How to Use the ICT Trading Strategy



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.

Plus500 - Best Forex broker for 2025 (United States)
Inner Circle Trader (ICT) is a trading strategy that combines advanced technical analysis, market psychology, price action, analysis of large players’ actions, and other types of analysis. Some of the ICT trading concepts are:
KillZone: An area where clusters of numerous retail traders’ stop losses presumably are.
Inducement: Price movement induced by Smart Money to activate stop losses before the beginning of a new trend.
Fair Value Gap (FVG): An imbalance pattern that serves as a signal to enter a position.
Market Structure Shift: An interruption of an established sequence of highs and lows that indicates a potential change of the trend.
Comprehension of the causes of market price movement, based on the motives of institutional players, or the so-called “Smart Money”, can be an advantage and a foundation for decision making. Developed by Michael Huddleston, the ICT methodology helps novice traders better understand how Smart Money drives the market and benefit from this knowledge. The ICT strategy focuses on key aspects, such as liquidity zones, market structure shift, inducement, and optimal trade entry (OTE).
For traders who are beginning their journey in the world financial markets, ICT can become the key to price action logic. In this article, I will introduce you to the basics of ICT trading and give recommendations on how to start using this knowledge in practice. I will try to provide information in the simplest possible way so that beginners can learn ICT step by step and apply it in their trading.
What is ICT trading?
Michael J. Huddleston, known as the Inner Circle Trader, found his niche in the world of trading education thanks to a methodology called ICT trading. Michael’s path in trading started with losses, which prompted him to learn and become more successful. His development was facilitated by Larry Williams’ courses that helped him achieve a streak of 9 consecutive profitable months in the mid-1990s. However, this success was followed by a considerable loss when market conditions changed, which became a valuable lesson for him in terms of risk and strategy.
ICT trading philosophy is deeply rooted in comprehension of market psychology, supply and demand, and price action. Michael emphasizes that to trade Forex successfully, it’s important to analyze the sentiment of institutional participants, or Smart Money. ICT combines various concepts, including the Wyckoff method and market making strategies, in order to teach traders to interpret market tendencies and make informed decisions.
 ICT YouTube channel
ICT YouTube channelHuddleston shares his knowledge through numerous resources, including his YouTube channel with over 1 million subscribers.
Below, I will provide a very short explanation of the mechanics of market price movement to make it easier for you to understand the ICT trading strategy.
ICT trading concepts
Put simply, there are 2 types of traders:
Those who lose. They are the majority. Usually they are enthusiastic retail traders who try to earn quickly and easily, but then get disappointed. With time, their funds decrease.
Those who win. They are the minority. With time, their funds increase. They are often called “Smart Money”.
Profits of the latter depend on losses of the former, as trading is a zero-sum game. This is an important fact that helps understand the causes of price movement when learning the ICT strategy.
Smart Money players’ problem is that large capital makes it difficult for them to open trades. For example, if they place an ХХХL-sized order to buy Bitcoins, stocks, fiat currency, or another asset, the price will immediately rise, which is unfavorable for them. Level by level, all sell limit orders will be gradually removed from the Level II order book. This is why the average price of the whole position may turn out to be much worse than expected.
How to resolve this problem? A smart player buys during a price drop when sellers create sufficient liquidity, i.e., place enough sell orders, making it possible to open a long position.
A special case of this approach is to open a long position using stop losses of other buyers – usually, numerous retail traders. The triggering of stop losses creates a sell order flow that Smart Money participants can use to go long. It means that long positions come from the accounts of many small retail traders over to the accounts of professionals.
Best Forex brokers
| Plus500 | Pepperstone | OANDA | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Min. deposit, $ |
100 | No | No |
|
One click trading |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
ECN |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Scalping |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Currency pairs |
60 | 90 | 68 |
|
Open account |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
How does the ICT trading strategy work?
To understand the process, let’s look at a screenshot from a video by the author of the ICT strategy.
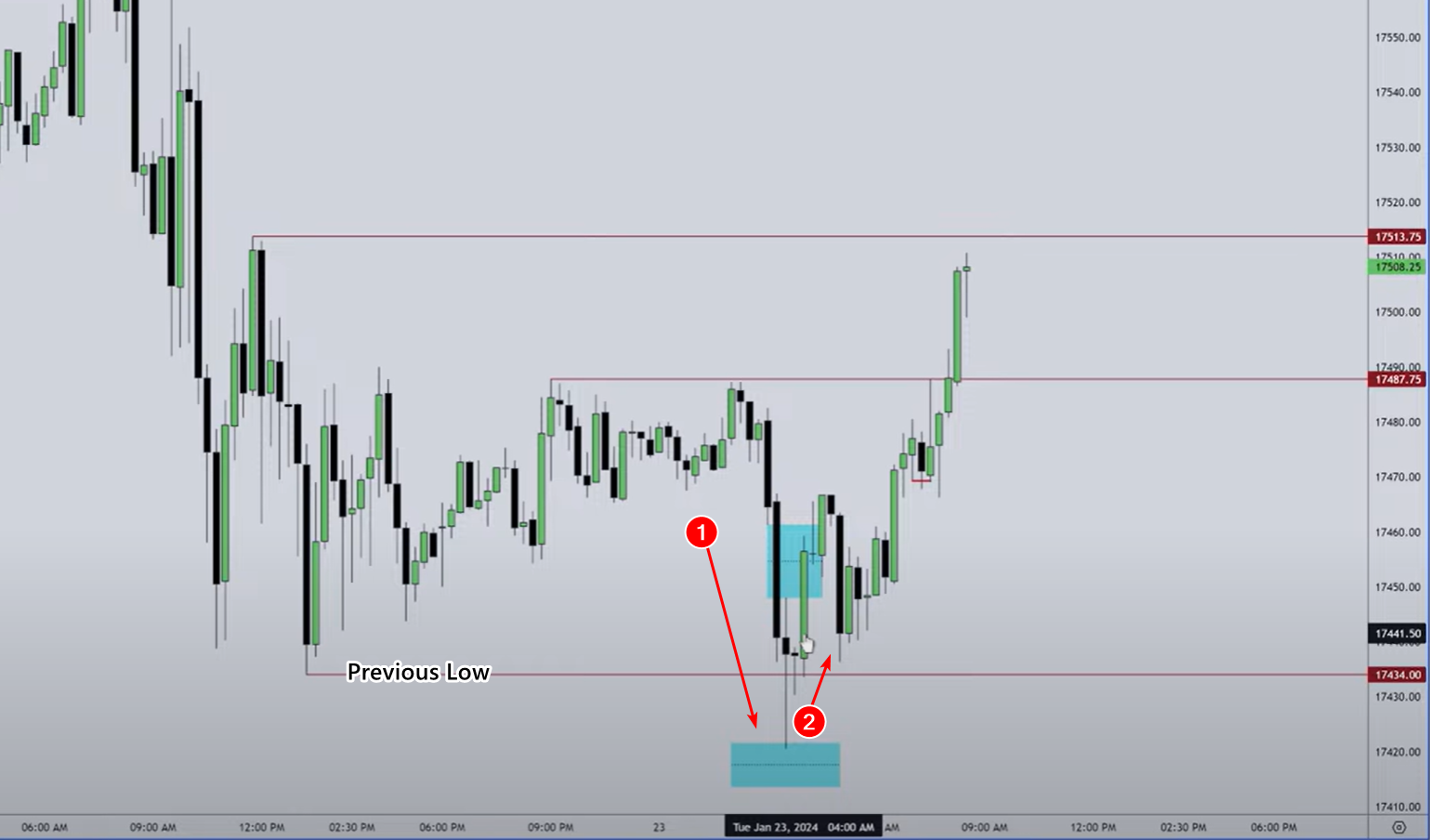 How the ICT trading strategy works
How the ICT trading strategy worksThe numbers show:
(1) – The price fell below the previous local low (Asian session). Buyers’ stop losses were presumably a few ticks below this low.
(2) – The price rose after a large number of retail traders closed (sold) their positions through stop losses. Who bought them? That’s right, Smart Money that benefited from it.
This seems not entirely fair. But imagine you are one of the biggest market participants. Your task is to buy at the lowest possible price and sell at the highest possible price. The first solution is to prompt other (inexperienced) traders to sell on lows and buy on highs.
The upward movement (2) is part of the pattern that provides an opportunity to enter a long trade in harmony with the intentions of Smart Money. As an independent trader, you should not argue with those who can influence the price.
Let’s see how to achieve this.
ICT trading strategy rules
The basic pattern you can use to enter a long trade is the Fair Value Gap (FVG). The screenshot below is from the ICT Trading Strategy pdf document:
 FVG example
FVG exampleThe pattern consists of 3 candles:
The first candle is bearish. It means the price has dropped because smart players need a sell order flow to open their own long positions. The candle can go below a psychological level of round numbers or the preceding low, or form in response to the news. In the ICT trading terminology, this is called inducement.
The second candle is bullish. Together with the first one, they often generate bullish reversal patterns.
The third candle is bullish. Its low does not reach the first candle’s high.
It often resembles the formation of the “Three white soldiers” pattern after a failed bearish breakout. But in fact, the ICT trading strategy can be explained more rationally.The formation of the FVG indicates an advantage of buyers (Smart Money players who have already formed their long positions or are still forming them) over sellers (a large number of retail traders who rushed to sell at the current price, but quickly saw that it was a mistake).
Entering a long trade in harmony with the intentions of Smart Money implies buying when the FVG is tested.
Below, I will illustrate how this works, but first I will list the pros and cons of ICT that must be taken into account when considering examples of trades.
Is ICT good for beginners?
Like any other trading strategy, ICT has its merits and demerits.
- Pros
- Cons
- Trading is based on the changes in supply and demand that drive price movement.
- Trading is performed in harmony with Smart Money participants. ICT aims to interpret their intentions.
- ICT’s author is a popular trader with an informative educational YouTube channel.
- The strategy is described in detail through patterns and events, such as the FVG.
- Complexity. This is not a simple strategy where you trade moving average crossovers. When applying ICT, you have to make your own judgments.
- Like any other strategy, ICT does not guarantee profits and therefore it’s necessary to place stop losses and practice ICT trading on a demo account.
It’s also worth noting that the use of candlestick charts for ICT trading creates additional difficulties. In my opinion, the application of more professional cluster charts with market profiles and volume breakdowns into market buys and market sales adds transparency, makes it easier to understand various situations, and therefore simplifies traders’ work.
An example of opening a buy trade in ICT trading
Let’s consider buying in the EUR futures market. Unlike the decentralized Forex market, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange where EUR futures are traded – their dynamics rather accurately repeat spot EUR/USD rates – allows users to analyze trading volumes in much more detail through footprint charts.
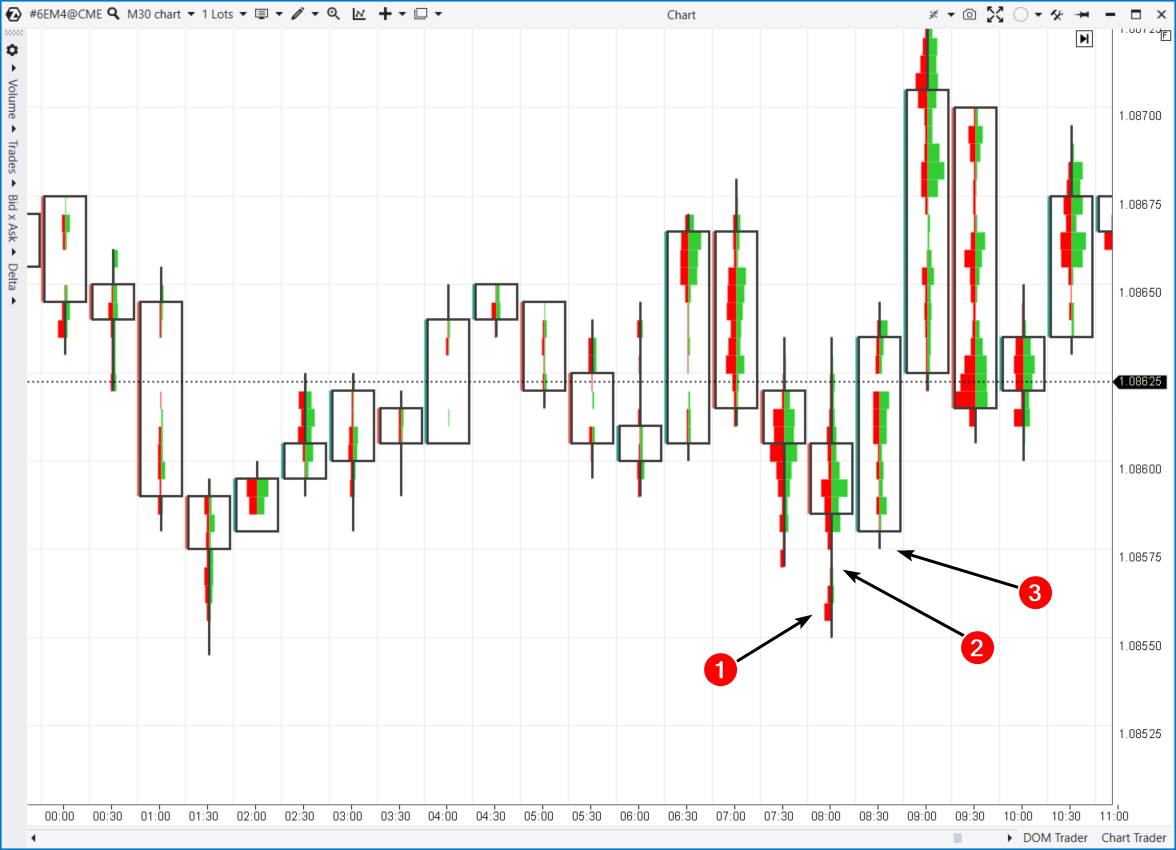 Buying in ICT
Buying in ICTNumbers on the footprint show:(1) – The price drops and the selling pressure increases (note the red clusters) near a low in the Asian session. But despite the selling pressure at the candle’s low, the price closes in the middle. It could mean that Smart Money players are forming long positions by absorbing the sells of retail (usually losing) traders.(2) – The thin profile indicates an imbalance. This is the aforementioned FVG.(3) – The thin profile level is tested, and participants get a chance to enter long positions.
An example of a sell signal in ICT trading
This is an example from the Bitcoin market with data from Binance Futures. The red horizontal line on the chart shows the maximum price on 500 candles, and the indicator below is Delta.
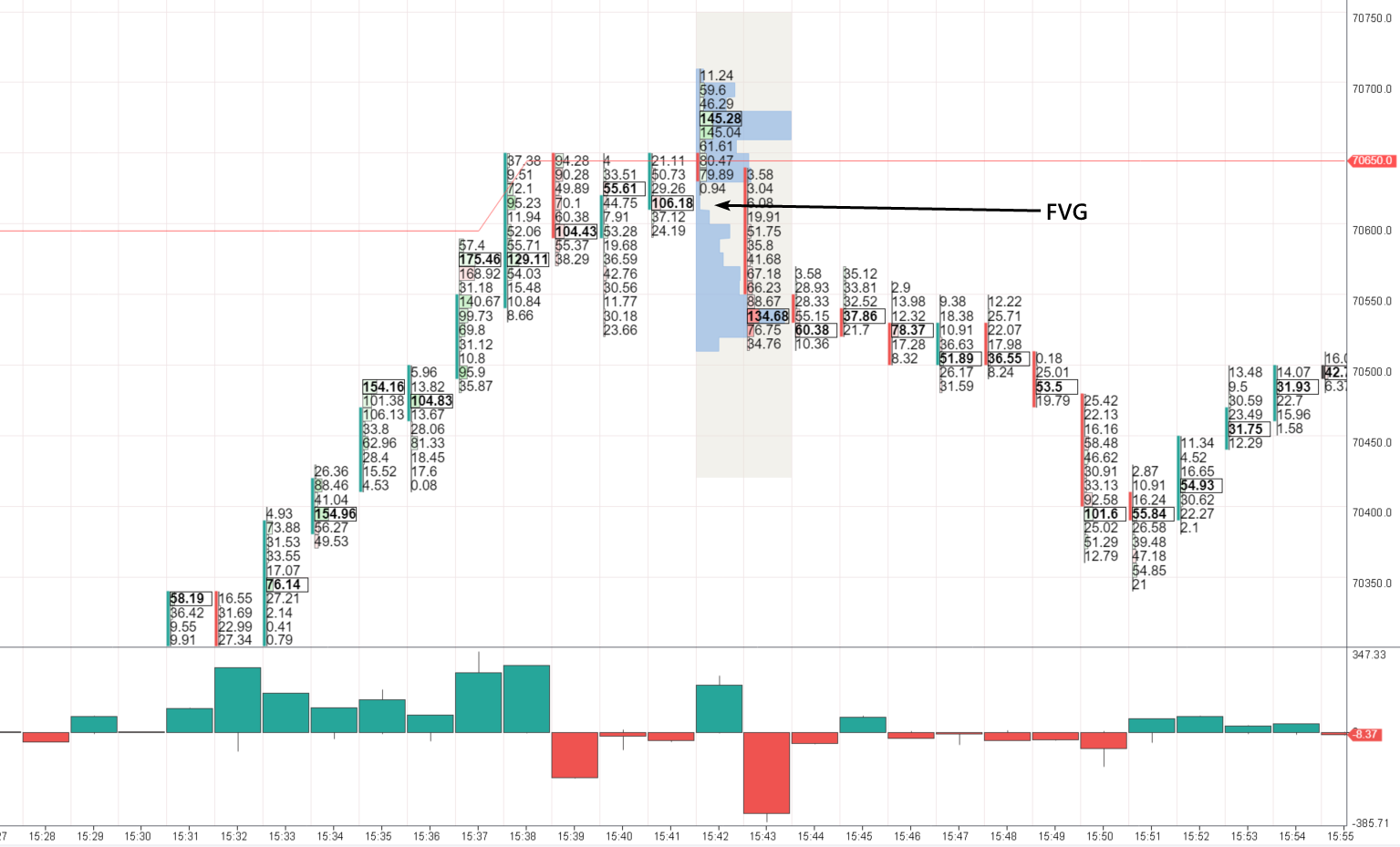 Sell signals in ICT trading
Sell signals in ICT tradingNote that at 15:38, as soon as the Bitcoin price exceeded the highest value on the last 500 candles, a red bar appeared on Delta (at 15:39). This could mean that sellers were responding to a flow of buys.
At 15:42-15:43, there was a Market Structure Shift. You can see it in the efforts of buyers whose trades failed. The efforts are displayed by the green clusters of more than 140 Bitcoins traded at 2 levels. The price went down due to the buys.
Is it counterintuitive? Not if you apply the ICT logic and strategy. Smart Money traders opened short positions at the highest price using other traders’ FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out). The Market Profile indicator displays FVG levels at which short trades can be opened. On the above chart, the FVG level wasn’t actually tested, which should be taken into account.
Which is better: SMC or ICT?
SMC (Smart Money Concept) and ICT (Inner Circle Trader) both aim to decode market movements and predict future price action based on the presumable activity of large institutional players, or “Smart Money”. ICT can be deemed a more extensive approach, as it takes into account a wide range of technical analysis tools, psychological elements, and other components.
Both methods are worth considering and require significant efforts to be mastered. Your final choice will depend on how well you can apply these methods in training mode.
How to start ICT trading?
The pattern consists of 3 candles:
The first candle is bearish. It means the price has dropped because smart players need a sell order flow to open their own long positions. The candle can go below a psychological level of round numbers or the preceding low, or form in response to the news. In the ICT trading terminology, this is called inducement.
The second candle is bullish. Together with the first one, they often generate bullish reversal patterns.
The third candle is bullish. Its low does not reach the first candle’s high.
It often resembles the formation of the “Three white soldiers” pattern after a failed bearish breakout. But in fact, the ICT trading strategy can be explained more rationally.The formation of the FVG indicates an advantage of buyers (Smart Money players who have already formed their long positions or are still forming them) over sellers (a large number of retail traders who rushed to sell at the current price, but quickly saw that it was a mistake).
Entering a long trade in harmony with the intentions of Smart Money implies buying when the FVG is tested.
Below, I will illustrate how this works, but first I will list the pros and cons of ICT that must be taken into account when considering examples of trades.
Expert Opinion
I believe ICT offers some useful insights if applied appropriately.
One strength is its emphasis on order flow analysis. Tracking the placement of blocks of buys and sells on order book footprints, as shown in the article examples, allows you to spot potential areas of liquidity where smart money may look to engage. For day traders, this can provide high-probability trade ideas.
However, ICT may try to do too much too soon for beginners. Concepts like "inducement" and "market structure shifts" risk overcomplicating the approach. These are advanced topics that require a depth of experience to reliably identify.
I would recommend new traders start simply. Paper trade just the basic Fair Value Gap pattern on daily charts of liquid Forex majors like EUR/USD. Look for gaps between 0.75-1.25% of the average true range that get quickly filled. Use a 3:1 reward to risk with stops below the lowest swing low. Take partial profits at the 61.8% retracement.
Concentrate initially on strict algorithms and risk management over multiple trade attempts before progressing to higher time frames or additional concepts.
Mastering any one component of ICT, such as order block analysis, could prove very valuable over the long run. However, a gradual, systematic approach focused on core strategy development will better serve most beginners looking to apply this approach.
Conclusion
The ICT trading strategy is intended to analyze the trading activity of institutional traders and can be profitable when used properly, i.e., if you can interpret market data correctly, adhere to your plan, manage risks, and learn constantly. ICT is applicable in both swing trading and intraday trading by focusing on liquidity levels and using market structure shifts to initiate trades.
FAQs
Why do we need a strategy in trading?
A trading strategy is necessary because it ensures a structured approach to decision making under high volatility and unpredictability of financial markets. It helps traders manage risks, make conscious choices based on analysis and not emotions, and achieve consistent trading results.
What is the ICT strategy?
The Inner Circle Trader (ICT) strategy is a set of trading concepts and techniques aimed at understanding the causes of price action. ICT encompasses technical analysis and price action patterns, giving close attention to psychological aspects of trading and teaching traders discipline and patience.
Who started ICT trading?
Michael Huddleston, known in the trader community as the developer of the ICT methodology, has significantly influenced the approach of many traders to markets.
Is the ICT method profitable?
Profitability of ICT, like any other trading strategy, can vary greatly depending on the trader. While some traders successfully apply ICT, others may have difficulties earning profits. Beginners are advised to thoroughly test any strategy on a demo account before risking real funds.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
For over 15 years, Oleg worked as a copywriter and journalist at advertising and marketing agencies, as well as radio and television companies. His writing style is aimed at using simple terms to explain only those things that matter to the reader – benefits, risks, and realizable ideas. During the 2008 financial crisis, Oleg got interested in the stock and Forex markets and thoroughly explored price action to start working as an independent expert in 2018.
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
A long position in Forex, represents a positive outlook on the future value of a currency pair. When a trader assumes a long position, they are essentially placing a bet that the base currency in the pair will appreciate in value compared to the quote currency.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that relies on cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology.
A limit order is a type of order used in trading where an investor specifies a particular price at which they want to buy or sell a financial asset. The order will only be executed if the market price reaches or exceeds the specified limit price, ensuring that the trader gets the desired price or better when the trade is executed.
FOMO in trading refers to the fear that traders or investors experience when they worry about missing out on a potentially profitable trading opportunity in the financial markets.
In trading, a supply and demand zone refers to specific price levels on a chart where there is an imbalance between buyers (demand) and sellers (supply). A demand zone represents a price area where buying interest is strong, potentially leading to price increases, while a supply zone indicates an area where selling interest is significant, possibly resulting in price declines.





























































































































