
Volatility
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.
-
4
Index
Index in trading is the measure of the performance of a group of stocks, which can include the assets and securities in it.
-
5
CFD
CFD is a contract between an investor/trader and seller that demonstrates that the trader will need to pay the price difference between the current value of the asset and its value at the time of contract to the seller.
Team that worked on the article
Vuk stands at the forefront of financial journalism, blending over six years of crypto investing experience with profound insights gained from navigating two bull/bear cycles. A dedicated content writer, Vuk has contributed to a myriad of publications and projects. His journey from an English language graduate to a sought-after voice in finance reflects his passion for demystifying complex financial concepts, making him a helpful guide for both newcomers and seasoned investors.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).