Top mean reversion trading strategies
According to Traders Union’s experts, the top 5 mean reversion strategies are:
-
1
Bollinger Bands Strategy
-
2
Moving Average Crossover Strategy
-
3
Mean Reversion Channel Strategy
-
4
RSI Divergence Strategy
-
5
Fibonacci Retracement Strategy
The world of foreign exchange (Forex) trading can be a dynamic and challenging environment, with prices constantly fluctuating based on various factors. Traders are always on the lookout for effective strategies that can help them navigate these market movements and increase their chances of profitable trades. One popular approach is mean reversion trading, which capitalizes on the notion that prices tend to return to their average or mean over time. By identifying instances where the price has deviated significantly from its average, traders can take positions with the expectation that the price will eventually revert back to its mean value. In this article, the experts at TU will explore the top five Forex mean reversion strategies that can provide traders with simple and easy-to-understand techniques to potentially capitalize on these reversion patterns.
Do you want to start trading Forex? Open an account on RoboForex!What is the mean reversion trading?
Mean reversion trading is a strategy that revolves around the concept that market prices have a tendency to revert back to their long-term average. When values deviate significantly from this average, they are likely to reverse direction and move back towards the prevailing trend. This theory is based on the understanding that while there may be short-term deviations from the underlying trend, prices ultimately correct themselves and realign with the broader market direction.
Mean reversion traders capitalize on this theory by developing various approaches to take advantage of these price reversals. The essence of mean reversion lies in the belief that extreme price movements are difficult to sustain over extended periods of time. As a result, traders employ different methods to identify these instances and make informed trading decisions.
In the realm of finance, mean reversion suggests that asset price volatility and historical returns will ultimately return to the long-run mean or average level observed in the entire dataset. This mean level can manifest in different contexts, such as economic growth, stock price volatility, price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio), or the average return of a particular industry.
Mean reversion trading strategies leverage these concepts and aim to identify opportunities where prices have deviated significantly from their average levels, presenting potential profit possibilities as they revert back to the mean. By understanding the principles of mean reversion and utilizing appropriate techniques, traders can enhance their trading strategies and potentially achieve favorable outcomes in the dynamic world of financial markets.
Mean reversion vs trend following
When it comes to trading strategies, they are typically categorized as either mean reverting or trend following, also known as momentum trading.
Mean reversion strategies aim to capture price movements that occur towards and away from an average or mean value. Traders employing these strategies look for instances where prices have deviated significantly from the average and take positions with the expectation that prices will eventually revert back to the mean.
On the other hand, trend following strategies focus on capturing the momentum of price movements, whether they are upward, downward, or even in a range-bound market. Traders utilizing these strategies open positions in the general direction of the trend and hold onto their trades until the market shows signs of reversal.
While mean reversion strategies seek to profit from price reversals towards the average, trend following strategies aim to ride the wave of a sustained market trend. Each approach has its own set of techniques and indicators that traders use to identify suitable trading opportunities and manage their positions effectively. By understanding the distinctions between mean reversion and trend following strategies, traders can choose the approach that aligns best with their trading style and objectives.
How does mean reversion work?
Mean reversion theory is a statistical analysis approach utilized in trading strategies to identify abnormal market activity that is expected to return to a normal pattern. It aligns with the concept of buying low and selling high, aiming to capture opportunities when prices deviate significantly from their average values.
The driving force behind mean reversion is primarily the behavior and sentiments of traders when prices deviate from the norm. When a stock price starts rising, traders and investors rush to buy, fearing they might miss out on potential gains. This increased demand pushes the price even higher. As the price continues to climb, more traders join in, resulting in a peak where selling begins. At this point, the supply exceeds the demand, causing the price to decline. Anticipating further price drops, many traders sell their stocks to avoid losses, creating an excess supply and driving the price down even faster. Eventually, at a low price level, some traders start buying again, leading to a balance between supply and demand, and ultimately causing the price to revert back to its average or mean value.
The mean reversion concept revolves around the idea that extreme price movements are difficult to sustain over the long term. Traders employing mean reversion strategies aim to identify these instances of price deviation and take positions based on the expectation that prices will eventually revert back to their mean levels. By understanding the dynamics of mean reversion and the underlying trader sentiments, traders can potentially capitalize on these market movements to achieve profitable outcomes.
Pros and cons of mean reversion trading strategy
👍 Pros
• Simplicity: One of the significant advantages of mean reversion trading strategies is their simplicity. These strategies are straightforward to understand and implement, making them accessible to traders of all experience levels. Traders can quickly grasp the basic concept of identifying deviations from the mean and taking positions based on the expectation of price reversals
• Historical evidence: Mean reversion strategies have a strong historical basis. Many studies and analyses have demonstrated their effectiveness in various financial markets over time. This historical evidence provides traders with confidence in the strategy and its potential for generating profits
• Well-defined entry and exit points: Mean reversion strategies offer clear entry and exit points. Traders can establish specific criteria to identify when prices have deviated significantly from the mean, allowing them to enter positions at favorable levels. Likewise, predefined exit points help manage risk and secure profits. Having well-defined entry and exit points enhances trading discipline and reduces emotional decision-making
• Exploiting market inefficiencies: Mean reversion strategies take advantage of market inefficiencies, which can arise due to temporary imbalances in supply and demand or overreactions to news and events. By identifying these inefficiencies and capitalizing on them, traders can potentially profit from the subsequent price corrections as the market reverts to its mean value
👎 Cons
• Not a sure-shot risk-free approach: While mean reversion strategies have shown success in the past, there is no guarantee that they will continue to be profitable in the future. Market conditions can change, and strategies that were once effective may lose their edge. Traders must regularly assess and adapt their mean reversion strategies to align with evolving market dynamics
• Prolonged deviation from mean: Although mean reversion assumes that prices and other metrics will eventually return to their long-term average, there is a risk that deviations from the mean may persist for longer periods. This can result in prolonged drawdowns and potential losses for traders utilizing mean reversion strategies. Traders need to carefully manage their risk and employ proper position sizing techniques to mitigate the impact of extended periods of deviation
• Difficulty in identifying the mean: Identifying the long-term average or mean can be challenging. Different methods and chart time frames can produce varying mean values, and the mean itself can change over time due to shifting market dynamics. Traders must use reliable statistical tools and techniques to determine an appropriate mean value that aligns with the market's characteristics
• Requires discipline and patience: Successful implementation of mean reversion strategies demands discipline and patience. Traders need to wait for prices or other metrics to move back towards the mean, which may take time. It can be challenging for traders who prefer more active trading approaches or have a shorter-term mindset. The ability to exercise patience and adhere to the predefined entry and exit criteria is crucial for effectively executing mean reversion strategies
Top 5 mean reversion strategies
Moving Average Crossover Strategy
The Moving Average Crossover strategy involves plotting two moving averages on a chart, a shorter-term moving average and a longer-term moving average. This strategy aims to capture potential oversold or overbought conditions in the market.
Entry point:
When the shorter-term moving average crosses above the longer-term moving average, it suggests a potential oversold condition. Traders can consider taking a long position, expecting the price to revert back towards the mean or the longer-term moving average
When the shorter-term moving average crosses below the longer-term moving average, it indicates a potential overbought condition. Traders can consider taking a short position, anticipating a reversion of the price towards the mean or the longer-term moving average
Exit point:
Traders can exit the trade when the price reverts back to the mean or when the moving averages cross again, indicating a potential reversal in the price movement.
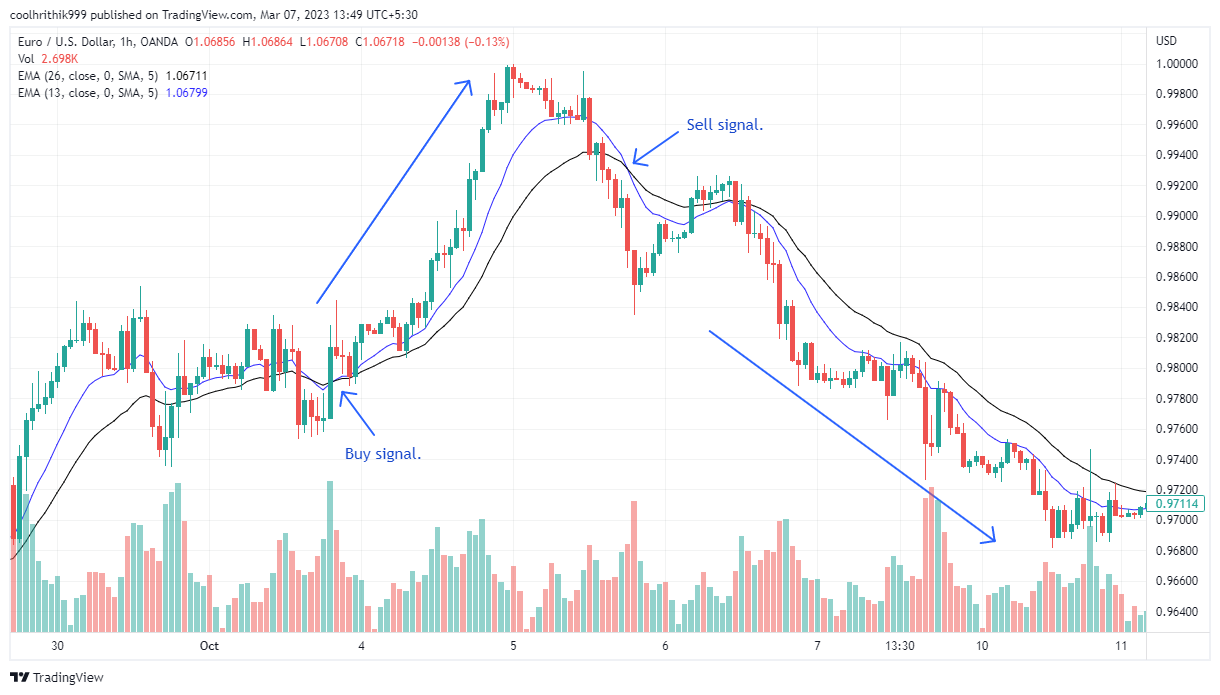
Moving Average Crossover Strategy
RSI Divergence Strategy
The RSI Divergence strategy utilizes the Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator to identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market. It focuses on divergences between the price and the RSI, which can indicate potential reversals.
Entry point:
When the price forms higher highs, but the RSI forms lower highs, it suggests bearish divergence. Traders can consider taking a short position, anticipating a reversion of the price back towards the mean or a potential downward move
When the price forms lower lows, but the RSI forms higher lows, it indicates bullish divergence. Traders can consider taking a long position, expecting the price to revert back towards the mean or a potential upward move
Exit point:
Traders can exit the trade when the price reverts back to the mean or when the divergence pattern ends, indicating a potential reversal in the price movement.
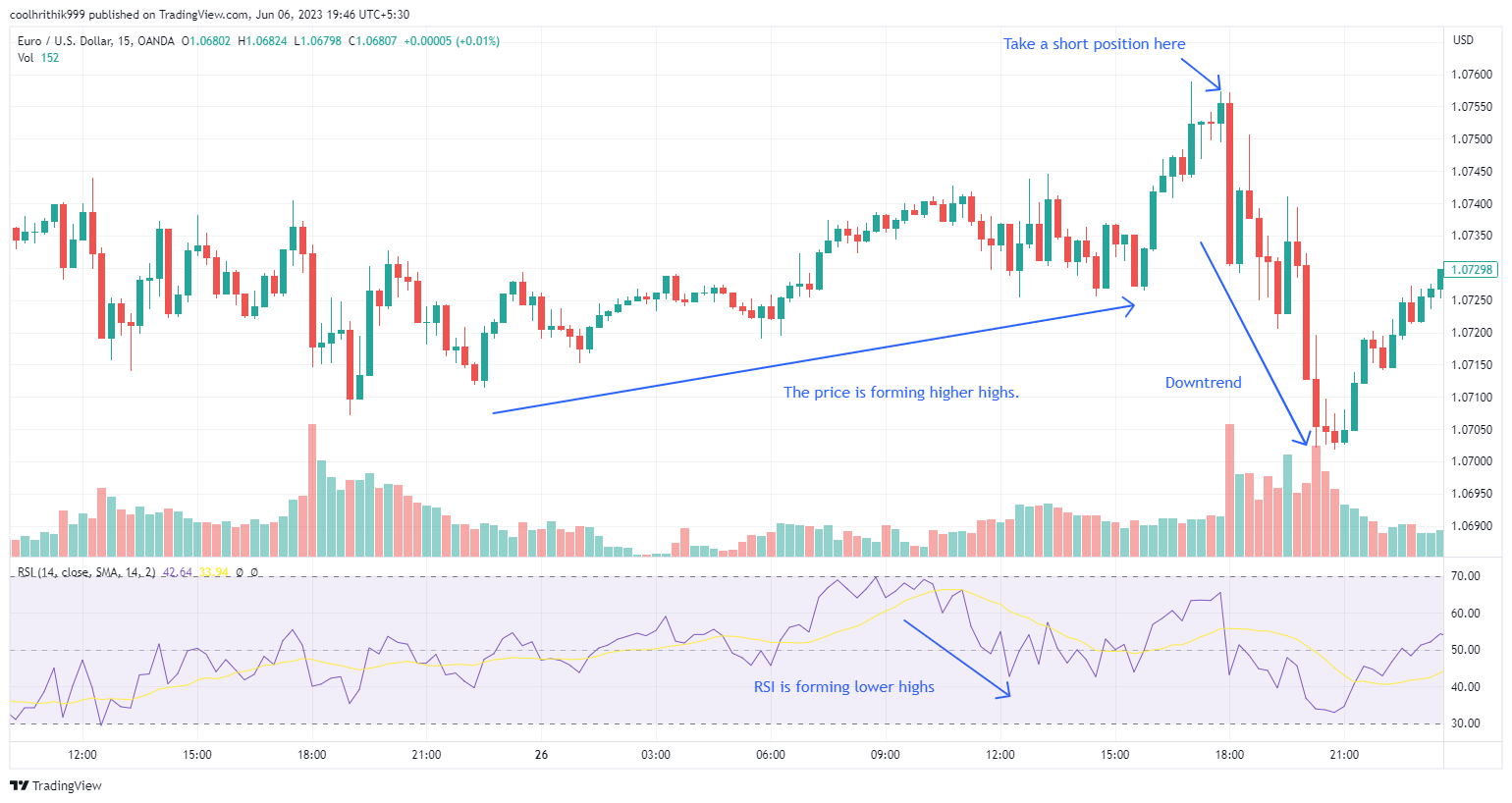
RSI Divergence Strategy
Stochastic Oscillator Strategy
The mean reversion strategy using the Stochastic Oscillator aims to identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market and take advantage of potential price reversals. The Stochastic Oscillator is a momentum indicator that compares the closing price of an asset to its price range over a given period. It consists of two lines, %K and %D, which oscillate between 0 and 100.
Entry point:
To enter a trade using the Stochastic Oscillator mean reversion strategy, traders look for the following conditions:
Overbought condition: When the %K line crosses above a specified threshold (e.g., 75) and then crosses back below it, it signals an overbought condition. This indicates that the price may have moved too far away from its average and is likely to revert back towards it
Oversold condition: When the %K line crosses below a specified threshold (e.g., 25) and then crosses back above it, it signals an oversold condition. This suggests that the price may have moved too far below its average and is expected to revert back upwards
Traders typically wait for these entry signals to confirm a potential mean reversion trade.
Exit point:
For exiting the trade, traders using the Stochastic Oscillator mean reversion strategy can consider the following options:
Reversion to the mean: Once the price starts to reverse and move towards the mean, traders may choose to exit the trade. This can be identified by the %K line crossing back towards the midrange (e.g., 50) from the overbought or oversold levels
Stop-loss and take-profit levels: Traders can also set predefined stop-loss and take-profit levels based on their risk tolerance and desired profit targets. These levels help manage risk and lock in profits if the price continues to move against the anticipated mean reversion
Stochastic Oscillator Strategy
Fibonacci Retracement Strategy
The Fibonacci Retracement strategy involves drawing Fibonacci retracement levels on a chart to identify potential support and resistance levels. Traders use these levels to anticipate price reversals and mean reversion opportunities.
Entry point:
When the price retraces to a Fibonacci level (e.g., 50% or 61.8%) after a strong trend, it suggests a potential mean reversion trade. Traders can consider taking a long position if the price retraces from a previous downtrend or a short position if it retraces from an uptrend.
Exit point:
Traders can exit the trade when the price reaches the next Fibonacci level or when the trend resumes, indicating a potential reversal or continuation in the price movement.
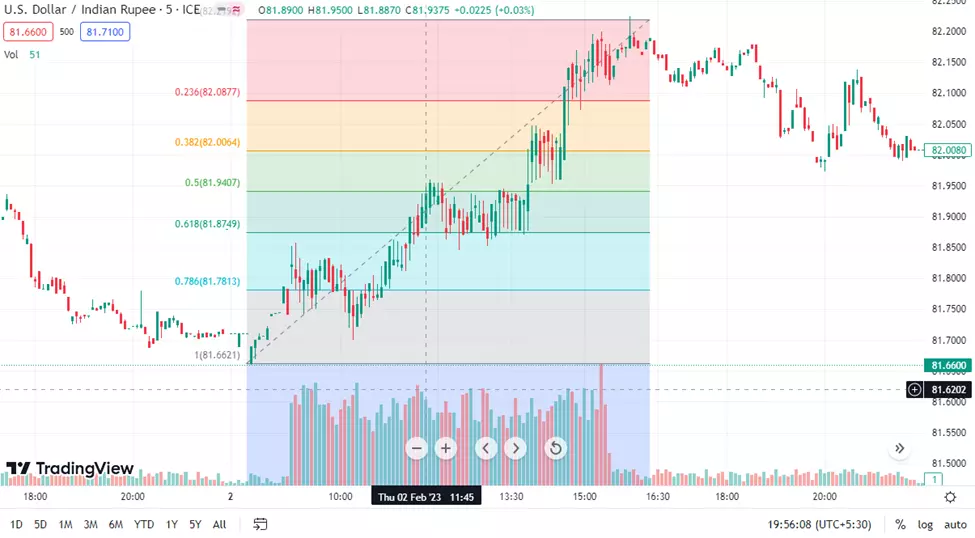
Fibonacci Retracement Strategy
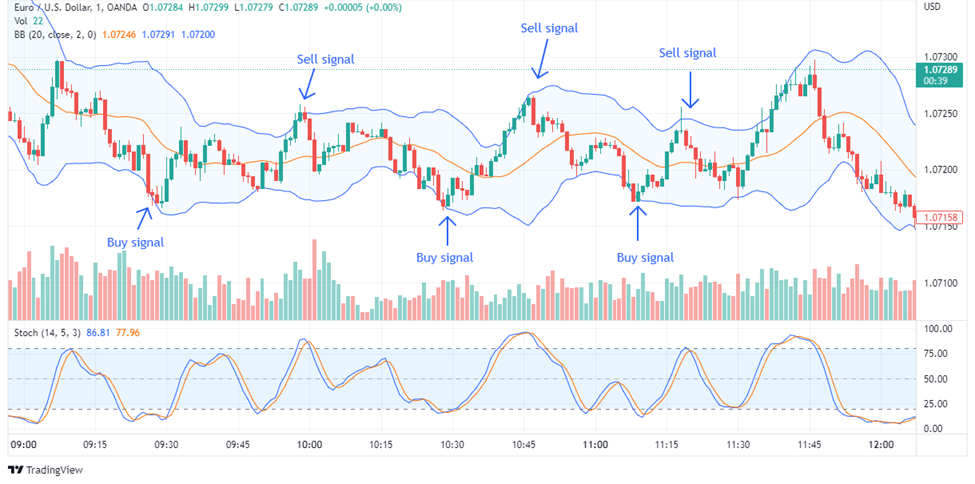
Bollinger Bands Strategy
The Bollinger Bands strategy is based on the Bollinger Bands indicator, which consists of a simple moving average (typically 20 periods) and two standard deviation bands plotted above and below the moving average. This strategy helps identify periods of high volatility in the market.
Entry point:
When the price moves outside the upper band, it suggests that the market is overbought. Traders can consider taking a short position, anticipating a reversion of the price back towards the moving average or the lower band
When the price moves below the lower band, it indicates that the market is oversold. Traders can consider taking a long position, expecting the price to revert back towards the moving average or the upper band
Exit point:
Traders can exit the trade when the price reverts back to the moving average or reaches the opposite band. This indicates a potential return to the mean and a potential reversal in the price movement.
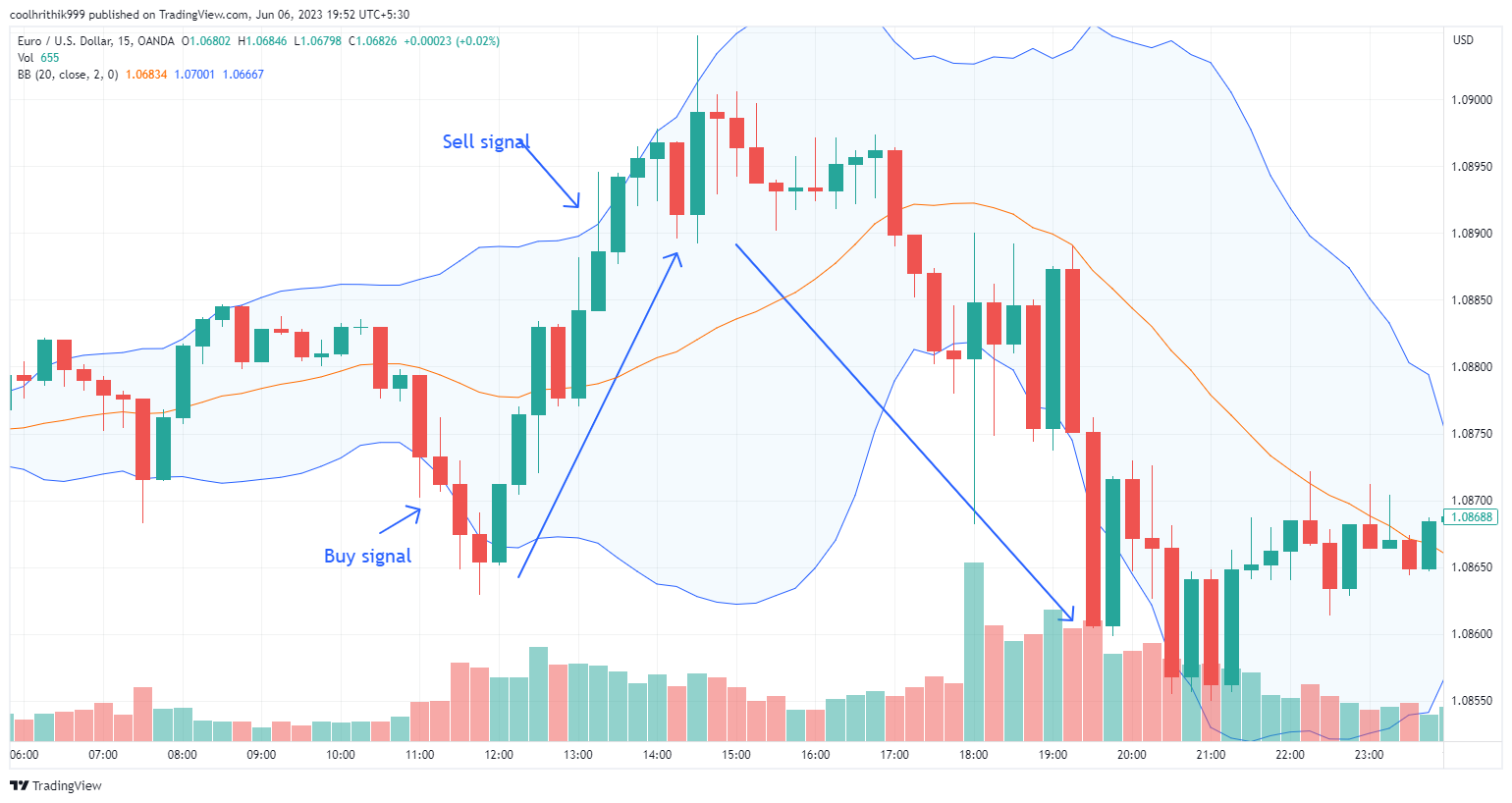
Bollinger Bands Strategy
Does mean reversion strategy work?
Yes, mean reversion strategies have been proven to be effective in trading. However, it's important to note that mean reversion doesn't happen immediately. It can take a considerable amount of time for the market to correct itself, if it does at all. Traders who employ mean reversion strategies need to have patience and be willing to wait for the price to revert back to its average.
Mean reversion may not be suitable for extremely short-term trading strategies like scalping, as the process of reversion can be a gradual one. It is best utilized as part of an overall trading strategy, alongside other approaches.
Before implementing a mean reversion strategy, it is crucial to thoroughly analyze the specific asset or market. Changes in market conditions or underlying fundamentals can significantly impact the likelihood of a mean reversion occurring. Therefore, careful evaluation and assessment are necessary to identify suitable mean reversion opportunities.
How to trade mean reversion strategy?
Here are some expert tips to help you trade a mean reversion strategy successfully:
Identify the mean: Determine the average or mean value of the asset you wish to trade. This can be done using various indicators or statistical tools
Identify deviations: Monitor the price of the asset and look for instances where it deviates significantly from the mean. These deviations can be identified using technical indicators or price patterns
Determine entry points: Once a significant deviation from the mean is identified, look for a suitable entry point. This could be when the price reaches an extreme level, such as overbought or oversold conditions, or when a reversal pattern emerges
Set stop loss and take profit levels: Establish appropriate stop loss order and take profit levels to manage your risk and protect your capital. These levels should be based on your analysis of the asset's volatility and the potential for the price to revert back to the mean
Implement risk management: Incorporate risk management techniques, such as position sizing and risk-to-reward ratios, to ensure that your losses are controlled and your potential gains are maximized
Monitor trade and exit criteria: Keep a close eye on the trade as it progresses. Exit the trade when the price starts to revert back to the mean or reaches predetermined profit targets. Be prepared to exit the trade if the price continues to move against your position
Adapt to changing market conditions: Continuously monitor the market conditions and adjust your strategy accordingly. Market dynamics can change, and it is essential to adapt your mean reversion strategy to align with the evolving trends and patterns
Best Forex brokers 2024


FAQs
Is mean reversion trading profitable?
Mean reversion trading can be profitable, but the same is not guaranteed. Success depends on various factors such as market conditions, strategy implementation, risk management, and trader skill.
What is the best timeframe for mean reversion strategy?
The best timeframe for a mean reversion strategy depends on the asset being traded and the trader's preference. It can range from intraday time frames, such as minutes or hours, to longer-term timeframes, such as daily or weekly charts.
What is the best indicator for mean reversion?
There is no single best indicator for mean reversion. Traders often use a combination of indicators, such as Bollinger Bands, moving averages, RSI, or stochastics, to identify potential mean reversion opportunities. The choice of indicators depends on the trader's trading style and the asset being traded.
What is the 3-day mean reversion strategy?
The 3-day mean reversion strategy is a trading approach focused on ETFs that utilizes the price highs and lows observed over a consecutive three-day period to establish potential trade opportunities. The strategy involves initiating a buy position when an ETF exhibits a consistent pattern of lower highs and lower lows over three consecutive days, with the anticipation that the price will eventually return to its average level.
Glossary for novice traders
-
1
Broker
A broker is a legal entity or individual that performs as an intermediary when making trades in the financial markets. Private investors cannot trade without a broker, since only brokers can execute trades on the exchanges.
-
2
Trading
Trading involves the act of buying and selling financial assets like stocks, currencies, or commodities with the intention of profiting from market price fluctuations. Traders employ various strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management practices to make informed decisions and optimize their chances of success in the financial markets.
-
3
Deviation
The deviation is a statistical measure of how much a set of data varies from the mean or average value. In forex trading, this measure is often calculated using standard deviation that helps traders in assessing the degree of variability or volatility in currency price movements.
-
4
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands (BBands) are a technical analysis tool that consists of three lines: a middle moving average and two outer bands that are typically set at a standard deviation away from the moving average. These bands help traders visualize potential price volatility and identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market.
-
5
Stochastic Oscillator
The Stochastic Oscillator is a technical indicator used in financial analysis to gauge the momentum of a security's price and identify overbought or oversold conditions by comparing the closing price to a specified price range over a defined period.
Team that worked on the article
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO).









