Forex Market Volatility | Full Guide



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
Forex market volatility refers to the frequency and magnitude of price movements. It is influenced by various factors such as economic data releases, geopolitical events, changes in interest rates, and market sentiment. Traders often use volatility as a measure to adjust their strategies, manage risk, and determine the best times to enter or exit trades.
The Forex market, known for being the largest and most liquid financial market globally, offers vast opportunities for traders. However, with great opportunities come great challenges, one of the most significant being market volatility. Understanding and playing around this volatility is important for both beginners and experienced traders alike. So to help you better, this article discusses Forex market volatility, offering insights, strategies, and tools to help traders make smarter trading decisions.
What is Forex market volatility?
Forex market volatility refers to the degree of variation in the exchange rates of currency pairs over a specific period.
Types of volatility
Historical volatility: This measures the past price movements of a currency pair over a set period. It looks retrospectively at a currency's volatility, using standard deviation to quantify these fluctuations.
Implied volatility: Unlike historical volatility, implied volatility is forward-looking. It estimates the potential volatility based on market expectations, often derived from the pricing of options contracts.
Factors influencing Forex market volatility
Several factors contribute to the volatility in the Forex market:
Geopolitical events like political instability, wars, and natural disasters can cause sudden and significant market movements.
Market sentiment and central bank policies - trader sentiment and central bank interventions can also drive volatility. Through their monetary policies and interventions, central banks play a major role in stabilizing or destabilizing their currencies.
Economic indicators can have noticeable impacts on currency values. Key indicators include:
GDP growth: Reflects the economic health of a country. Higher growth rates generally boost the currency value;
Inflation rates: Rising inflation can devalue a currency, while stable inflation can have a positive impact;
Interest rates: Central bank policies on interest rates, often led by inflation, directly impact currency fluctuations;
Employment data: Employment rates can influence consumer spending and economic stability, impacting currency strength.
Impact of volatility on trading decisions
Volatility affects trading decisions in various ways:
Profitability and risk: While volatility can present profit opportunities, it also increases risk. Traders must balance the potential for higher returns with the increased chance of losses;
Trade execution and timing: Volatile markets require precise timing and quick execution to capitalize on price movements. Delays can result in missed opportunities or unexpected losses;
Psychological impact on traders: High volatility can lead to heightened stress and emotional decision-making. Traders must maintain discipline and stick to their strategies to avoid panic-induced mistakes.
Strategies to manage Forex market volatility
To manage volatile markets, traders often employ these strategies:
Diversification: Spreading investments across different assets can help manage risk. For instance, diversifying into various currency pairs or asset classes can reduce exposure to any single market movement;
Hedging: Hedging involves taking opposite positions in correlated assets to offset potential losses. For example, a trader might go long on EUR/USD and short on USD/JPY to balance risks;
Use of stop-loss and take-profit orders: These orders help manage risk by automatically closing positions at predetermined levels, preventing excessive losses, or securing profits;
Scalping and day trading techniques: These short-term strategies involve making multiple trades within a day to capitalize on small price movements, minimizing exposure to long-term volatility;
Position sizing and leverage management: Adjusting the trades' size and leverage level used can control risk. Smaller positions and lower leverage reduce the impact of adverse market movements.
Tools for analyzing Forex market volatility
Several tools can help traders analyze and predict volatility:
Technical indicators:
Bollinger bands: These provide a visual representation of volatility by placing bands above and below a moving average;
Average true range (ATR): Measures market volatility by calculating the average range of price movements over a specified period;
Standard deviation: Quantifies the dispersion of price movements from the average, indicating the degree of volatility.
Economic calendars:
Keeping track of upcoming economic events and data releases can help traders anticipate potential volatility spikes.
Volatility index (VIX):
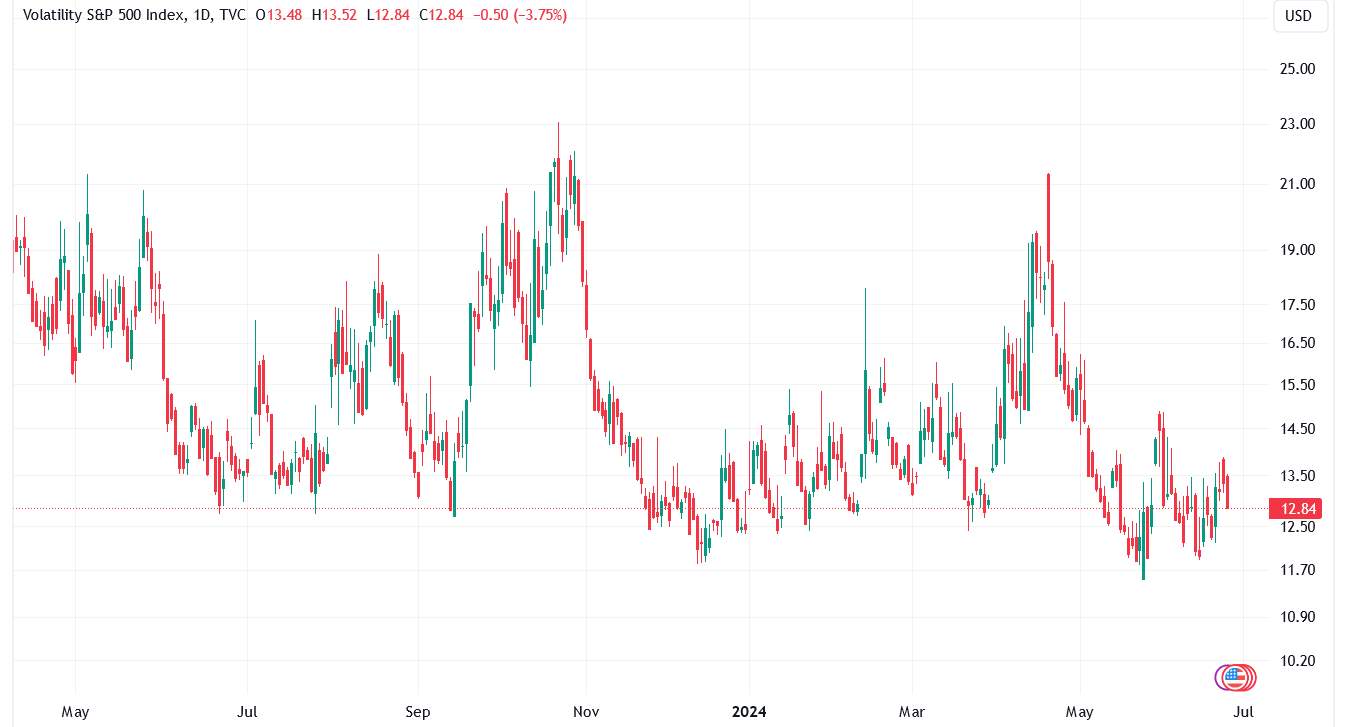
The VIX, often called the "fear index," measures market volatility expectations. Although primarily used for equities, it can provide insights into broader market sentiments that affect Forex.
We have compared several brokers with Volatility index (VIX), so we suggest you check out their conditions:
| Pepperstone | OANDA | FOREX.com | IG Markets | Thinkorswim | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VIX |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Demo |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
|
Min. deposit, $ |
No | No | 100 | 1 | 2000 |
|
Max. leverage |
1:500 | 1:200 | 1:50 | 1:200 | 1:100 |
|
Negative balance protection |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Min Spread EUR/USD, pips |
0,5 | 0,1 | 0,7 | 0,6 | 0,2 |
|
Max Spread EUR/USD, pips |
1,5 | 0,5 | 1,2 | 1,2 | 0,4 |
|
Open account |
Open an account Your capital is at risk.
|
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Study review | Study review | Study review |
Considerations for beginner traders
Beginners should focus on understanding basic concepts and developing simple strategies to manage risk.
Basic understanding of volatility: Beginners should start with fundamental knowledge about volatility and how it impacts trading;
Simple strategies for risk management: Using basic tools like stop-loss orders and practicing proper position sizing can help beginners manage risk effectively;
Educational resources and learning tools: Engaging with tutorials, eBooks, and online courses can build a strong foundation;
Common mistakes to avoid: Understanding and avoiding common pitfalls, such as over-leveraging and emotional trading is important for all traders, especially for beginners.
Considerations for advanced traders
Experienced traders can get into more sophisticated techniques and analyses:
Advanced technical analysis: Using complex indicators and patterns to predict market movements more accurately;
Complex hedging techniques: Implementing advanced hedging strategies to protect investments from unexpected market swings;
Using leverage and managing margin: Using leverage cautiously, making sure that the post-leverage risk does not exceed the trader’s per-trade-loss budget;
Case studies and in-depth market analysis: Looking at past cases to judge how markets play out in specific situation;
Algorithmic and automated trading strategies: Leveraging technology to automate trading decisions and capitalize on market movements efficiently.
Global economic events drive Forex market volatility
Understanding and managing Forex market volatility is unavoidable for any trader aiming for long-term success, as it offers both opportunities and challenges through its rapid and unpredictable currency price changes.
Based on my years of experience, the impact of global economic events is quite deep on market volatility. Major announcements like interest rate changes by central banks, geopolitical events, and economic data releases can cause big market swings. If you look to trade during such events, I advise you to set stop-loss orders, diversify your trades, and never risk more than a small percentage of your trading capital on one trade. Over-leveraging or poor risk management can quickly wipe out your account.
Additionally, creating a solid trading plan that accounts for different volatility scenarios can also help as backtesting your strategies under various market conditions helps you understand how they perform during high volatility periods.
Summary
Forex market volatility, which refers to the rapid and unpredictable changes in currency prices, presents both opportunities and challenges for traders. Influenced by factors like GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rate changes, employment data, geopolitical events, and central bank policies, this volatility requires traders to be up to date with global economic events. To manage risk, it becomes important to diversify trades, set stop-loss orders, and avoid over-leveraging. Developing a solid trading plan that accounts for different volatility scenarios and backtesting strategies under various market conditions can also help.
FAQs
What causes Forex market volatility?
Economic data releases, central bank decisions, geopolitical events, and sudden market sentiment shifts primarily cause forex market volatility. For example, non-farm payroll data in the US or changes in interest rates by the European Central Bank can lead to significant price movements.
How can traders manage risk during volatile market conditions?
Traders can manage risk by using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying their trades to spread risk, and maintaining a strict risk management plan that includes not risking more than a small percentage of their trading capital on any single trade.
Are there specific times when the Forex market is more volatile?
Yes, the Forex market tends to be more volatile during major economic announcements, such as interest rate decisions or GDP reports. Additionally, market volatility often increases during the overlap of major trading sessions, such as when the London and New York sessions are both open.
What are the benefits of trading in a volatile Forex market?
Trading in a volatile Forex market offers the potential for higher profits due to the significant price movements. Volatility can create opportunities for traders to capitalize on rapid changes in currency values, provided they have a solid trading strategy and risk management plan in place.
How can emotional discipline affect trading in volatile markets?
Rapid price movements can lead to emotional decisions, such as panic selling or over-leveraging, often resulting in losses. Maintaining a calm and disciplined approach, sticking to your trading plan, and avoiding impulsive decisions are essential for successful trading in volatile conditions.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Parshwa is a content expert and finance professional possessing deep knowledge of stock and options trading, technical and fundamental analysis, and equity research. As a Chartered Accountant Finalist, Parshwa also has expertise in Forex, crypto trading, and personal taxation. His experience is showcased by a prolific body of over 100 articles on Forex, crypto, equity, and personal finance, alongside personalized advisory roles in tax consultation.

Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Economic indicators — a tool of fundamental analysis that allows to assess the state of an economic entity or the economy as a whole, as well as to make a forecast. These include: GDP, discount rates, inflation data, unemployment statistics, industrial production data, consumer price indices, etc.
Diversification is an investment strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce overall risk.
Trade execution is knowing how to place and close trades at the right price. This is the key to turning your trading plans into real action and has a direct impact on your profits.
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.
The informal term "Forex Gods" refers to highly successful and renowned forex traders such as George Soros, Bruce Kovner, and Paul Tudor Jones, who have demonstrated exceptional skills and profitability in the forex markets.






























































































































