Forex Exotic Currency Pairs Definition And Trading Rules



Editorial Note: While we adhere to strict Editorial Integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for How We Make Money. None of the data and information on this webpage constitutes investment advice according to our Disclaimer.
Exotic currency pairs combine one major currency (such as USD, EUR, or GBP) and one currency from an emerging or smaller economy (such as the Turkish Lira or the South African Rand). These pairs are less liquid and less frequently traded than major and minor pairs, leading to higher volatility and wider spreads.
Forex trading offers a various opportunities for traders, from the well-known major currency pairs like EUR/USD to less commonly traded pairs known as exotics. In this article, we will learn about trading exotic currency pairs, exploring their definitions, unique characteristics, trading strategies, risks, and potential earnings.
Characteristics of exotic currency pairs
Exotic currency pairs are those that consist of one major currency paired with the currency of an emerging or smaller economy. Unlike major and minor currency pairs, exotic pairs tend to be less liquid, more volatile, and subject to wider spreads, which makes them both riskier and potentially more rewarding.
| Exotic currency Pair | Major currency | Emerging market currency |
|---|---|---|
US Dollar (USD) | Turkish Lira (TRY) | |
US Dollar (USD) | South African Rand (ZAR) | |
Euro (EUR) | Polish Zloty (PLN) | |
US Dollar (USD) | Singapore Dollar (SGD) | |
GBP/THB | British Pound (GBP) | Thai Baht (THB) |
Understanding exotic currency pairs is crucial for diversifying portfolios and leveraging unique trading opportunities. They are characterized by:
Thin trading volumes: They are traded less frequently than major pairs, leading to lower liquidity;
Wider spreads: The difference between the bid and ask price is larger, making them more expensive to trade;
Increased volatility: Price movements can be more erratic due to lower liquidity and sensitivity to political and economic events.
Advantages of trading exotic currency pairs
Trading exotic currency pairs can offer unique opportunities and benefits that are not typically found in major or minor currency pairs. Let us discuss some key advantages.
Diversification benefits
Trading exotic pairs can help diversify your portfolio, reducing exposure to any single currency or economic region. This diversification can mitigate risk and enhance potential returns.
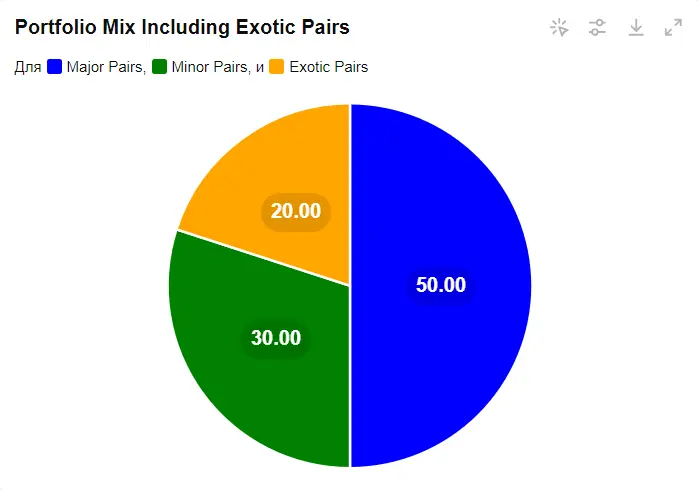 Portfolio Mix Including Exotic Pairs
Portfolio Mix Including Exotic PairsPotential for higher profits
Due to their higher volatility, exotic pairs offer significant profit opportunities for traders who can correctly predict market movements.
Unique trading opportunities
Exotic forex pairs offer distinct trading opportunities that you won't find with major currency pairs. These pairs often mirror the economic conditions and geopolitical factors of the smaller economies involved.
Step-by-step guide to trading exotic currency pairs
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the complexities of trading exotic currency pairs:
1. Choose a reliable forex broker and create a trading account. Research and select a Forex broker that offers a variety of exotic currency pairs. Ensure the broker is reputable, regulated, and provides a user-friendly trading platform.
Here is a list of brokers that you can choose for trading exotic currency pairs:
| Bybit | XM Group | Vantage Markets | FxPro | VT Markets | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Min. deposit, $ |
No | 5 | 50 | 100 | 100 |
|
Currency pairs, number |
61 | 57 | 40 | 70 | 55 |
|
Min Spread EUR/USD, pips |
Not supported | 0,7 | 0,3 | 0,9 | 0,4 |
|
Max Spread EUR/USD, pips |
Not supported | 1,2 | 1,4 | 1,7 | 1,2 |
|
Leverage, 1: |
Up to 1:500 | 1:30 (only for EU regulated Entity and AU). For all the other countries - 1:1000. | Up to 1:20 (for CFDs on stocks), up to 1:500 (for currency pairs) | Up to 1:500 subject to the jurisdiction. For example, maximum leverage for certain jurisdictions is up to 1:30 for currency pairs. | Up to 1:500 |
|
Trading platform |
MetaTrader5 | MT4, MT5, MobileTrading, XM App | MT4, MT5, TradingView, ProTrader, Vantage App | MT4, MobileTrading, MT5, cTrader, FxPro Edge | MetaTrader4, MetaTrader5, VT Markets App, Web Trader+ |
|
Open account |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
Open an account Your capital is at risk. |
2. Finding the exotic pair to trade. Access the trading platform - log in to your trading account using the broker’s platform (e.g., MetaTrader 4/5, cTrader). Locate the exotic pair - navigate to the market watch or asset list on the platform, search for the exotic currency pair you are interested in (e.g., USD/TRY, EUR/PLN) and add the selected pair to your watchlist for easy access.
3. Executing a trade - analyze the market (use charts, indicators, and news updates to support your decision). Then place buy/sell orders, choose whether to buy (go long) or sell (go short) the exotic currency pair based on your analysis. Set a stop-loss order to automatically close your trade if the market moves against you, limiting potential losses.
Risks and warnings
Trading exotic currency pairs can be both exciting and profitable, but it also comes with its own set of unique challenges and risks: highly volatile, liquidity issues and wider spreads.
High volatility
Exotic currency pairs are highly volatile, leading to rapid price changes that can result in significant gains or losses. For example, The Turkish Lira (TRY) can experience significant swings due to political events in Turkey. A sudden policy announcement can cause the USD/TRY pair to spike or drop dramatically within a short period.
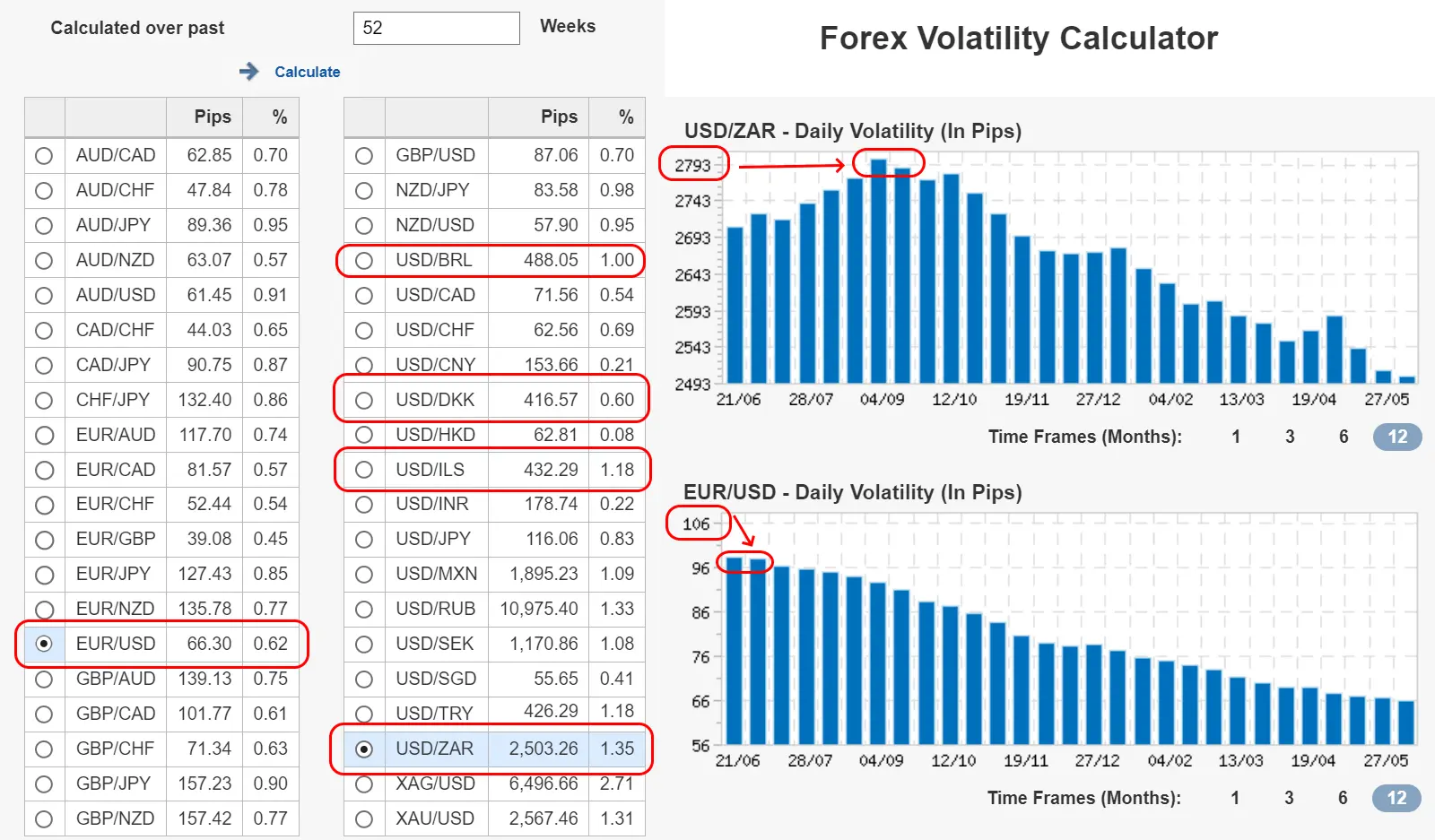 Historical volatility of select exotic currency pairs VS major pairs
Historical volatility of select exotic currency pairs VS major pairs Impact of volatility on exotic currency pairs
Impact of volatility on exotic currency pairsLiquidity issues
Lower trading volumes can lead to liquidity issues, making it difficult to enter or exit trades at desired prices. For instance, trying to buy or sell a large volume of USD/ZAR during a low liquidity period can result in less favorable prices.
Wider spreads and higher trading costs
The wider spreads associated with exotic pairs mean higher trading costs, which can eat into profits. For example, while the spread for a major pair like EUR/USD might be around 1 pip, it can be as high as 10 pips for an exotic pair like USD/TRY.
| Currency Pair Type | Currency Pair | Typical Spread (pips) |
|---|---|---|
Major Pair | EUR/USD | 1 |
Major Pair | GBP/USD | 2 |
Exotic Pair | USD/TRY | 10 |
Exotic Pair | USD/ZAR | 15 |
Trading strategies for exotic currency pairs
Trading exotic currency pairs successfully requires a strategy tailored to their unique characteristics. Let's learn some of these strategies.
Scalping - involves making numerous small trades to capitalize on minor price fluctuations throughout the trading day. This strategy requires quick execution, low transaction costs, and a keen eye for short-term market movements. Traders using this strategy often focus on tight spreads and high liquidity.
Example: A trader may use scalping to trade USD/TRY, taking advantage of small, rapid price movements by entering and exiting the market within minutes.
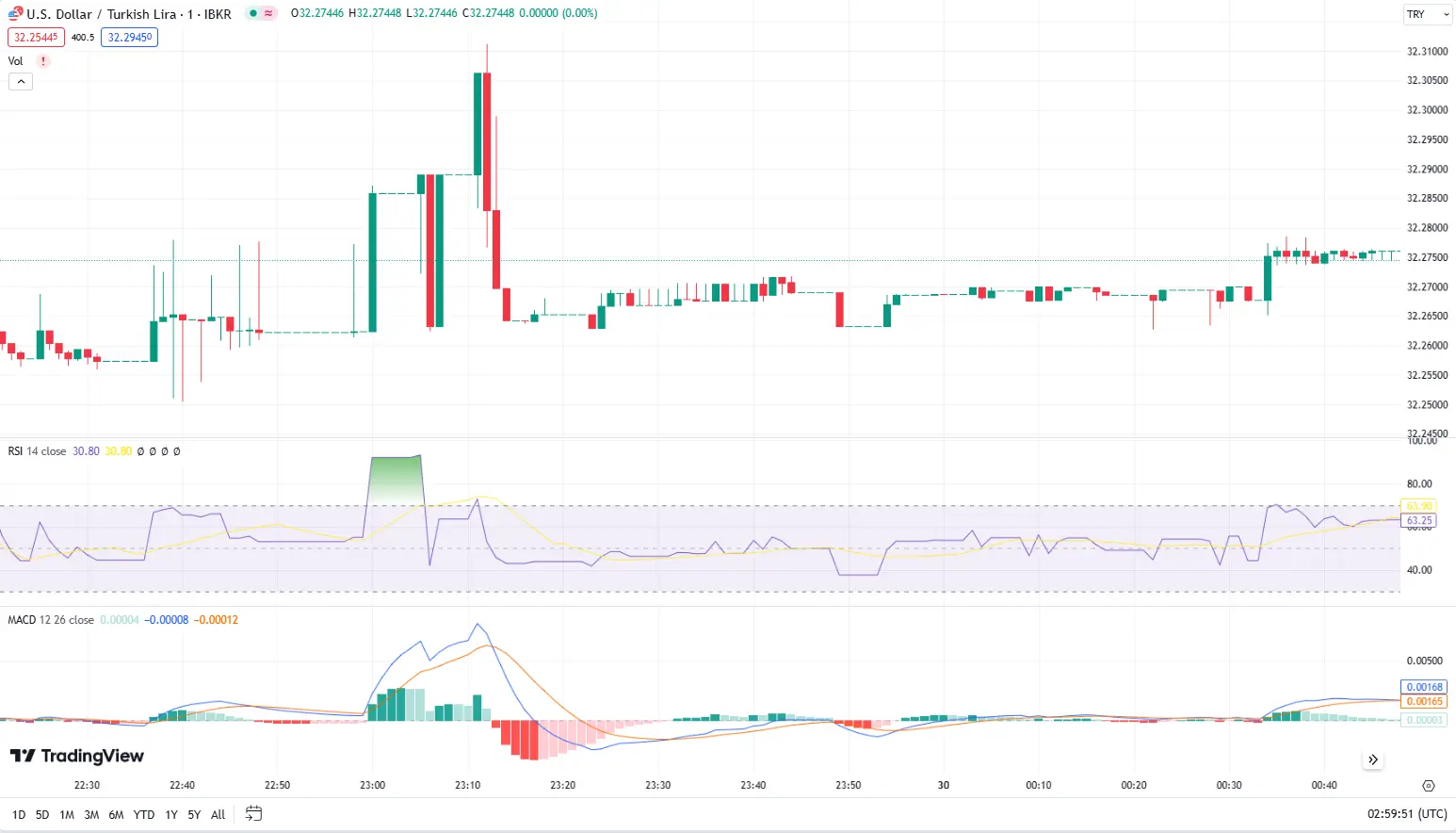 USD/TRY (1 minute chart)
USD/TRY (1 minute chart)Day trading - entails buying and selling currency pairs within the same trading day to avoid the risks associated with overnight positions. This strategy relies heavily on technical analysis to identify short-term trading opportunities and market trends.
Example: A day trader might trade USD/ZAR by analyzing intraday price patterns and technical indicators, executing trades based on expected price movements within the trading day.
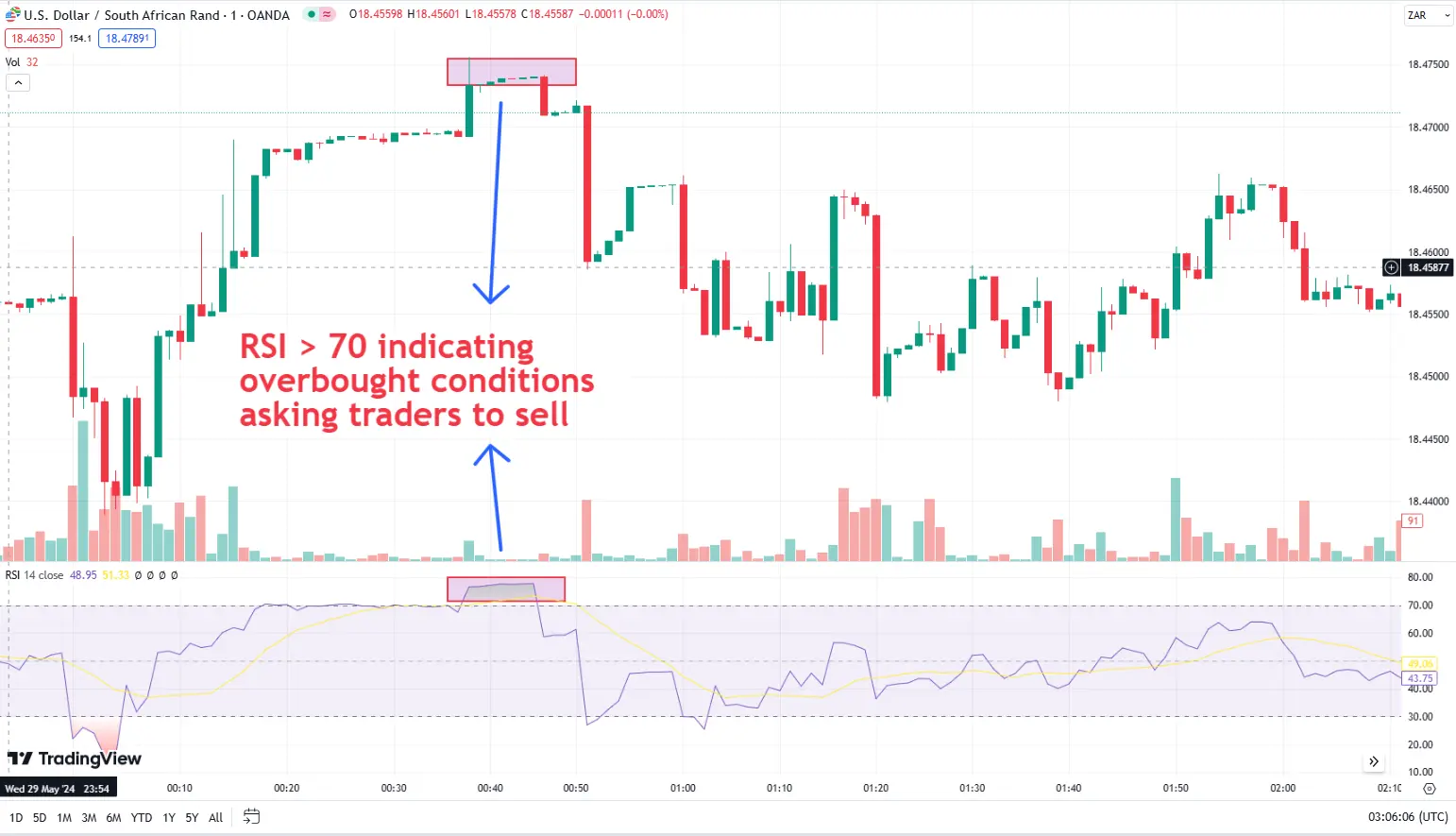 USD/ZAR (1 minute chart)
USD/ZAR (1 minute chart)Swing Trading - involves holding positions for several days to weeks to capture medium-term price movements. This strategy combines technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential market swings and trends.
Example: A swing trader might hold a position in EUR/PLN for a week, using both technical indicators and economic data from the Eurozone and Poland to predict the currency pair's direction.
 Trading Economics
Trading EconomicsPosition Trading is a long-term strategy where traders hold positions for months or even years. This approach focuses on fundamental factors and long-term trends rather than short-term price movements.
Example: A position trader might invest in USD/SGD based on long-term economic growth prospects and monetary policies of the US and Singapore, holding the position for an extended period.
 Monetary Policy of Singapore
Monetary Policy of SingaporeFundamental Analysis involves examining economic indicators, political events, and financial reports to forecast currency movements.
Example: Analyzing GDP growth, inflation rates, and central bank policies in Turkey to forecast the future movements of USD/TRY.
 CAPEX ( Understading forecast through fundamental analysis)
CAPEX ( Understading forecast through fundamental analysis)Technical Analysis - uses historical price data, chart patterns, and technical indicators to predict future price movements. This method helps traders identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential reversal points.
Example: Using moving averages, RSI, and MACD to analyze the price action of USD/ZAR and determine optimal entry and exit points.
 USD/ZAR chart ( Using RSI and MACD indicator)
USD/ZAR chart ( Using RSI and MACD indicator)Common mistakes to avoid
When trading exotic currency pairs, it’s essential to be aware of common pitfalls that can lead to significant losses. Here are some key mistakes to avoid:
| Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
Over-leveraging | Excessive leverage increases risk. Use it cautiously. |
Ignoring Risk Management | No stop-loss or risk plan can cause big losses. |
No trading plan | Trading without a plan leads to impulsive decisions. |
Overtrading | Frequent trades increase costs and errors. Focus on quality. |
No diversification | Investing in one pair increases risk. Spread your investments. |
Emotional trading | Emotions can lead to bad decisions. Stick to your strategy. |
Mastering exotic currency trading: key strategies for success
Trading Forex exotic pairs presents both opportunities and challenges. These pairs, combining major currencies with those from emerging economies, offer unique dynamics. Despite higher volatility and liquidity issues, trading exotics can diversify portfolios and yield higher profits.
However, it requires thorough research, risk management, and tailored strategies. Utilize tools like stop-loss orders and engage with trading communities to navigate these complexities effectively. By understanding their characteristics and employing sound practices, traders can capitalize on the distinct advantages of exotic currency pairs.
Conclusion
Trading exotic currency pairs requires bravery, strategy, and continuous learning. While these markets pose unique challenges, they also offer profitable opportunities for those willing to dive in. By understanding the dynamics of exotic pairs, using effective risk management, and staying connected with the trading community, traders can navigate these markets successfully. Remember, success in exotic currency trading comes with perseverance and a commitment to improving your skills over time.
FAQs
What are the main risks of trading exotic currency pairs?
Trading exotic currency pairs involves high volatility, which can lead to significant price swings and potential losses. These pairs often face liquidity issues, making it difficult to enter or exit positions at desired prices.
How can beginners start trading exotic currency pairs?
Beginners should start by conducting thorough research on the economic and political conditions of the countries involved. Select a reliable broker that offers competitive spreads and a robust trading platform. Practice trading using demo accounts.
What factors affect the prices of exotic currency pairs?
Prices of exotic currency pairs are influenced by economic indicators (like GDP growth and inflation), political stability, global events, and market dynamics.
What are some common exotic currency pairs and their characteristics?
Common exotic currency pairs include USD/TRY, influenced by Turkey's economic and political situation; USD/ZAR, affected by commodity prices and South Africa's economy; and EUR/PLN, impacted by Eurozone and Polish economic indicators.
Related Articles
Team that worked on the article
Parshwa is a content expert and finance professional possessing deep knowledge of stock and options trading, technical and fundamental analysis, and equity research. As a Chartered Accountant Finalist, Parshwa also has expertise in Forex, crypto trading, and personal taxation. His experience is showcased by a prolific body of over 100 articles on Forex, crypto, equity, and personal finance, alongside personalized advisory roles in tax consultation.

Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).
Risk management is a risk management model that involves controlling potential losses while maximizing profits. The main risk management tools are stop loss, take profit, calculation of position volume taking into account leverage and pip value.
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.
Options trading is a financial derivative strategy that involves the buying and selling of options contracts, which give traders the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price, known as the strike price, before or on a predetermined expiration date. There are two main types of options: call options, which allow the holder to buy the underlying asset, and put options, which allow the holder to sell the underlying asset.
Fundamental analysis is a method or tool that investors use that seeks to determine the intrinsic value of a security by examining economic and financial factors. It considers macroeconomic factors such as the state of the economy and industry conditions.
Risk management in Forex involves strategies and techniques used by traders to minimize potential losses while trading currencies, such as setting stop-loss orders and position sizing, to protect their capital from adverse market movements.






























































































































