7 Best Profit-Taking Strategies In Trading
Each of the seven take-profit strategies has its advantages and disadvantages, and varies in suitability for different trading styles. The seven main strategies are:
-
Percentage-Based Take Profit: At a fixed percentage above the entry point
-
Fixed-Pip Take Profit: At a fixed number of pips above the entry point
-
Average True Range (ATR) Take Profit: A value 2-3x the ATR indicator value
-
Technical Analysis Levels: Based on key support and resistance levels
-
Trailing-stop: A dynamic take-profit order that increases with the asset’s value
-
Time-based: Triggers the sale at a specified date or time
-
Fundamental-based: Closes the position based on market news or events
An integral aspect of being a successful trader is making sure that you have a clearly defined strategy, adhering to the approach that you have predefined in every trade. Using take-profit (TP) orders is a key component of a well-planned trading strategy – though it can be challenging to know what level to set your take-profit at. In this article, we look at seven different approaches to setting your take-order, examining the pros and cons of each one and explaining how to use them.
-
What is the best pips level for take profit?
The best pips for take-profit vary, with traders often considering factors like market conditions, risk tolerance, and their individual trading strategies. A general rule of thumb is to set take-profit at 3 times your stop-loss.
What are trading take-profit strategies?
When trading, it’s important to manage risk by utilizing the tools available to adhere to a predefined trading strategy. One such tool is a take-profit order. With a take-profit order, the trader specifies a price - higher than their asset’s current price - that they want their held asset to be sold at. When (or if) the price reaches that pre-set value, then the order is triggered and the asset is automatically sold. A take-profit order is so-called because the automatic sale closes the position, allowing the trader to take the profit.
Using take-profit orders is a crucial feature of a disciplined trading strategy with clearly outlined boundaries. Take-profit orders allow traders to lock in profits by securing gains, employ discipline to avoid emotional trading, and manage their risk by automating sales.
Though the act of setting a take-profit order is relatively simple, the tough part is deciding on what value the order should be. If you set the limit order too high, you risk losing any initial gains. Set it too low, and you might trigger the sale prematurely, limiting your opportunity for further profits. So how do you decide?
There are seven methods for calculating your take-profit levels that we will look at. Each strategy has varying suitability, largely depending on your trading style and financial goals. The seven we will look at are:
-
Percentage-Based Take Profit
-
Fixed-Pip Take Profit
-
Average True Range (ATR) Take Profit
-
Technical Analysis Levels
-
Trailing-stop
-
Time-based
-
Fundamental-based
These take-profit strategies are applicable to Forex and stock trading. Although we will focus mostly on Forex here, the same logic can be applied when trading in other financial markets.
Percentage-based take-profit
Choosing a take-profit level based on a percentage of the entry point value is perhaps the most simple and straightforward strategy to use. It involves setting a target profit at a specified percentage above the value of the position that you open. For example, if you open a trade at $100 USD, you could set the take-profit at 10%, which is $110 USD.
Example: Let’s imagine you’re aiming for a 5% profit in Forex trading. If you were to buy EUR/USD at 1.1250, you would set your take-profit at 1.1813, which is 0.0575 (5%) higher than your entry point. This approach has its advantages and disadvantages.
👍 Pros
• The percentage-based approach is easy to understand and implement. It’s consistent and lets you apply a standardized approach across different trades. It’s also simple, making it suitable for beginner traders. Using a percentage also accommodates varying account sizes as it is proportional.
👎 Cons
• Using a one-size-fits-all percentage-based approach overlooks the distinct characters of each asset, such as volatility or price behavior. They are also not tailored to specific market conditions. Using percentages also does not account for fundamental analysis.
Fixed-pip take profit
Much like using percentages, using a fixed-pip take-profit strategy is relatively simple. With this approach, you set a fixed number of pips above your entry point to determine where to set your take-profit level.
Example: Set a 100-pip take profit for EUR/USD bought at 1.1250, so your target is 1.1350. For example, if you buy EUR/USD at 1.1250, setting a 100-pip take profit would mean aiming for 1.1350.
👍 Pros
• This method provides consistency and clear profit targets, making it particularly suitable for range trading strategies where price movements are confined. It is also simple to apply, making it attractive for beginners.
👎 Cons
• However, it comes with the drawback of potentially missing out on more substantial profits during positive trending market conditions, and it lacks the ability to adjust to changing levels of volatility.
Average true range (ATR) take profit
The Average True Range (ATR) Take-Profit strategy leverages the ATR indicator to measure market volatility and adapt to price fluctuations. The ATR indicator is a moving average of the true ranges, typically from the past 14 days, and is made up of: the current high minus the current low, the current high minus the previous close, and the current low minus the previous close. It calculates the average range between high and low prices over a specified period to gauge volatility.
The ATR take-profit approach uses a multiple (typically 2 to 3 times) of the ATR indicator to determine what level to set the take-profit at. For example, let’s say you opened a position on the USD/JPY pairing at 144.736. Using the ATR indicator on a 1-hour candlestick chart, you find a 14-day ATR value of 0.325. Multiplying this by 3 gives you a value of 0.975, which is equal to 97.5 pips. So, you set an ATR take-profit level of 145.661.
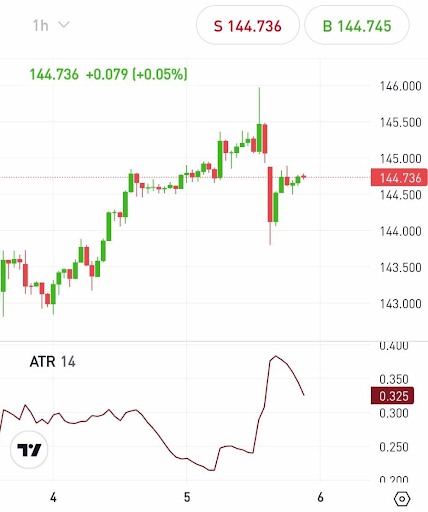
ATR indicator for USD/JPY on eToro
There are benefits and challenges to using the ATR take-profit approach.
👍 Pros
• It adjusts to market volatility, allowing for dynamic profit-taking based on current market conditions. An ATR-based take-profit is also flexible and adaptable for changing markets and different trading styles.
👎 Cons
• Setting a take-profit based on ATR can be quite complex for beginners compared to using fixed-value methods. It can also be influenced by short-term market noise, which could lead to take-profit values being set too low and prematurely triggered.
Other technical indicators, such as Bollinger Bands, could also be used in a similar way.
Technical analysis levels
Technical analysis is a key component of disciplined and mathematical trading strategies. Likewise, a take-profit order based on technical analysis allows you to evaluate trading opportunities and optimal exit points.
There are several aspects of technical analysis you could use in determining your take-profit level. You can take profits at key technical levels like support or resistance zones or channel lines. You can use divergence signals like the MACD or Awesome Oscillator (AO) to assess a potential trend reversal or weakening trend and decide on the best exit point. You can observe chart patterns like triangles, heads and shoulders, or double tops/bottoms, and use them to determine potential price targets.
👍 Pros
• Using technical analysis for take-profit can enhance your overall strategy by incorporating technical analysis principles. Additionally, it can lead to profitable exits by leveraging identified technical levels.
👎 Cons
• The downside is that you need a solid understanding of technical analysis, which may be a steep learning curve for some traders. Furthermore, the subjective nature of interpreting indicators and patterns may result in missed opportunities or premature exits.
Trailing-stop
You may have heard of a trailing stop-loss order. With a trailing stop-loss, the stop-loss order price adjusts if an asset’s value moves upward, staying at a fixed level below the highest price that the asset reaches. A trailing take-profit works by only triggering the stop-loss once a certain profit level has been reached. It is typically used when trading cryptocurrencies.
Let’s say you open a trade worth $200 (on any asset) and set a take-profit of 10% at $220, and then a trailing take-profit of 5%. If the price reaches $210, nothing happens. If the price reaches $220, a stop-loss order is automatically set at 5% below this value, at $209. If the price moves down to $210 again, the stop-loss stays at $209, but if the price moves up to $240, the stop-loss adjusts to $228. It works very similarly to a trailing stop-loss order, except it is only triggered when the initial take-profit level is reached.
👍 Pros
• It adjusts to changing market conditions and captures additional gains in trending markets. Trailing take-profits lock in profits while allowing flexibility for potential upward movements.
👎 Cons
• Using a trailing take-profit requires understanding and monitoring market dynamics to optimize results.
Time based take profit
One of the more easy-to-use take-profit setting methods is to simply trigger the sale of an asset when a certain date or time is reached, or when a specific amount of time has passed since opening the trade. This is known as a time-based conditional order. If you want to avoid holding onto a position over the weekend for example, you could set an order that triggers the asset’s sale on Friday evening, but bear in mind – your position wouldn’t be guaranteed to be in the green.
This approach might be useful if you want to limit your exposure to market volatility or are trying to take advantage of specific market conditions that you expect to expire at a specific time. It can also be useful if you want to time your exit when you know a certain market-related event will happen.
For example, Take-Two Interactive, the company behind the famous Grand Theft Auto series, recently announced a trailer for their new game, GTA 6, with the trailer release set for 9AM on December 5th. If you wanted to try to capitalize on the hype surrounding this, you could buy TTWO stocks and trigger the sale of the stocks at the time of market opening (9:30AM) on the day of the trailer’s release.
👍 Pros
• The set-and-forget approach of a time-based strategy enforces disciplined trading without constant monitoring. It also prevents the temptation to constantly adjust take-profit levels, reducing the risk of impulsive decisions.
👎 Cons
• However, market unpredictability could lead to exits without profit, and a fixed time frame could cause you to miss out on potential profits.
Fundamental based take profit
Setting a fundamental-based take-profit involves setting exit levels based on fundamental factors affecting an asset, such as company earnings, economic indicators, or geopolitical events. This strategy relies on analyzing the intrinsic value of the asset rather than market trends or technical indicators.
Let’s say you were trading stocks - a fundamental-based take-profit could be triggered by negative news about a competitor's earnings, influencing the perceived value of a similar stock. For instance, if a major competitor of META stock reports poor earnings, you might decide to take profit on META stock, anticipating a potential negative impact on the industry.
👍 Pros
• Using fundamentals for setting take-profits aligns with long-term investment strategies, and is based on tangible factors that can affect the value of the traded asset.
👎 Cons
• The in-depth understanding of fundamental analysis required for this approach can make it quite difficult to use. Additionally, market reactions to fundamental events are not always straightforward and can lead to unpredictable events.
Best Forex brokers


Tips for calculating a take profit
-
Don't be greedy: It’s easy for the desire for more profit to cloud your judgment and lead you to set a high-take profit. Be realistic and set a limit that aligns with your trading strategy and is based on analysis, not optimism.
-
Account for risk-reward ratio: Whichever take-profit strategy you use, ensure that it offers a favorable risk-reward ratio. This helps maintain a balance between potential profit and acceptable risk.
-
Regularly review and adjust: Markets are dynamic, so maintain flexibility by regularly reviewing and adjusting your take-profit levels based on changing conditions. A set-and-forget approach might not be suitable for all scenarios.
Summary
In conclusion, it’s best to choose a take-profit strategy that aligns with your trading strategy. The seven approaches that we looked at here each have their own best use cases. It’s advisable to combine multiple approaches and constantly adapt your take-profit levels based on continuous market analysis.
Glossary for novice traders
-
1
Broker
A broker is a legal entity or individual that performs as an intermediary when making trades in the financial markets. Private investors cannot trade without a broker, since only brokers can execute trades on the exchanges.
-
2
Take-Profit
Take-Profit order is a type of trading order that instructs a broker to close a position once the market reaches a specified profit level.
-
3
Trading
Trading involves the act of buying and selling financial assets like stocks, currencies, or commodities with the intention of profiting from market price fluctuations. Traders employ various strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management practices to make informed decisions and optimize their chances of success in the financial markets.
-
4
ATR Indicator
ATR (Average True Range) is a volatility indicator that helps traders assess the potential price range or volatility of a financial instrument. It calculates the average of true price ranges over a specified period, providing insight into the level of price fluctuations within that timeframe.
-
5
Volatility
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.
Team that worked on the article
Jason Law is a freelance writer and journalist and a Traders Union website contributor. While his main areas of expertise are currently finance and investing, he’s also a generalist writer covering news, current events, and travel.
Jason’s experience includes being an editor for South24 News and writing for the Vietnam Times newspaper. He is also an avid investor and an active stock and cryptocurrency trader with several years of experience.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
Tobi Opeyemi Amure is an editor and expert writer with over 7 years of experience. In 2023, Tobi joined the Traders Union team as an editor and fact checker, making sure to deliver trustworthy and reliable content. The topics he covers include trading signals, cryptocurrencies, Forex brokers, stock brokers, expert advisors, binary options.
Tobi Opeyemi Amure motto: The journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step.









