Best indicators for Forex scalping
The top 9 indicators used for scalping by seasoned traders are:
-
1
Bollinger Bands
-
2
RSI
-
3
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
-
4
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
-
5
Parabolic SAR
-
6
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
-
7
Stochastic Oscillator
-
8
Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
-
9
Fibonacci Retracement
In the fast-paced world of Forex scalping, selecting the most effective indicators is the key to success. These indicators serve as essential tools for traders aiming to capitalize on rapid price movements within short timeframes. By analyzing market trends, momentum, and volatility, scalpers can make swift and informed decisions. Key indicators such as Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands provide crucial insights into market trends and volatility, aiding traders in identifying optimal entry and exit points. To explain this better, the experts at TU have prepared a list of the best indicators for scalping. They have also discussed their key features and enter and exit points to provide a holistic overview for traders who wish to incorporate them into their trading strategies.
Bollinger Bands
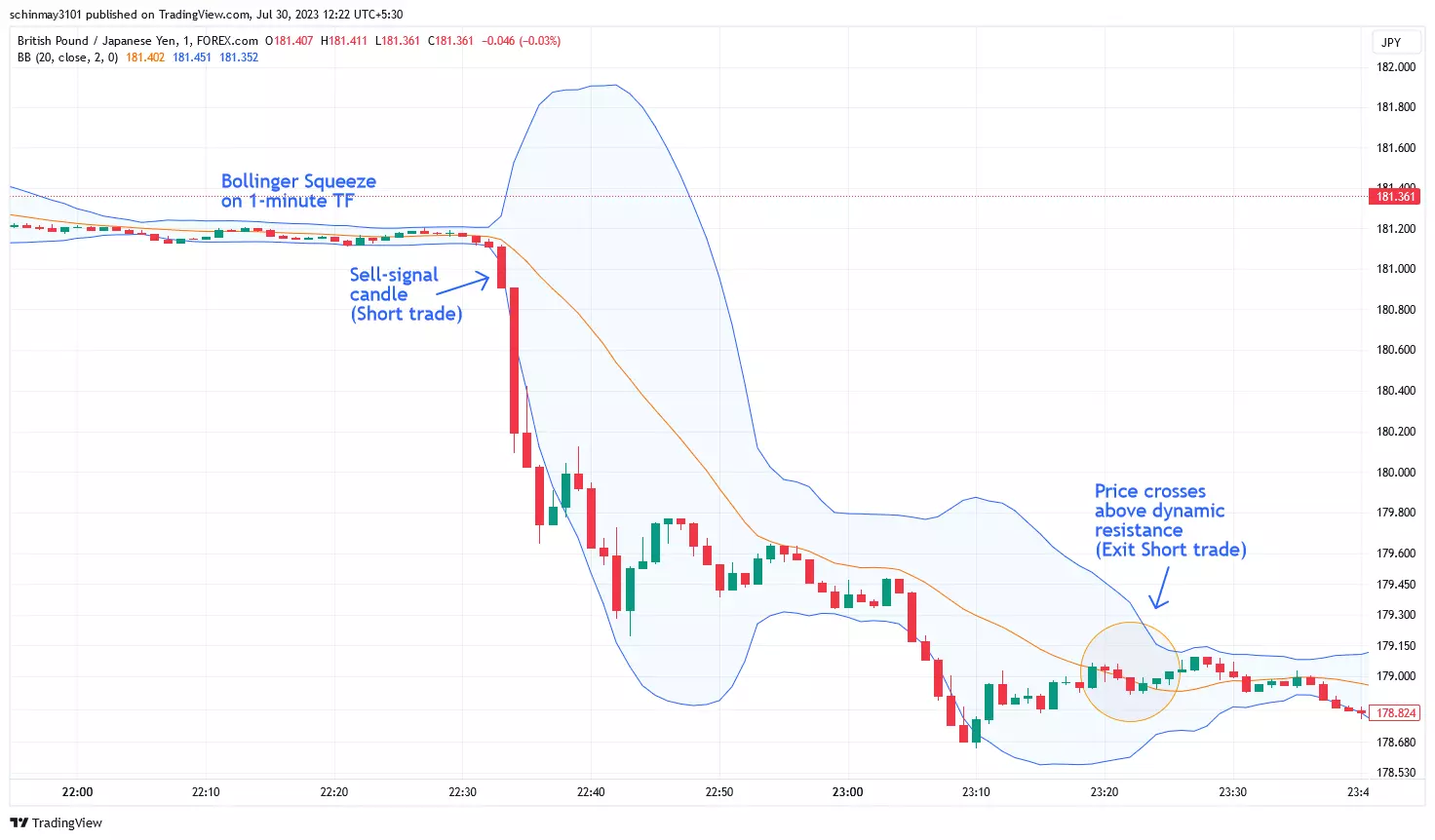
Bollinger Bands Indicator Illustration
Features
Bollinger Bands serve as a popular tool in the toolkit of traders for assessing market volatility and pinpointing possible moments for entering or exiting trades. Bollinger Bands are composed of three lines that are plotted on a price chart. The first line is a simple moving average (SMA) and the other two lines are standard deviation lines, one located above the SMA and the other below it. These bands dynamically adjust their width based on market volatility. When volatility increases, the bands widen, and when it decreases, they contract. The bands visually represent price volatility and potential price levels where trends could reverse. Traders commonly use Bollinger Bands to identify overbought or oversold conditions and potential trend shifts.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
Bollinger Bands are instrumental in signalling entry and exit points. Price touching or exceeding the upper band can suggest overbought conditions, possibly indicating an upcoming price decrease or reversal. On the other hand, when price touches or breaches the lower band, it may signify an oversold situation, and could be an early signal for a bounce or reversal. Further, a Bollinger Bands squeeze occurs when the bands narrow, indicating a period of low volatility that often precedes a significant price movement. Traders watch for this squeeze as a potential setup for entry. When the bands suddenly expand after a squeeze, it can signify the start of a new trend or a breakout, prompting traders to consider an entry point. Exit points can be chosen when the price movement following the squeeze loses momentum or reaches the dynamic resistance level.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
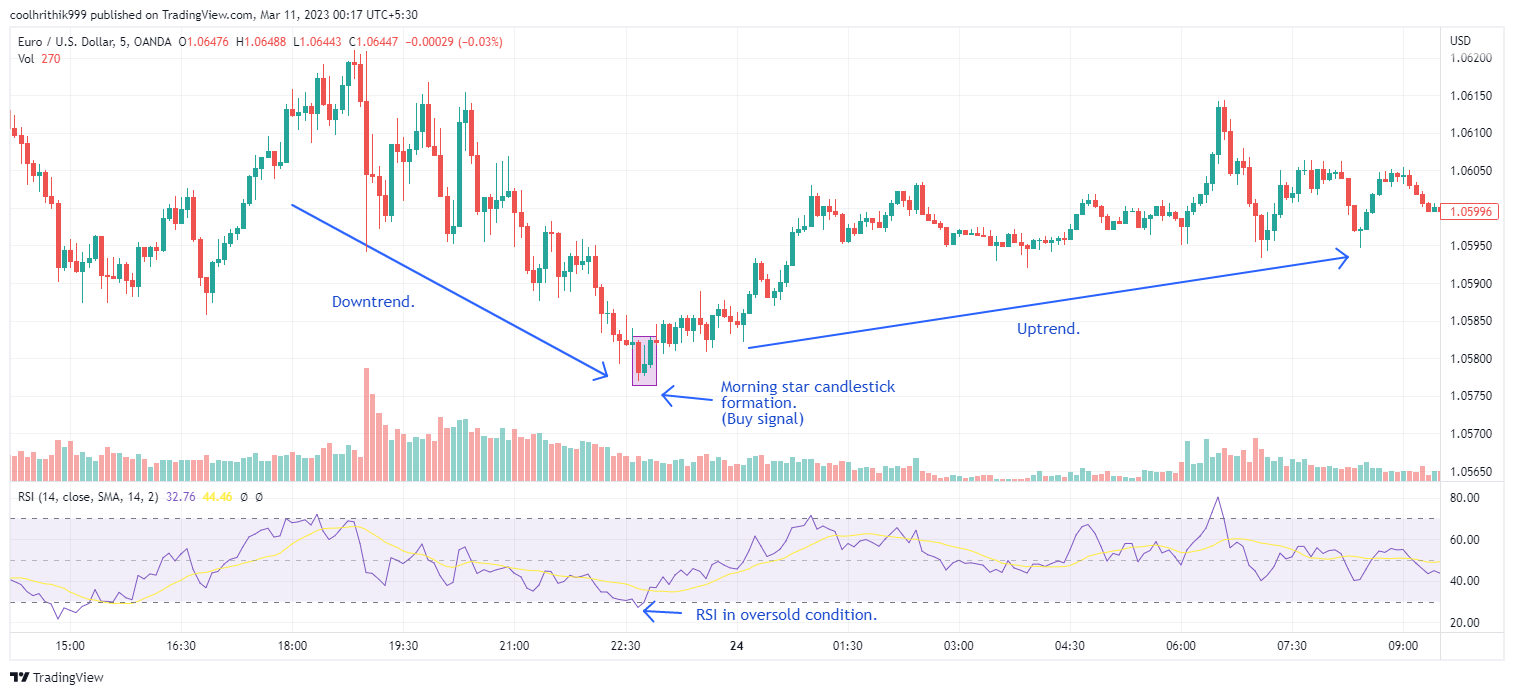
RSI Indicator Illustration
Features
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a prominent momentum oscillator used in technical analysis. It contrasts the speed and magnitude of price movements, indicating whether an asset is overbought or oversold. The value of RSI ranges from 0 to 100. Generally, if the RSI is reading above 50, traders will consider the trend to be bullish, and if it is below 50, traders will often consider the momentum to be bearish. However, above 70, it suggests potential overbought conditions, while readings below 30 indicate possible oversold conditions. RSI also helps identify divergences between price and momentum, offering insights into potential trend reversals. Lastly, it's important to note that the RSI doesn't make comparisons between different assets. Instead, it assesses the asset's power based on its own previous prices, and not the entire market.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
When RSI rises above 70, it might suggest that the asset is becoming overvalued, signalling a possible time to short or exit a trade. Conversely, when RSI drops below 30, it could indicate that the asset is oversold, potentially indicating a buying opportunity. However, relying solely on these levels might lead to false signals. Traders often wait for RSI to reverse direction before acting, or they consider divergences between RSI and price movements. Moreover, integrating RSI with other indicators can refine decisions and improve the accuracy of entry and exit strategies.
Simple Moving Average
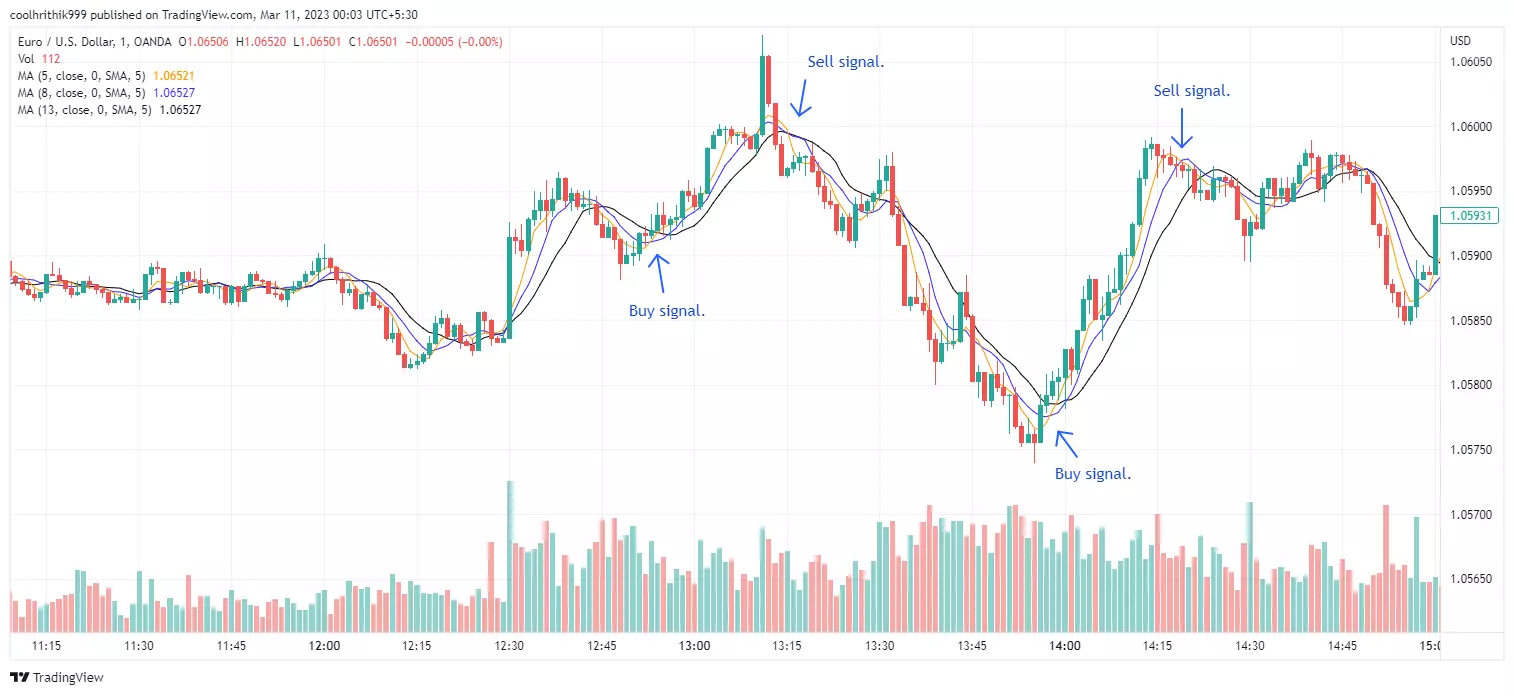
SMA Indicator Illustration
Features
Simple moving averages serve as a tool for traders to grasp the trend's direction in the market. The name "moving" is fitting since it consistently updates itself by recalculating with the most recent price information available. Traders employ moving averages to understand support and resistance by studying how an asset's price moves. However, a limitation is that this indicator reflects only an asset's past price movement, and so, it is considered a lagging indicator, trailing the asset's price movements to generate signals or reveal trend directions.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
The crossing points of different Moving Averages can indicate changes in trends. If a shorter Simple Moving Average (SMA) crosses above a longer one, it might mean that the trend could go up, suggesting a good time to buy. Conversely, if a shorter SMA crosses below a longer one, it might imply that the trend could go down, hinting at a suitable time to sell. To make their trading decisions more accurate, traders often increase the number of moving averages or combine them with other tools and market analysis. This synergy helps them better understand market movements and refine their trading strategies.
Best Brokers for Scalping

Exponential moving average
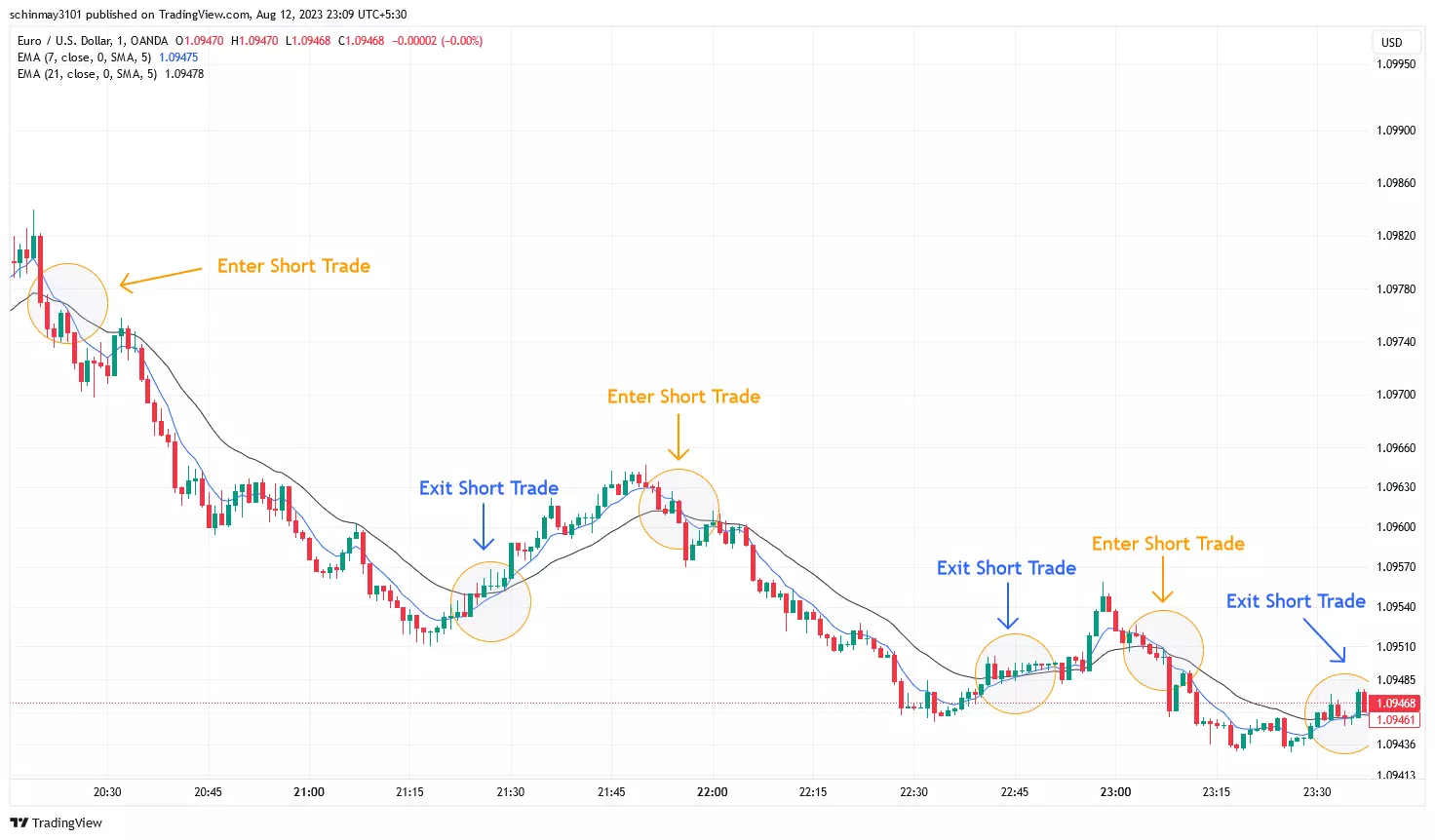
EMA Indicator Illustration
Features
An exponential moving average (EMA) belongs to the moving average (MA) family and gives more importance to the latest data points. It's also known as the exponentially weighted moving average. Unlike the simple moving average (SMA), which treats all data points equally, the EMA reacts more substantially to recent price shifts. EMA's weighting approach enhances its ability to capture emerging trends swiftly, making it popular among traders seeking up-to-date insights. Its adaptability to different timeframes and conditions adds to its appeal, aiding traders in tracking evolving trends effectively.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
EMA serves as a guide for entry and exit decisions. Traders often focus on EMA crossovers, where a shorter EMA intersects with a longer EMA. When the shorter EMA crosses above the longer one, it can indicate a potential uptrend and a favorable time to enter a trade. Conversely, a shorter EMA crossing below a longer EMA might suggest a potential downtrend and a suitable moment to exit or consider short positions. Integrating EMA signals with other tools, like support and resistance levels, enhances traders' accuracy in timing their trades.
Parabolic Stop and Reverse (SAR)
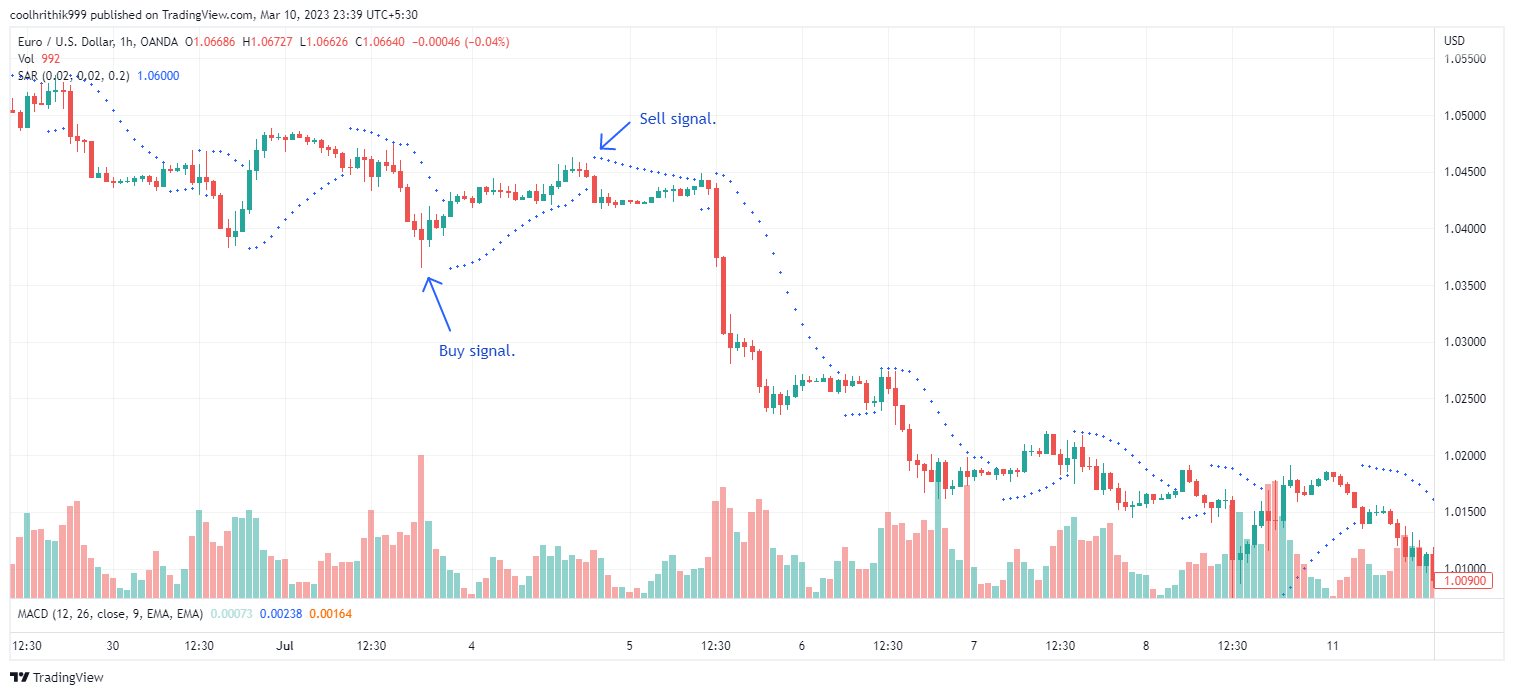
EMA Indicator Illustration
Features
Parabolic Stop and Reverse (SAR) is a technical indicator used in trading to determine potential stop-loss levels and reversals. It appears as dots on a price chart, indicating the direction in which the trend might change. When the dots are below the price, it suggests an upward trend, and when above, a downward trend. Parabolic SAR dynamically adjusts itself based on price movements, tightening during stable periods, and widening during volatile phases. Traders often use Parabolic SAR in conjunction with other tools to refine their entry and exit decisions.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
During an uptrend, if the asset's price is below the SAR dots, it suggests a potential buying opportunity. In a downtrend, if the price is above the SAR dots, it indicates a possible selling chance. Traders can also use these dots as trailing stop-loss levels to protect profits during trends. When the dots switch direction, it can signal a potential reversal, guiding traders to exit or consider a new position. Do note that using Parabolic SAR alongside other indicators can enhance its effectiveness in making informed trading decisions.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
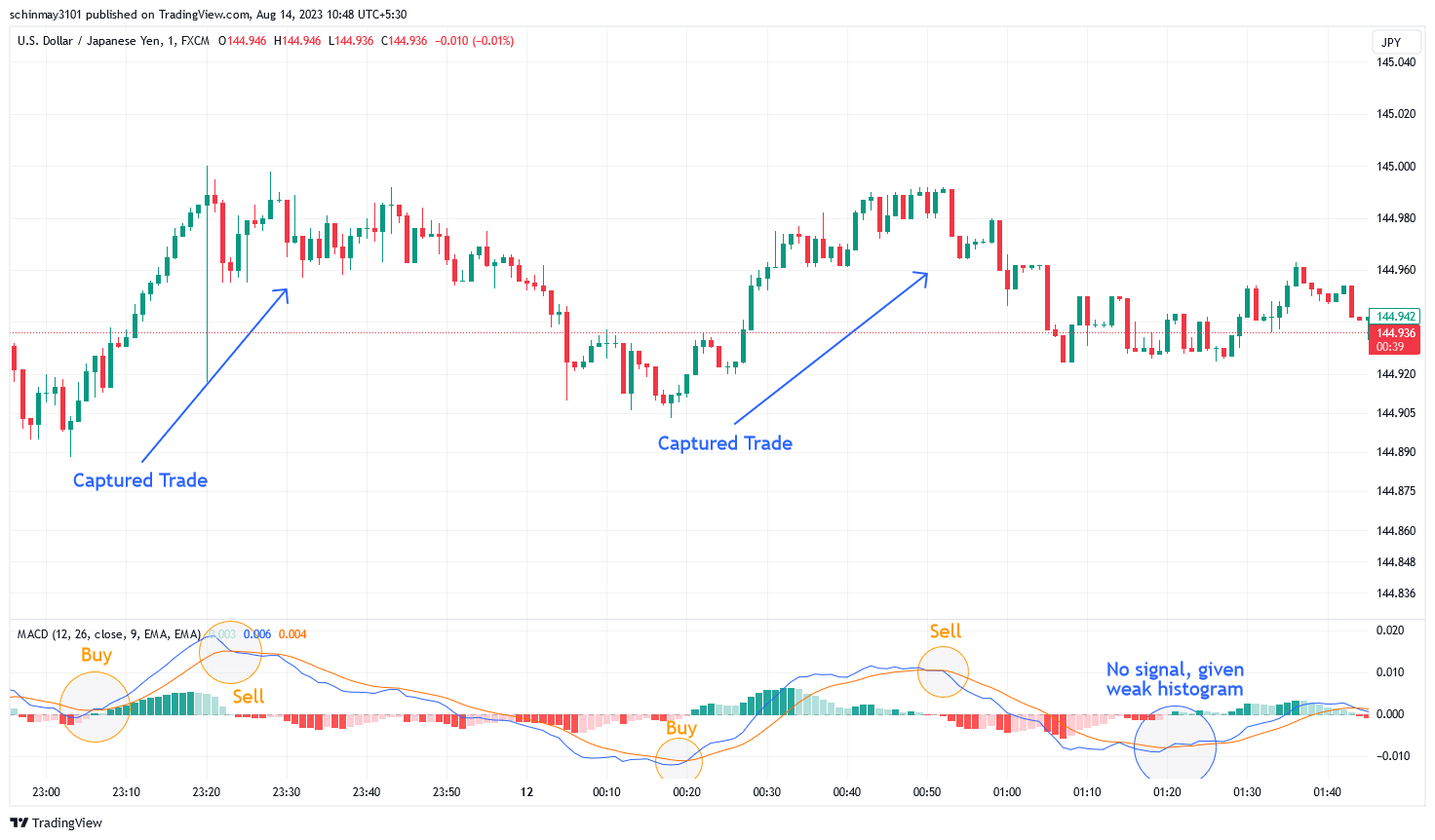
MACD Indicator Illustration
Features
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a technical indicator that generates trading signals based on exponential moving average (EMA) relationships. The indicator comprises of an MACD line (blue), signal line (red), and histogram (green or red depending on the trend). Calculated from the difference between 12 and 26-period EMAs, the MACD line reflects momentum. The signal line, formed by a 9-period EMA of the MACD line, represents trend strength. The MACD's zero line is pivotal: crossing above signifies an upward trend, while below indicates a downward one. Crossovers between the MACD and signal lines generate buy (above) or sell (below) signals. Oscillating near zero, the MACD is primarily used for identifying overbought or oversold conditions for trading.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
An upward trend is signaled when the MACD line crosses above the zero line, suggesting a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, a downward trend is indicated when the MACD line crosses below the zero line, hinting at a potential selling chance. Moreover, the crossover of the MACD line above the signal line often triggers a buy signal, while its crossover below the signal line prompts a sell signal. Traders can also refer to the length of histogram bars to gauge the strength of the signal. Lastly, do note that combining MACD signals with other indicators can enhance accuracy, helping traders make well-informed decisions amidst market fluctuations.
Stochastic oscillator
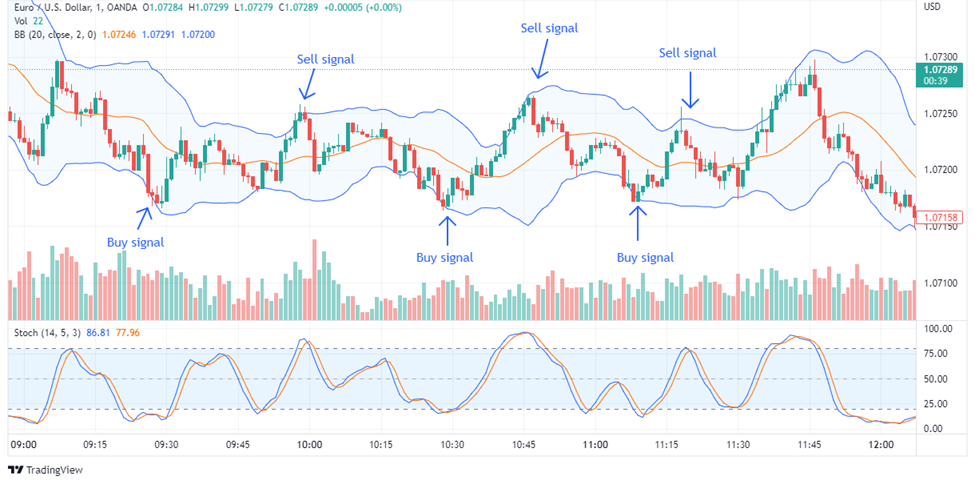
Stochastic Indicator Illustration
Features
The stochastic oscillator is a momentum indicator that compares a security's closing price with its price range over a specific time frame. It generates overbought and oversold signals in a range of 0–100, where readings above 80 indicate overbought conditions and readings below 20 indicate oversold conditions. The indicator features two lines – one reflects the daily oscillator value, and the other its three-day simple moving average. Since price tends to follow momentum, the point where these lines intersect is a potential reversal signal, signifying a significant momentum shift. Divergence between the oscillator and price action is also crucial. For instance, if a bearish trend makes a lower low but the oscillator marks a higher low, it suggests weakening bearish momentum and a possible bullish reversal.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
When %K crosses above %D, it can signal an upward trend, offering a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, %K crossing below %D might indicate a downward trend and a possible selling chance. Overbought and oversold conditions, as indicated by %K values exceeding 80% or falling below 20%, respectively, can suggest potential reversal points. Finally, note that combining Stochastic signals with other tools or confirmation techniques, such as Bollinger bands, can enhance precision in trade decisions, contributing to more effective risk management and profit maximization.
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
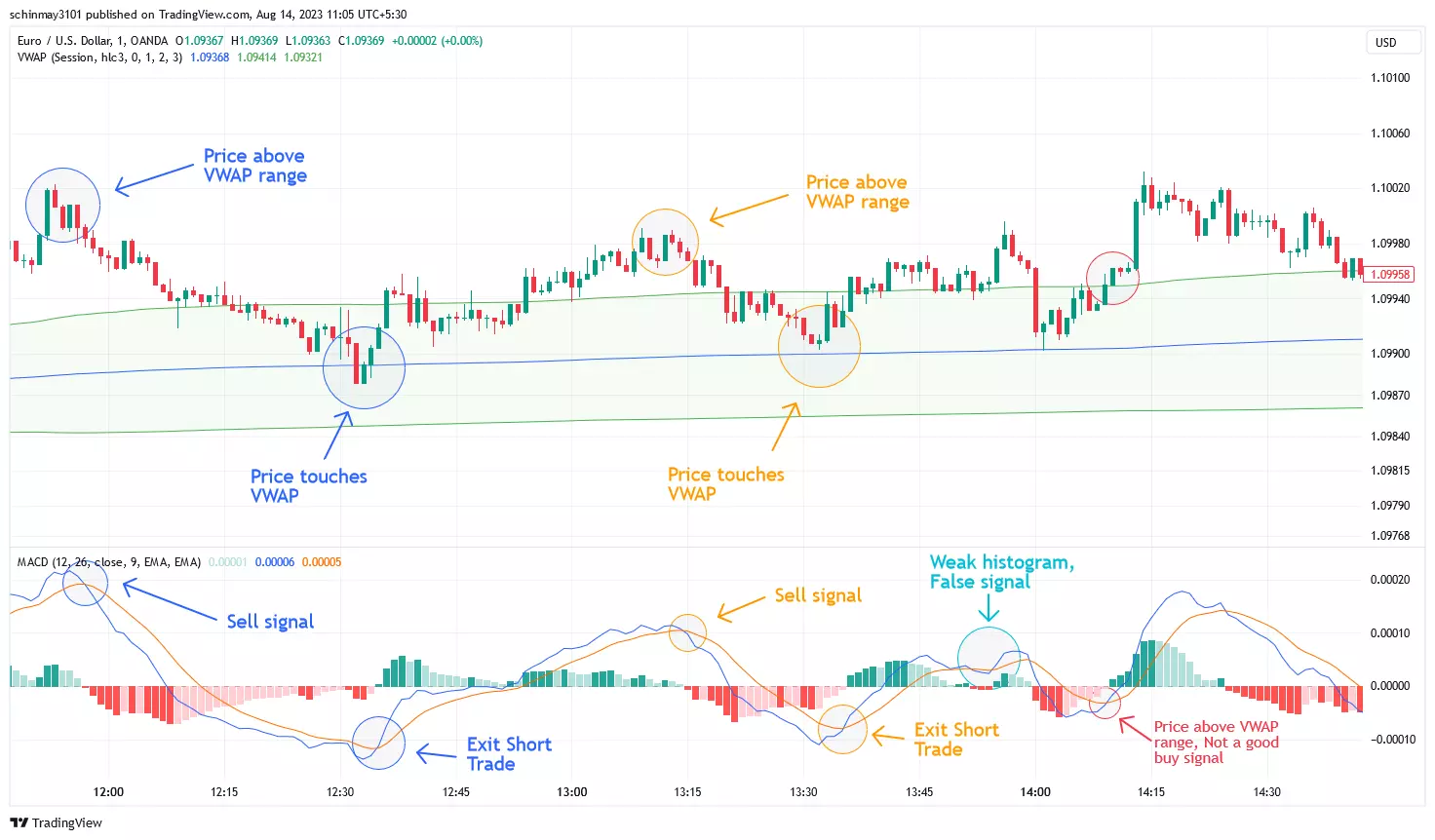
VWAP Indicator Illustration
Features
The Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) evaluates the average price at which a security has traded within a defined time frame, factoring in traded volume. Its calculation entails summing the total dollar value of trades during the stipulated period and dividing it by the total number of shares traded. This approach amalgamates price and trading volume for a more accurate average price representation than a simple arithmetic average. VWAP functions as an execution strategy in algorithmic trading, helping to achieve an improved average price for substantial share volumes over a specific duration. Moreover, VWAP's role in assessing market liquidity is valuable, with higher values denoting more buying and selling activity, and lower values suggesting reduced liquidity.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
When the current price is above VWAP, it could signify a potential selling chance, considering the price relatively high. Conversely, when the price below VWAP, it might suggest a buying opportunity, as the price could be relatively low. Monitoring price movements around VWAP throughout the day helps assess trend strength. Moreover, combining VWAP analysis with other indicators, such as MACD, refines entry and exit decisions, aiding traders in making well-informed choices.
Fibonacci Retracement
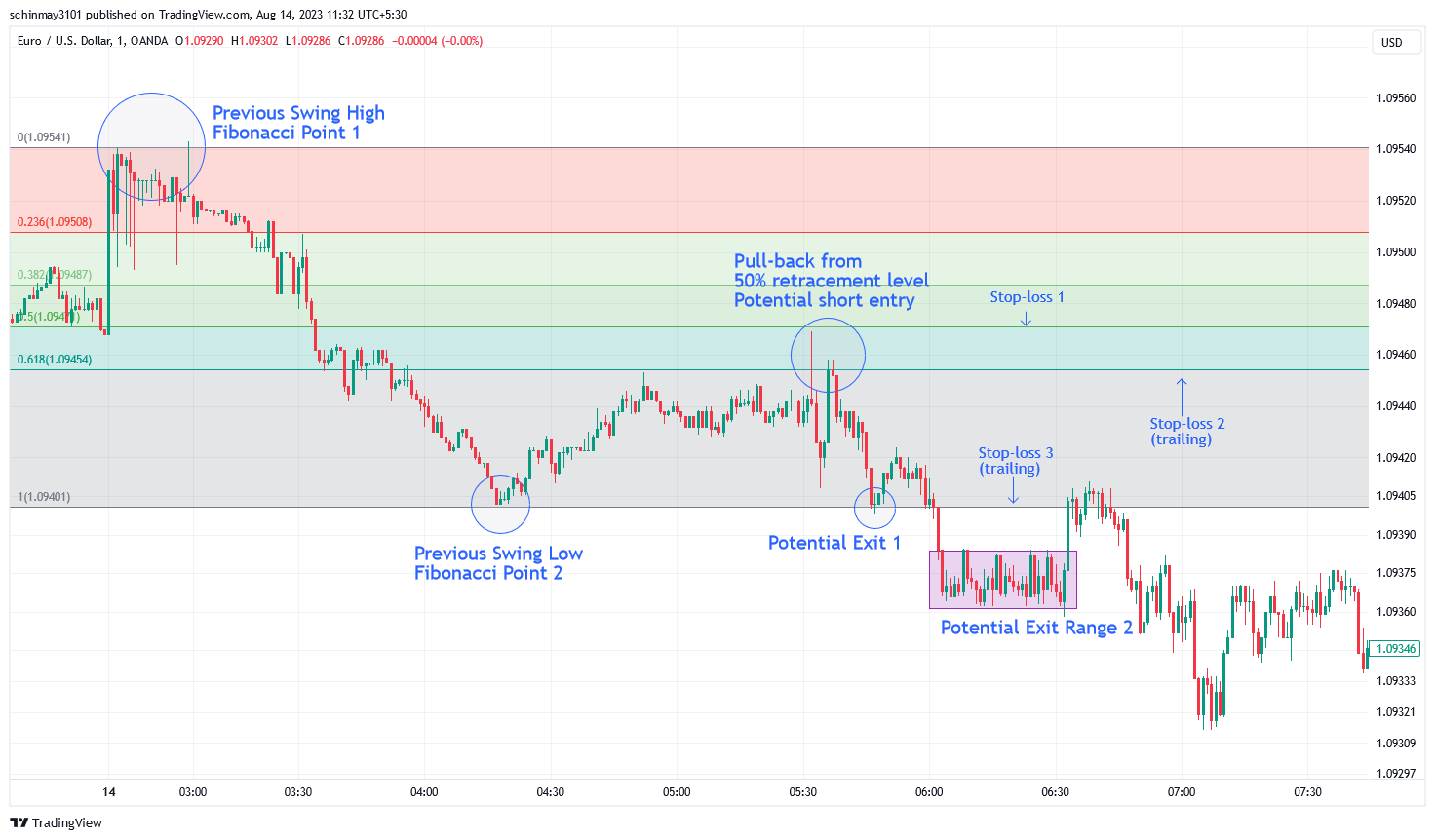
Fibonacci Day Trading Illustration
Features
Fibonacci Retracement is a popular technical analysis tool based on the Fibonacci sequence, which highlights potential support and resistance levels in financial markets. Traders use key Fibonacci levels (typically 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%) to identify potential price reversals after a significant market move. These levels are drawn from the high to low or low to high of a specific price range. The tool assumes that markets often retrace a portion of their previous movement before continuing in the original direction. Fibonacci Retracement is particularly useful in identifying potential entry points, stop-loss placements, and assessing the strength of market trends. It aids traders in understanding market psychology and making more informed trading decisions. Read more in the article: Why The Fibonacci Indicator Is Important.
Example (Entry and Exit Points)
Key Fibonacci levels (e.g., 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%) highlight potential support or resistance after market moves. Traders may consider buying or selling near these levels, anticipating reversals. For instance, entering around the 50% level might signal trend continuation. By coupling Fibonacci levels with other indicators, traders enhance their decision-making precision, leading to optimized trading strategies.
Is Scalping Profitable?
Yes, scalping can make money, but it's a complex strategy. According to experts, scalping is best-suited for traders who can commit a lot of time to trading and are okay with taking higher risks. To do well, you need practice and gain a deeper understanding of how markets work. Further, you also need to learn a lot about charts and indicators to decide when to buy or sell. Traders must be well-versed in technical analysis, closely monitoring charts and indicators to identify optimal entry and exit points. Equally crucial is efficient risk management, as rapid trades can expose traders to heightened volatility and unexpected market shifts. A well-defined risk-reward ratio and strict stop-loss orders are also essential to safeguard against potential losses. Furthermore, scalping necessitates a reliable and fast trading platform with low latency to capitalize on fleeting price movements. It is paramount to keep transaction costs, including spreads and commissions, in check, as they can impact overall profitability. Finally, just remember that success in scalping comes with careful planning prudent risk management, and the awareness that success demands substantial effort and continuous learning.
Top Scalping tips
If you are considering taking up scalping as your trading style, the following expert tips might help you:
Learn the basics - Before diving in, understand the basics of scalping, including its strategies, risks, and rewards
Quick decision making - Develop the ability to make rapid decisions based on technical signals and price action
Minimal exposure - Avoid holding positions for extended periods to reduce exposure to market risks
Tight spreads - Trade in markets with low spreads to minimize trading costs, which are critical in scalping
Limited indicators - Focus on a few key indicators that align with your strategy instead of overcrowding your charts
Profit targets and Stop-loss - Set clear profit targets and stop-loss levels to secure gains and mitigate losses
Continuous learning - Stay updated with market trends, trading techniques, and refine your skills through continuous learning
Summary
Scalping, a fast-paced trading strategy, aims to capitalize on minor price fluctuations within short timeframes. Various indicators enhance scalpers' decision-making process, including Bollinger Bands, moving averages, RSI, and many more. Scalping demands quick decision-making, efficient risk management, and proficiency in chosen indicators. Traders should opt for liquid markets, use short timeframes, and maintain minimal exposure. Learning, practice, and adaptability are key to success in this dynamic and intense trading approach. However, its only suitable for time-rich traders, requiring dedication and a solid understanding of the chosen indicators and market dynamics.
FAQs
What is the best 1 min scalping indicator?
According to seasoned traders, the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) are among the best 1 min scalping indicators offering reasonable accuracy and reliability.
What are the best hours for scalping?
Experts suggest that liquidity is highest when there are the trading sessions of various countries overlap. Based on the same argument, the best hours for Forex scalping is considered to be during the New York and London trading sessions that are live at 13:00 - 22:00 GMT/BST and 08:00 – 17:00 GMT/BST respectively.
What win percentage is good for scalping?
For scalping, experts suggest maintaining a win percentage of at least 50%+ in order to reap rewards that are comparable to the risky nature of this trading style.
Is scalping even profitable?
Yes. Scalping may be profitable for traders who follow a disciplined approach to the trading style and do not give away to emotions. Doing so requires high trading experience and a strong trading psychology.
Team that worked on the article
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Dr. BJ Johnson is a PhD in English Language and an editor with over 15 years of experience. He earned his degree in English Language in the U.S and the UK. In 2020, Dr. Johnson joined the Traders Union team. Since then, he has created over 100 exclusive articles and edited over 300 articles of other authors.
The topics he covers include trading signals, cryptocurrencies, Forex brokers, stock brokers, expert advisors, binary options. He has also worked on the ratings of brokers and many other materials.
Dr. BJ Johnson’s motto: It always seems impossible until it’s done. You can do it.
Mirjan Hipolito is a journalist and news editor at Traders Union. She is an expert crypto writer with five years of experience in the financial markets. Her specialties are daily market news, price predictions, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICO). Mirjan is a cryptocurrency and stock trader. This deep understanding of the finance sector allows her to create informative and engaging content that helps readers easily navigate the complexities of the crypto world.










