How To Use Market Structure In Forex Trading | Traders Union



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
How to use market structure in Forex trading:
Identify the trend.
Recognize key levels.
Use swing points.
Look for Breakouts & Retests.
Apply confluence.
Adjust stop-loss & take-profit.
For beginners in trading, understanding Forex market structures is a fundamental step toward making informed decisions. This guide provides an in-depth look at market structures, explaining key concepts, their role in price action, and how traders can leverage them for financial success. We'll explore the characteristics of different market conditions, how they operate, and strategies traders can use to capitalize on these trends. So, get comfortable and immerse yourself in the essentials of Forex market structures!

What is market structure in Forex?
Forex market structure is the framework that governs how buyers and sellers interact in the global currency market. It helps traders understand price movements, market trends, and overall sentiment. Instead of being centralized like stock exchanges, Forex operates through a network of banks, financial institutions, and individual traders, each playing a role in shaping price action.
At its core, market structure is driven by key participants: major institutions, retail traders, and liquidity providers. It also reflects how currency pairs behave in terms of trends, volume, and volatility. By analyzing these elements, traders can identify potential entry and exit points, anticipate market shifts, and make well-informed trading decisions.
How to use market structure in Forex trading
Identify the trend – determine if the market is in an uptrend (higher highs, higher lows), downtrend (lower highs, lower lows), or range-bound.
Recognize key levels – mark support and resistance zones where price reacts frequently.
Use swing points – analyze recent swing highs and lows to understand price direction and momentum.
Look for breakouts & retests – confirm trend continuation or reversal when price breaks key levels and retests them.
Apply confluence – combine market structure with indicators like moving averages or Fibonacci levels for stronger signals.
Adjust stop-loss & take-profit – place stops beyond key structure levels to reduce risk and maximize reward.
Understanding market structure helps traders make informed decisions, improve entry points, and manage risk effectively.
Types of Forex market structures
Understanding market structures is a crucial advantage in the ever-changing world of Forex trading. Market conditions influence price movements and trading strategies, making it essential to recognize the three primary market structures: bullish, bearish, and sideways trends. Let’s break them down and analyze their impact on trading strategies.
Bullish market structure
A bullish market structure is characterized by an upward trend, where buyers dominate the market, pushing prices higher. Traders in a bullish market anticipate future price increases, creating a cycle of optimism that sustains the uptrend.
A bullish trend consists of higher highs (HH) and higher lows (HL), signifying continuous upward momentum. The trend remains intact until the price forms a lower low (LL), signaling a potential reversal.
Example of a bullish structure
The daily chart of ETSY stock demonstrates an uptrend with a series of higher highs and higher lows. However, a green box highlights a point where the price reaches an equal low. For the uptrend to persist, the price must break above the 250 resistance level.
Why traders favor bullish markets:
Increased buying pressure and strong investor confidence;
Positive economic news fuels further price appreciation;
High trading volumes support sustained upward movement.
A bullish market offers lucrative trading opportunities, encouraging investors to take risks and capitalize on growth potential. As the saying goes, when the bulls are charging, it's time to ride the momentum!
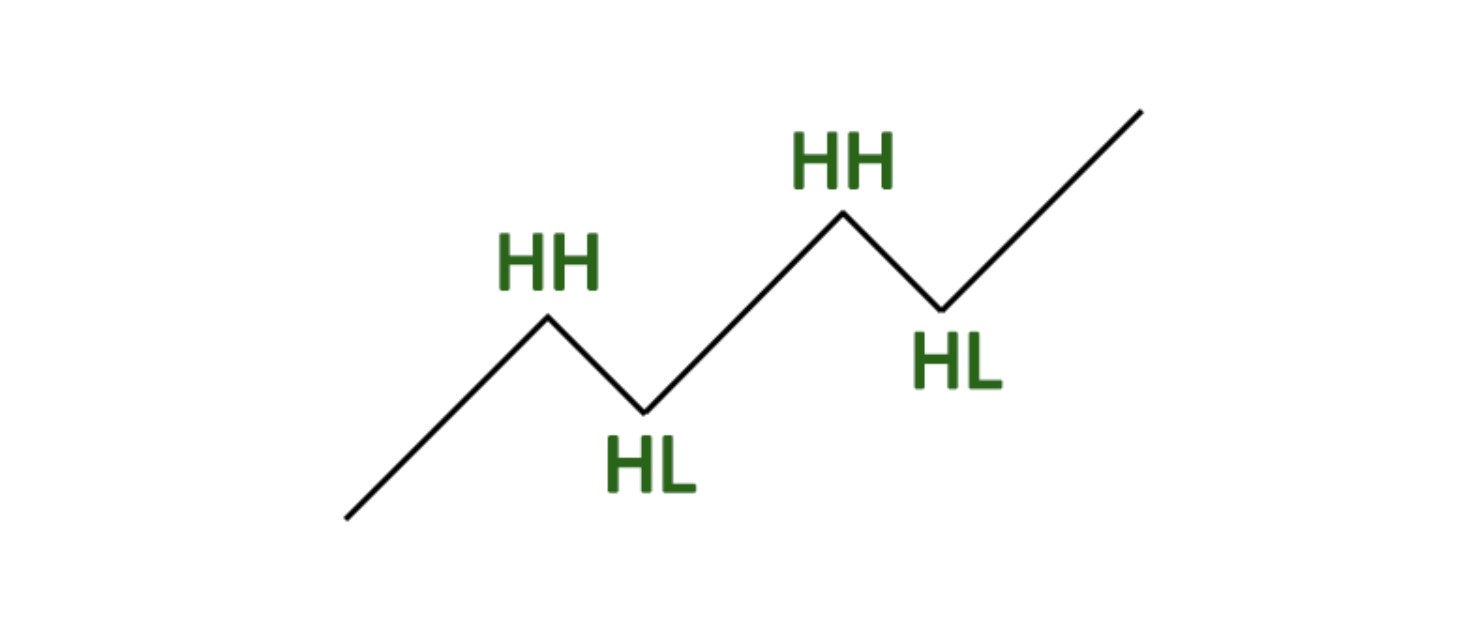
Bearish market structure
A bearish market structure represents a sustained downtrend where sellers overpower buyers, driving prices lower. This market condition is identified by lower highs (LH) and lower lows (LL), reflecting declining investor confidence and strong selling pressure.
Key features of a bearish market structure:
Lower highs: the price fails to reach previous peaks, confirming a weakening market.
Lower lows: continuous drops in price indicate downward momentum.
Breakouts: support levels are frequently broken, triggering further selling.
Momentum: bearish trends often accelerate as traders rush to exit positions.
Volume: trading volume spikes as selling pressure intensifies.
Example of a bearish structure
A TESLA stock chart illustrates a classic bearish trend, with progressively lower highs and lower lows, showing a strong downward push.
In bearish markets, traders often shift to short-selling strategies or seek safe-haven assets to hedge against losses. Identifying a bearish structure early can help traders mitigate risks and adjust their strategies accordingly.
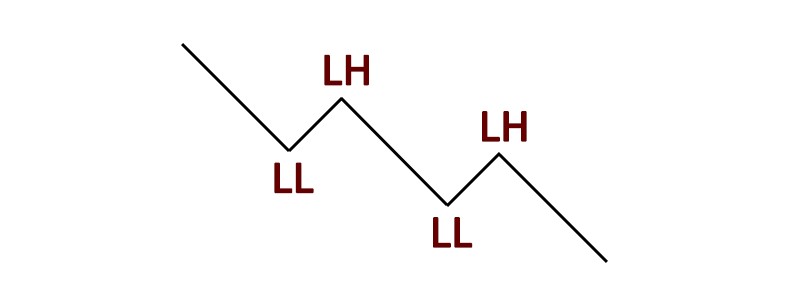
Sideways market structure (Consolidation)
A sideways market, also known as a choppy or range-bound market, occurs when prices move within a restricted range without significant upward or downward trends. This structure is marked by indecisiveness among traders, leading to low volatility and uncertain price action.
Characteristics of a sideways market:
Price fluctuates within a narrow range, forming equal highs (EH) and equal lows (EL).
Trading volume is relatively low, reflecting hesitation among market participants.
Price action appears choppy, making it difficult to establish strong trends.
The market tests support and resistance levels multiple times before eventually breaking out.
Example of a sideways market
A sideways price movement can be seen when assets consolidate before a significant breakout. While these markets lack clear direction, they often precede strong price movements, providing breakout opportunities for traders.
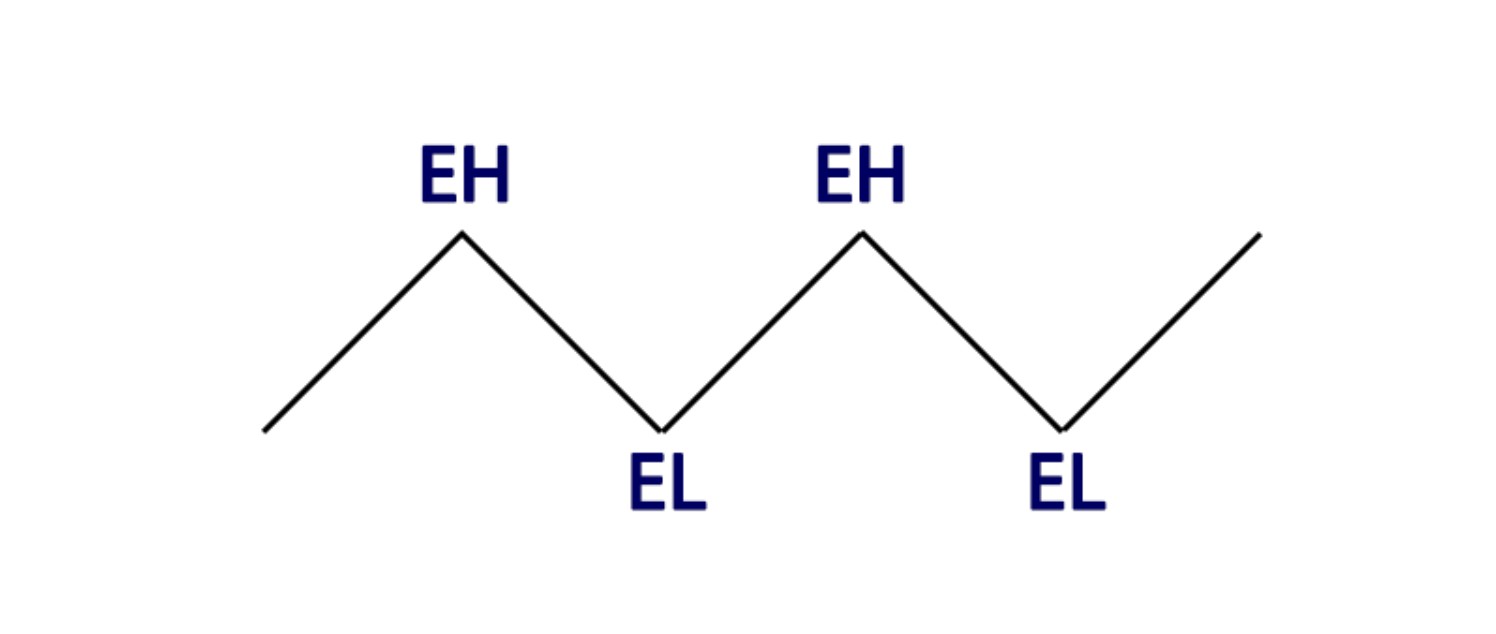
Recognizing and understanding bullish, bearish, and sideways market structures is crucial for any Forex trader. Each market type presents different challenges and opportunities, requiring tailored strategies to maximize potential gains. Whether capitalizing on bullish momentum, navigating bearish declines, or preparing for breakout moves in a sideways market, a deep understanding of market structures can significantly enhance trading success.
How to identify market structure in Forex
Recognizing market structure in Forex involves analyzing price movements and using various tools to determine trends and patterns. Here are some key methods:
Analyze price action. Observing candlestick patterns and overall price behavior helps in identifying the prevailing market structure.
Identify key levels. Support and resistance zones indicate where price movements may reverse or continue, shaping the market structure.
Assess market trends. Determining whether the market is trending upward, downward, or sideways provides valuable insight into structure.
Utilize technical indicators. Tools like moving averages, RSI, and MACD can confirm trends and structural shifts.
Monitor volatility. High volatility often signals market structure changes, offering opportunities for strategic adjustments.
By combining these techniques, traders can gain a clearer understanding of market conditions and make informed trading decisions.
Examples of market structure charts
A 10-minute chart of the S&P 500 reveals its micro-structure, highlighting how 4-hour support levels reinforce the ongoing uptrend. These key levels act as strong price zones where buyers maintain control.
By analyzing the higher highs (HH) and higher lows (HL) of a bullish trend, traders can pinpoint potential entry points for a long position. Price retracements often occur, either testing the previous breakout level or revisiting the impulse move that led to a new high, providing strategic opportunities for continuation trades.
The daily chart of SPY clearly shows the presence of higher highs and higher lows.
How to improve your use of Forex market structure charts
Enhancing your ability to read Forex market structure charts can improve your trading decisions. Here are some practical strategies to refine your approach:
1. Use multiple time frames
Analyzing different time frames, such as daily, hourly, and 15-minute charts, gives a broader view of trends and market structure. Higher time frames help spot overall trends, while lower time frames offer precise entry and exit points. For example, a trader may notice a bullish trend on the daily chart and use the hourly chart to time their trade.
2. Compare different currency pairs
Looking at multiple currency pairs helps identify patterns, correlations, and opportunities. Some pairs move in sync, while others move in opposite directions. Comparing different markets allows traders to choose the best setup based on momentum and trend strength.
3. Use technical indicators wisely
Indicators like moving averages, RSI, and MACD help spot trends, momentum shifts, and potential reversals. These tools should complement market structure analysis rather than replace it. A trader might use a 50-day moving average to gauge the trend and RSI to confirm whether an asset is overbought or oversold.
4. Practice on demo accounts
Trading with a demo account allows traders to test strategies and understand market behavior without risking real money. Practicing in real-time conditions helps refine decision-making and build confidence before trading with actual funds.
5. Identify role reversals
When a key support level breaks, it often turns into resistance, and vice versa. Recognizing these shifts helps traders anticipate future price movements. For example, if a price falls below a strong support level and then retests it, that level may now act as resistance, creating a potential selling opportunity.
6. Consider the bigger picture
Market structure should always be viewed within the broader context of price action and overall conditions. Economic data, central bank policies, and geopolitical events can impact price movements. Even strong technical setups can fail if external factors contradict them.
7. Wait for confirmation
Rushing into trades without confirmation can lead to losses. Waiting for price action, volume changes, or additional signals before entering a trade increases the chances of success. For instance, if a trader spots a reversal pattern, they might wait for a strong breakout or a close above a key level before taking action.
Why is market structure essential for traders?
Top traders emphasize that understanding market structure is fundamental to mastering the Forex market. It serves as the foundation for analyzing price behavior and making strategic decisions.
By studying trends and patterns, traders can identify profitable opportunities, avoid unnecessary risks, and refine their trading approach. Ignoring market structure often leads to misjudged trades and significant losses.
A strong grasp of market structure allows traders to:
Spot key price levels, such as support, resistance, and breakout zones.
Recognize trend shifts and adjust strategies accordingly.
Manage risk effectively by identifying areas of high volatility or low liquidity.
For instance, if a trader sees strong buying pressure, they might enter a long position, anticipating an upward move. Conversely, in a seller-dominated market, they could opt for a short position to capitalize on a downtrend.
Understanding market structure is not just useful — it’s critical for any trader looking to navigate the Forex market with confidence and precision.
When price briefly breaks a key level but instantly snaps back with heavy volume, that’s smart money entering
Forget textbook strategies — if you really want an edge, start thinking like the big players. Market makers love tricking retail traders with liquidity traps, pushing prices just past obvious support and resistance levels to trigger stop-losses before reversing hard. The best way to spot these traps? Watch for fake breakouts with sharp wicks, especially during volatile sessions. When price briefly breaks a key level but instantly snaps back with heavy volume, that’s smart money entering. Instead of reacting emotionally, wait for confirmation — a strong reversal candle or a quick retest — before jumping in.
Another game-changer? Timing your trades based on liquidity cycles. The market isn’t random — it moves with the flow of institutional orders. The most explosive price action happens when the London and New York sessions overlap, roughly between 7-10 AM GMT and 1-4 PM GMT. That’s when big players step in, creating momentum. Instead of overtrading, focus on these high-impact windows. You’ll avoid slow, frustrating price action and position yourself alongside serious money, not against it.
Conclusion
Grasping the various market structures within the Forex landscape is essential for both traders and investors. The Forex market is primarily divided into four key structures: the spot market, forward market, futures market, and options market. Each of these segments functions differently and caters to specific trading strategies.
Additionally, traders need to recognize the three predominant market trends: bullish, bearish, and sideways structures. A bullish market structure reflects a consistent increase in asset prices, indicating strong buyer momentum. Conversely, a bearish market structure is defined by declining prices, signaling seller dominance.
Meanwhile, a sideways market structure emerges when price movements remain confined within a limited range, lacking clear upward or downward trends. A thorough understanding of these market structures and trends enables traders to execute well-informed strategies, manage risks effectively, and optimize their trading performance in the Forex market.
FAQs
What are the key market structures in Forex?
Forex has four main market structures: the spot market (instant currency trading), forward market (future agreements at a fixed price), futures market (standardized contracts for future delivery), and options market (contracts allowing, but not obligating, a future trade).
What are the four phases of the Forex market?
The market moves through four phases: accumulation, where institutional traders build positions before a price move; markup, when prices rise as buying momentum increases; distribution, where selling pressure grows, signaling a potential reversal; and markdown, when prices decline as sellers take control.
Is learning about Forex market structures beneficial for beginners?
Yes, it helps beginners identify trends, reduce risks, and make informed decisions.
How can someone master Forex market structures?
Study educational materials, practice with demo accounts, analyze price charts, follow experienced traders, and test strategies in simulated trading.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Parshwa is a content expert and finance professional possessing deep knowledge of stock and options trading, technical and fundamental analysis, and equity research. As a Chartered Accountant Finalist, Parshwa also has expertise in Forex, crypto trading, and personal taxation. His experience is showcased by a prolific body of over 100 articles on Forex, crypto, equity, and personal finance, alongside personalized advisory roles in tax consultation.
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is the practice of buying and selling currencies in the global foreign exchange market with the aim of profiting from fluctuations in exchange rates. Traders speculate on whether one currency will rise or fall in value relative to another currency and make trading decisions accordingly. However, beware that trading carries risks, and you can lose your whole capital.
Crypto trading involves the buying and selling of cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other digital assets, with the aim of making a profit from price fluctuations.
A bear market is a period of time in which an investment asset, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities, experiences a decline in price for an extended period of time.
Uptrend is a market condition in which prices are generally rising. Uptrends can be identified by using moving averages, trendlines, and support and resistance levels.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that relies on cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology.






























































































































