Top trend reversal signals - patterns and indicators
The ability to identify trend reversals in trading is a valuable skill that can significantly enhance a trader's decision-making process and increase the probability of success. With markets constantly evolving, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the various patterns and indicators that signal trend reversals. So, in this comprehensive review, the experts at TU will explore the top nine trend reversal signals, through both chart patterns and technical indicators. By mastering these techniques, you will be well-equipped to capitalize on trend reversals and improve your overall trading performance.
According to Traders Union’s experts the 9 trend reversal signals that every trader should learn are:
-
Head and Shoulders chart pattern
-
Double Top and Double Bottom chart pattern
-
Rounding Top and Rounding Bottom chart pattern
-
Triple Top and Triple Bottom chart pattern
-
Falling and Rising Wedge chart pattern
-
Moving Averages (MAs) indicator
-
Bollinger Bands
-
MACD indicator
-
RSI indicator
What is a trend reversal?
A trend reversal is a significant shift in market direction, marking the end of an existing trend and the beginning of a new one. Traders need to recognize trend reversals to make informed decisions about their positions, as they can provide valuable opportunities to enter or exit trades. Here are some key points in identifying trend reversals as suggested by our experts.
Key Points:
Analyze price action to observe shifts in market direction, such as changes from higher highs and higher lows to lower highs and lower lows (or vice versa)
Recognize chart patterns that signal potential trend reversals, including Head and Shoulders, Double Top, Double Bottom, and other classic reversal patterns
Utilize technical indicators like MACD, RSI, and Stochastic Oscillator to generate trend reversal signals and confirm your observations from price action and chart patterns
Combine multiple signals and techniques for a more reliable assessment of potential trend reversals, increasing the probability of successful trades
Continuously refine and adapt your trend reversal identification strategy, as markets are dynamic and ever-changing
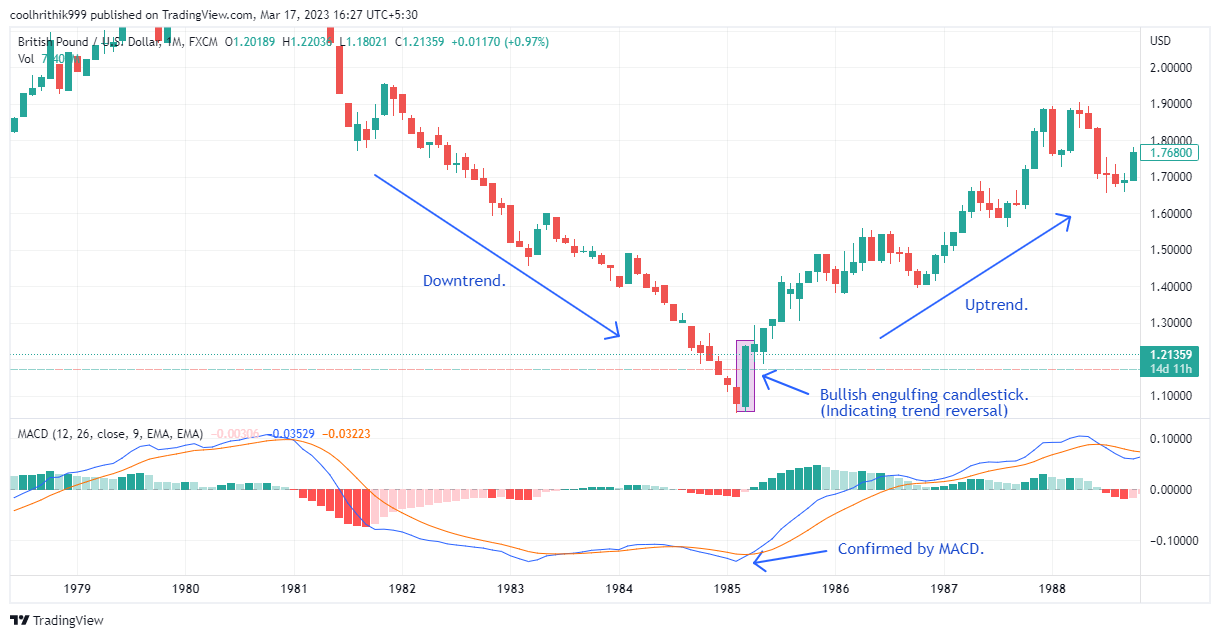
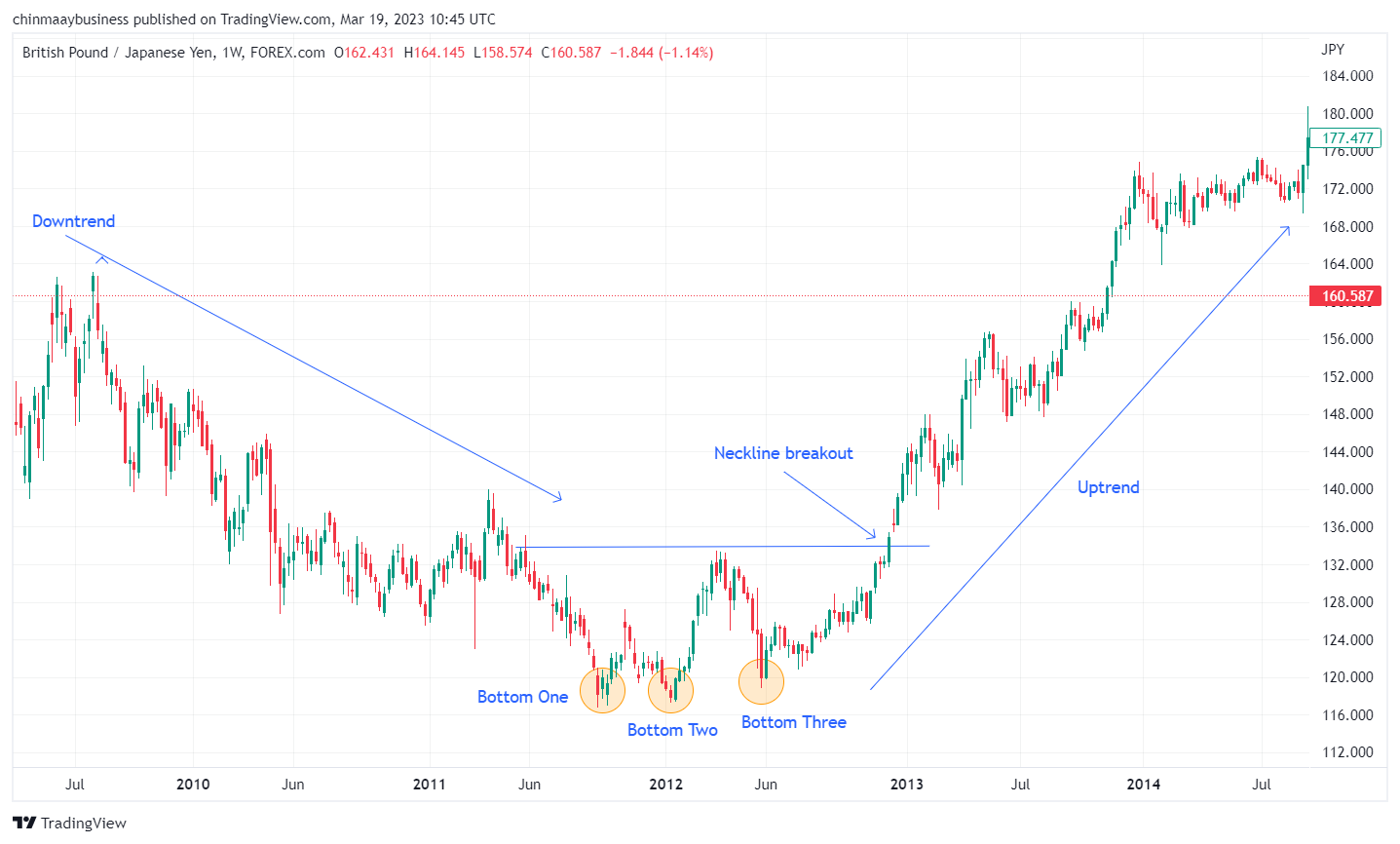
GBP/USD monthly chart
The above illustration portrays a significant trend reversal on the GBP/USD monthly chart, highlighted by a bullish engulfing candlestick pattern and supported by a positive MACD crossover, indicating a potential shift in momentum towards an upward trend.
Best Trend Reversal IndicatorsTop 5 trend reversal patterns
Understanding these key trend reversal patterns can give you a significant advantage in the trading arena. So, in this section, the experts will delve into some of the most significant patterns, explaining their characteristics and how they can signal an impending change in market direction.
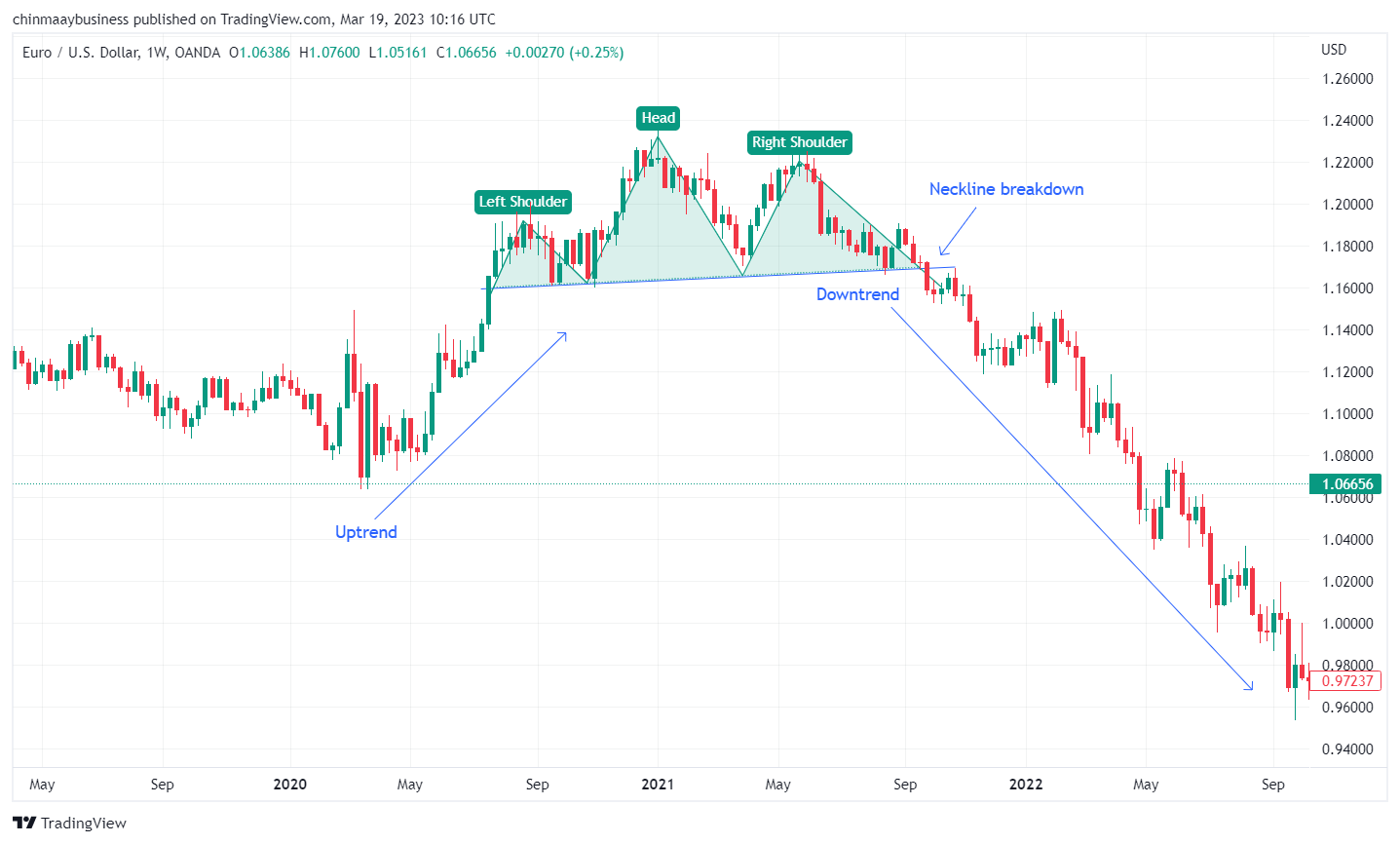
1. Head and Shoulders
The Head and Shoulders pattern is a classic reversal pattern that often signals the end of an uptrend. It consists of three peaks, with the middle peak (the "head") being the highest and the two adjacent peaks (the "shoulders") being lower. The pattern is completed when the price breaks the neckline, which is a support line drawn by connecting the two troughs between the peaks. When the neckline is breached, traders may look for a reversal in the trend, from bullish to bearish.
Head and Shoulders pattern
2. Double Top and Double Bottom
The Double Top and Double Bottom patterns are twin patterns that signal reversals at the end of an uptrend and downtrend, respectively. A Double Top forms when the price reaches a resistance level twice but fails to break through. Conversely, a Double Bottom occurs when the price reaches a support level twice without breaking below. These patterns are confirmed when the price breaks through the neckline, signaling a trend reversal from bullish to bearish for a Double Top and from bearish to bullish for a Double Bottom.
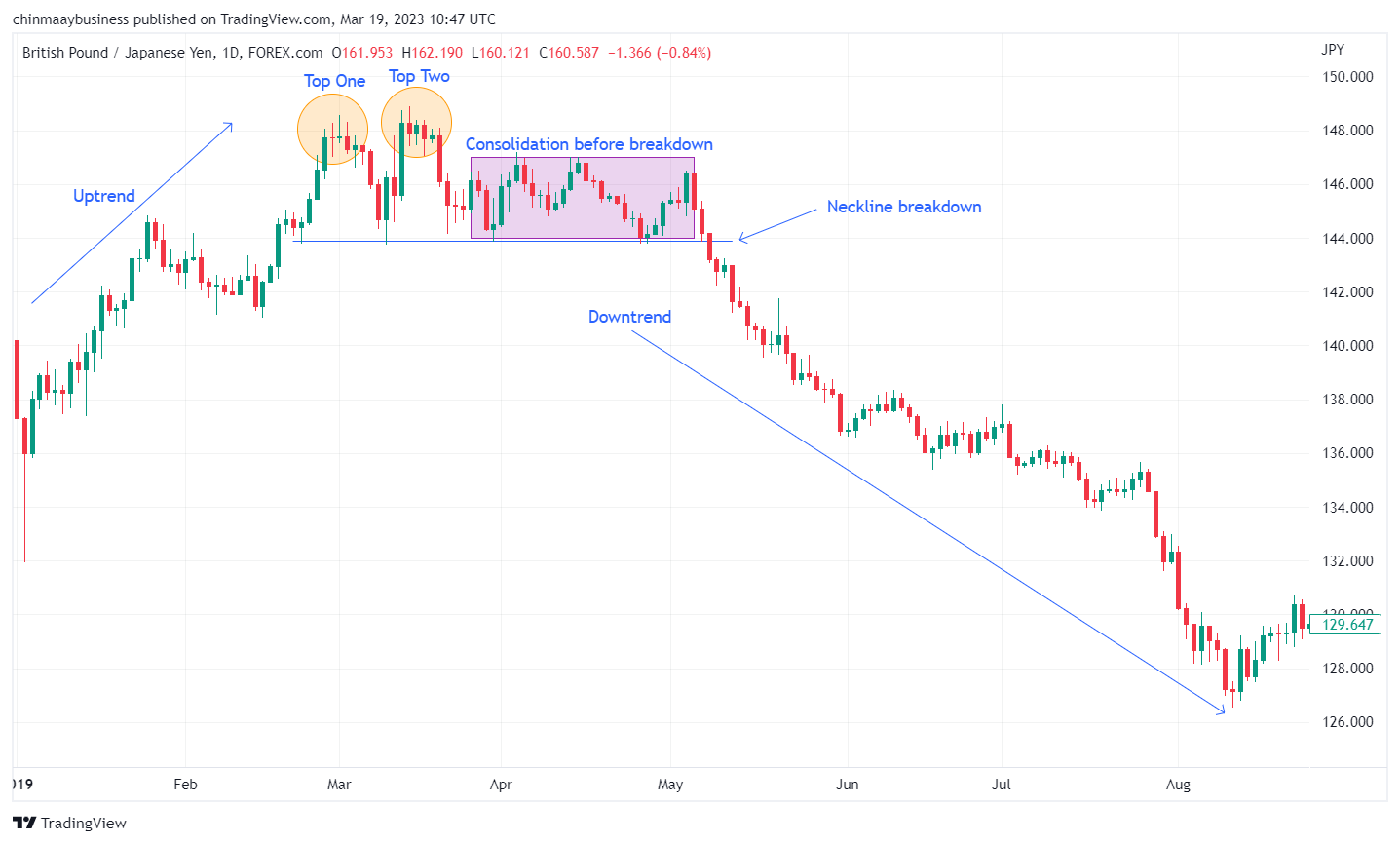
Double Top patterns
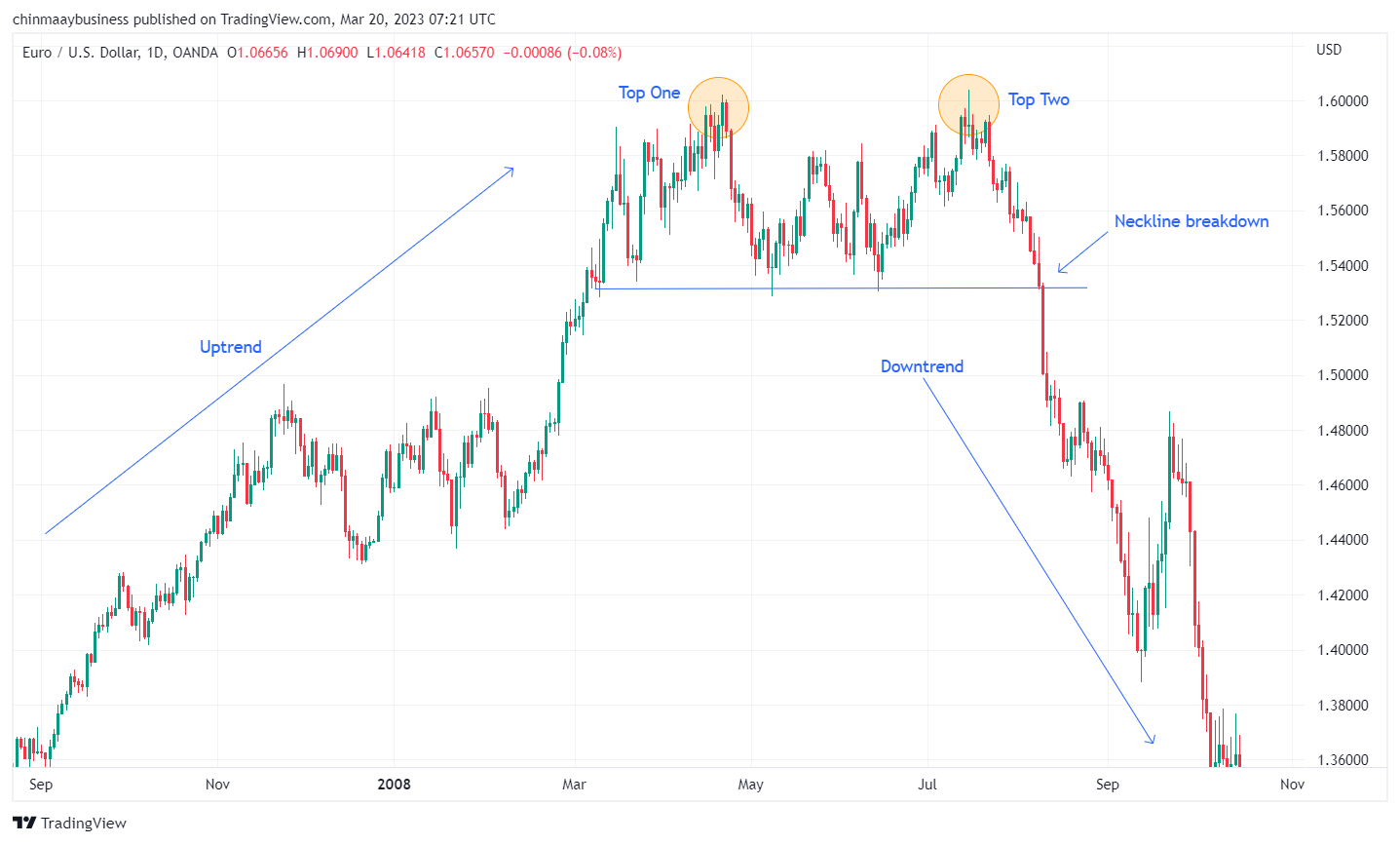
Double Bottom patterns
3. Rounding Top and Rounding Bottom
Rounding Top and Rounding Bottom patterns are reversal patterns that develop gradually over time. A Rounding Top forms at the end of an uptrend and resembles a dome-shaped curve, while a Rounding Bottom takes shape at the end of a downtrend and resembles a bowl-shaped curve. These patterns indicate a gradual shift in market sentiment, with buying or selling pressure slowly diminishing. The trend reversal is confirmed when the price breaks through the key support level (for a Rounding Top) or resistance level (for a Rounding Bottom).
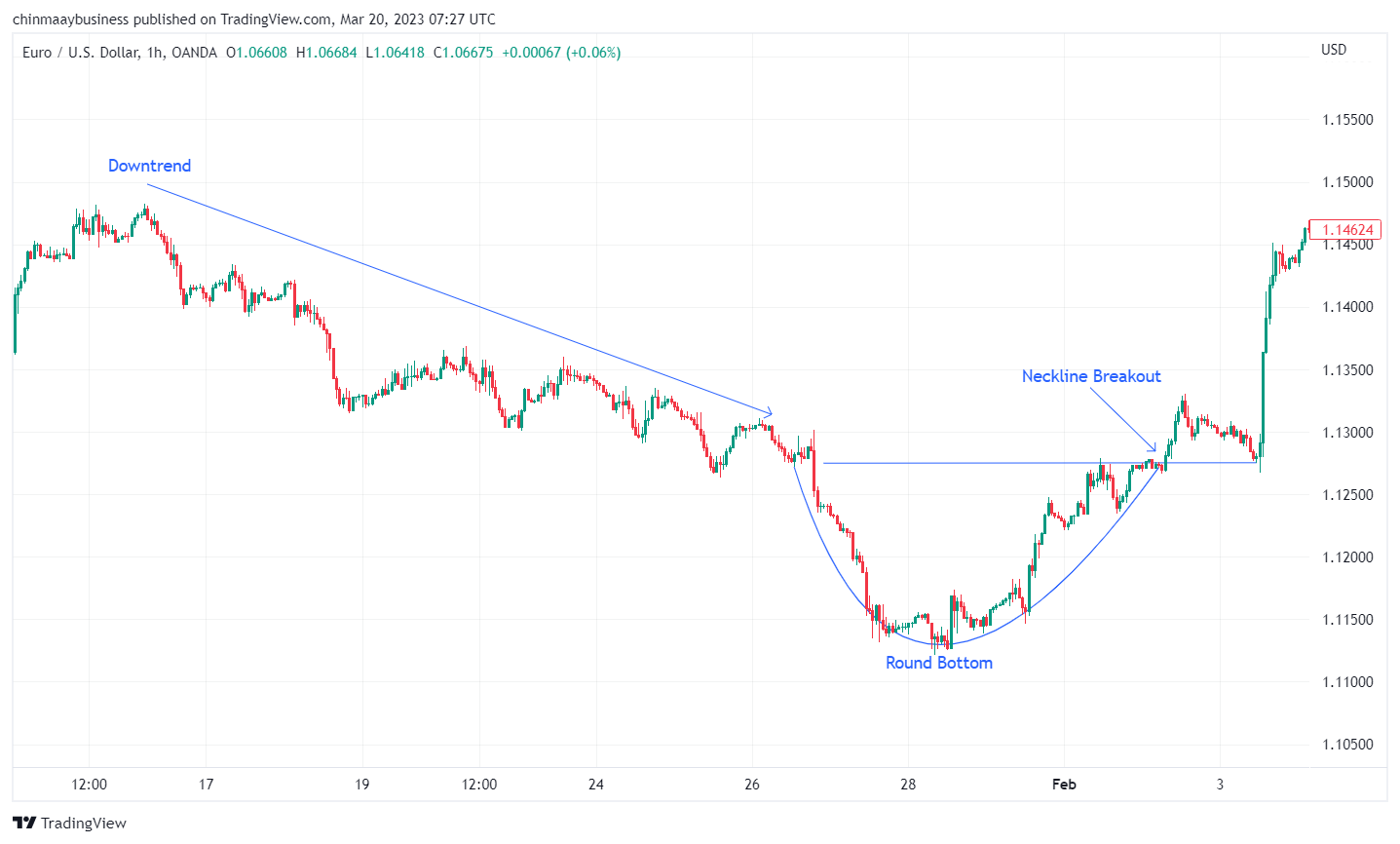
Rounding Top and Rounding Bottom patterns
4. Triple Top and Triple Bottom
Triple Top and Triple Bottom patterns are similar to their double-ended counterparts but consist of three peaks or troughs instead of two. A Triple Top forms at the end of an uptrend when the price reaches a resistance level three times without breaking through, while a Triple Bottom occurs when the price reaches a support level three times without breaking below. These patterns signal a potential trend reversal once the price breaks the neckline, with a shift from bullish to bearish for a Triple Top, and from bearish to bullish for a Triple Bottom.
Triple Top and Triple Bottom patterns
5. Falling and Rising Wedge
Falling and Rising Wedge patterns are formed by converging trend lines and can signal trend reversals depending on their context. For example, a Falling Wedge typically forms during a downtrend, with the price making lower highs and lower lows, but the slope of the support trendline is steeper than that of the resistance trendline. This pattern often signals a bullish reversal. Conversely, a Rising Wedge forms during an uptrend, with the price making higher highs and higher lows, but the slope of the resistance trendline is steeper than that of the support trendline. This pattern often indicates a bearish reversal. The reversal is confirmed when the price breaks through the respective trendline.
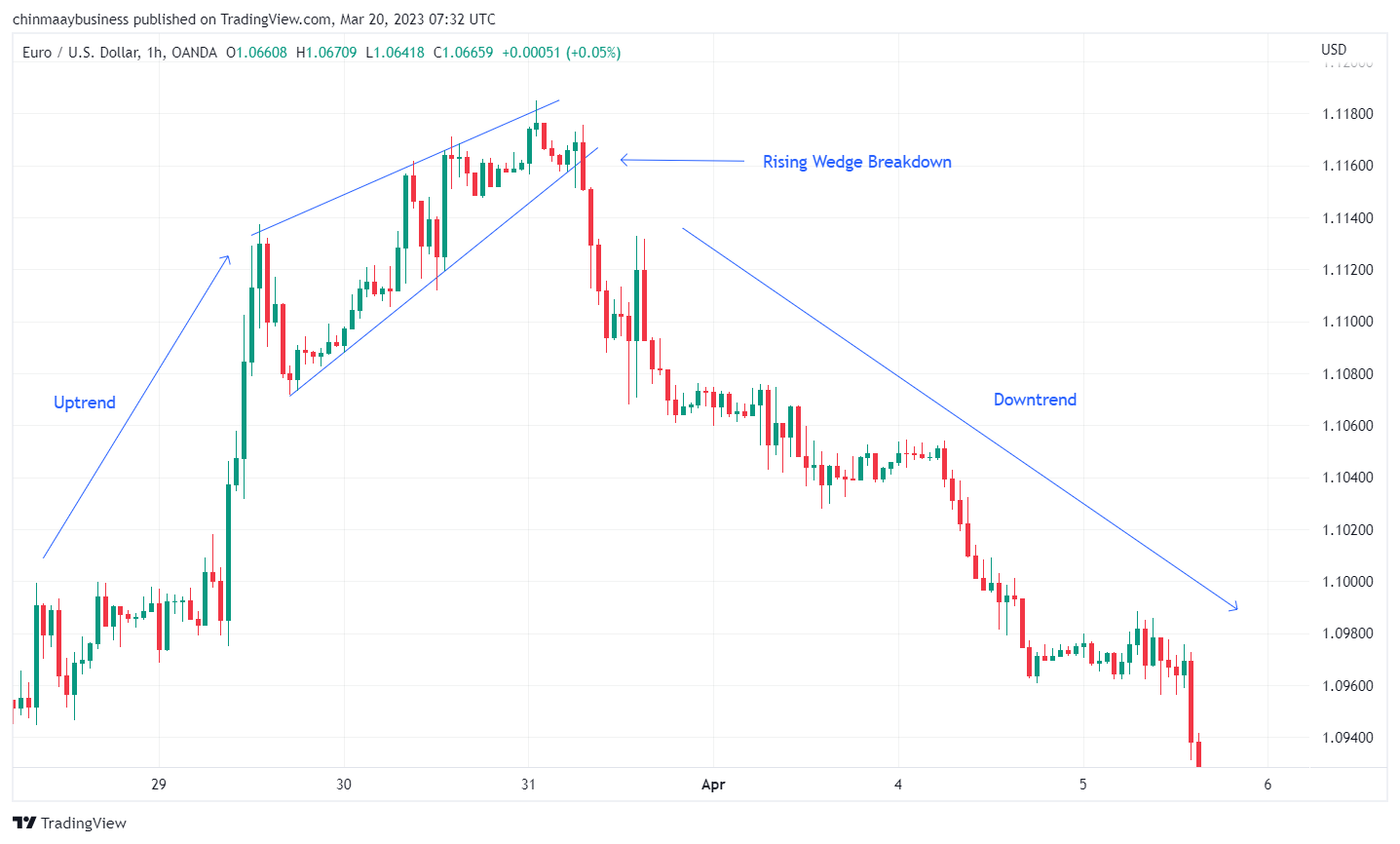
Falling and Rising Wedge patterns
Top 4 trend reversal indicators
The experts will now also explore the top four trend reversal indicators that traders can use to identify potential shifts in market direction. These indicators can provide valuable insights, allowing you to make informed decisions about your trades. We will analyze each indicator in detail, explaining its functionality and how it can be employed to spot trend reversals effectively.
Best Trend Indicators1. Moving Averages (MAs)
Moving averages are among the most widely used trading indicators in the market. They serve as the foundation for several other indicators, such as Donchian Channels and Bollinger Bands. The primary function of moving averages is to smooth out price data and reduce noise, enabling traders to identify trends more easily.
To utilize moving averages for identifying trend reversals, consider the following approach:
-
Select a moving average type and time period according to your trading strategy and preferences
-
Add the chosen moving average to your chart
-
Observe the price movement in relation to the moving average
A bullish reversal may be signaled when the price crosses above the moving average after a downtrend. Conversely, a bearish reversal might be indicated when the price crosses below the moving average following an uptrend. Remember that using multiple moving averages with different periods can provide additional confirmation and enhance the reliability of trend reversal signals.
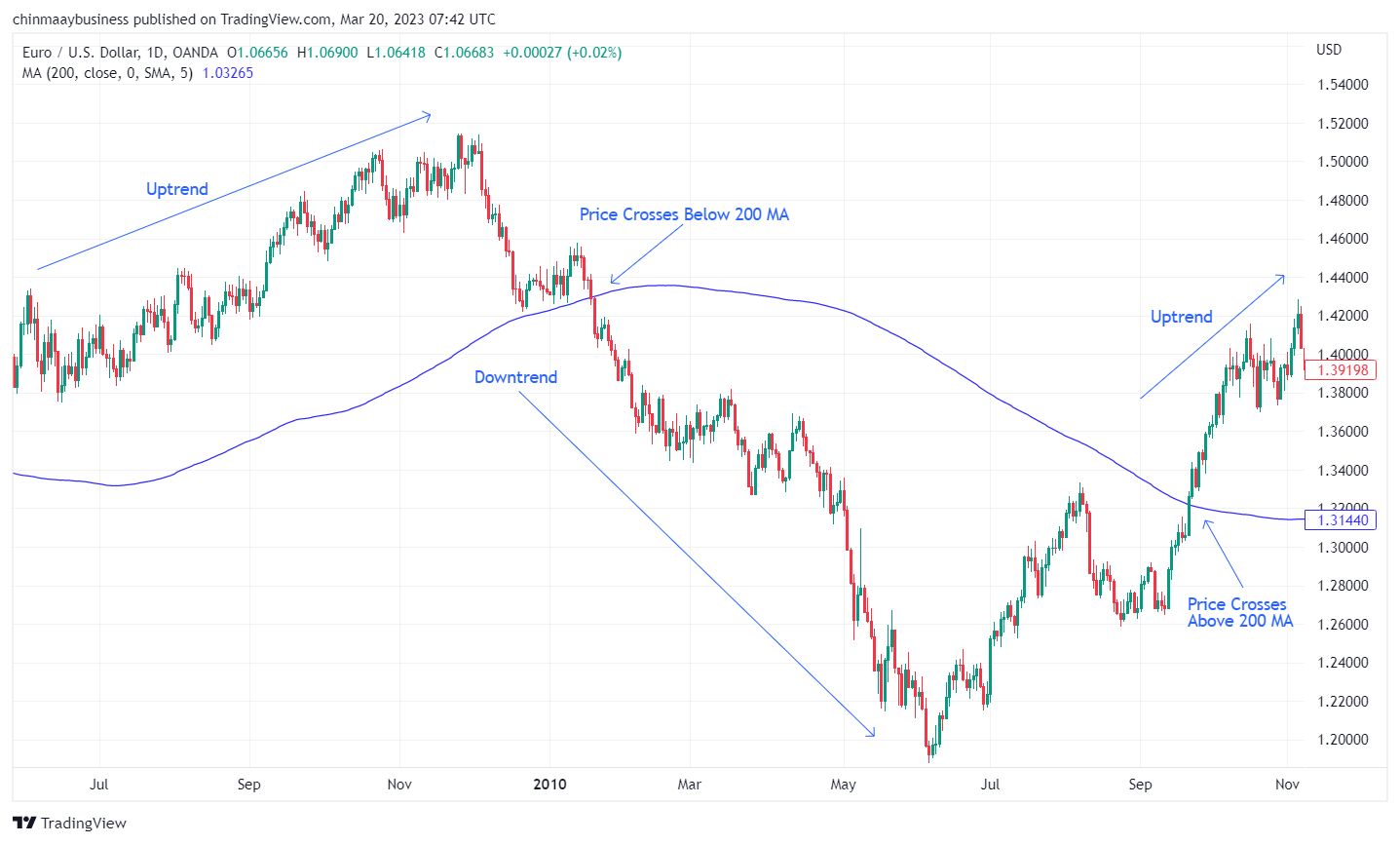
Moving averages indicator
2. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are a versatile and powerful technical analysis tool used by traders to identify potential trend reversals, among other applications. Developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, this indicator consists of three lines: a middle line, which is a simple moving average (SMA), and two outer bands that are standard deviations above and below the middle line. Bollinger Bands help traders to visualize the volatility in the market and gauge potential reversals by observing the price movement in relation to the bands.
To use Bollinger Bands effectively for identifying trend reversals, consider the following steps:
Add Bollinger Bands to your chart, typically using a 20-period SMA and a standard deviation of 2 for the upper and lower bands. However, you can adjust these parameters according to your trading strategy and preferences
Monitor the price action in relation to the bands. When the price moves around the upper band during an uptrend, it may indicate overbought conditions. If the price crosses above the SMA during such price action, it may suggest a potential bearish reversal. Conversely, when the price moves around the lower band during a downtrend and crosses above the SMA, it may point towards a possible bullish reversal
Pay attention to the width of the bands, as they can provide additional information about market volatility. When the bands narrow (also known as the "Bollinger Squeeze"), it suggests low volatility and may precede a significant price movement, potentially leading to a trend reversal. Conversely, when the bands widen, it indicates high volatility and may suggest the continuation of the current trend
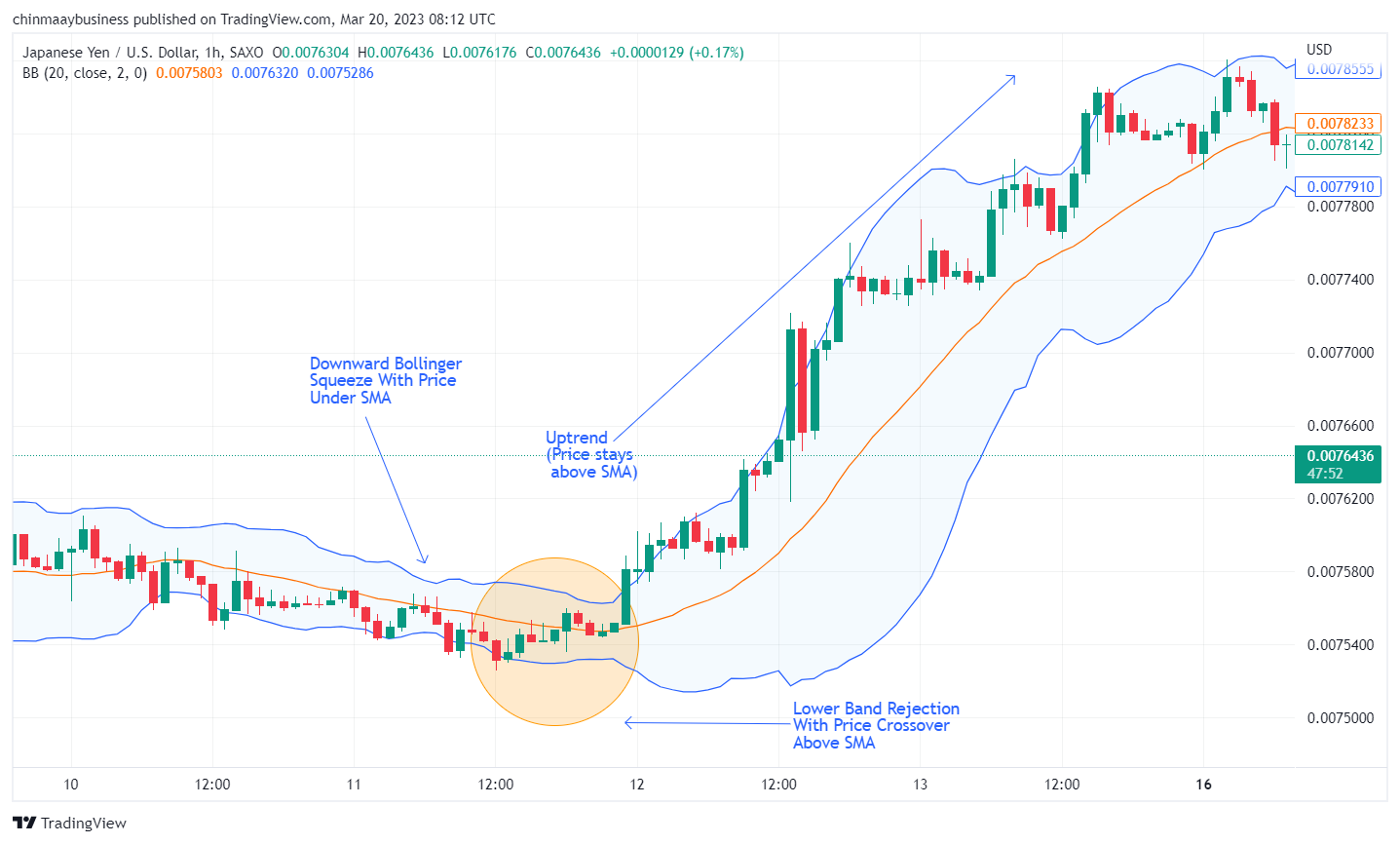
Bollinger Bands indicator
3. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a widely used momentum-oriented oscillator that helps identify both trend continuation and trend reversal signals. Invented by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s, the MACD is determined by taking the difference between a short-term Exponential Moving Average (EMA) and a longer-term EMA. Additionally, a signal line, commonly a 9-period EMA of the MACD itself, is drawn along with the MACD to produce trading signals.
To effectively employ the MACD for spotting trend reversals, follow this approach:
Incorporate the MACD indicator into your chart, usually applying the default settings of 12, 26, and 9 periods for the short-term EMA, long-term EMA, and signal line, respectively. Feel free to modify these parameters based on your trading strategy and personal preferences
Examine the MACD line (the difference between the short-term and long-term EMAs) and the signal line (9-period EMA of the MACD line) for potential crossovers. A bullish reversal might be indicated when the MACD line goes above the signal line, while a bearish reversal could be suggested when the MACD line drops below the signal line
Keep an eye on the MACD's position concerning the neutral (zero) line. A more noticeable trend reversal signal can be seen when the MACD crosses the neutral line. For example, a bullish reversal could be confirmed when the MACD rises above the neutral line, while a bearish reversal may be validated when it descends below the neutral line
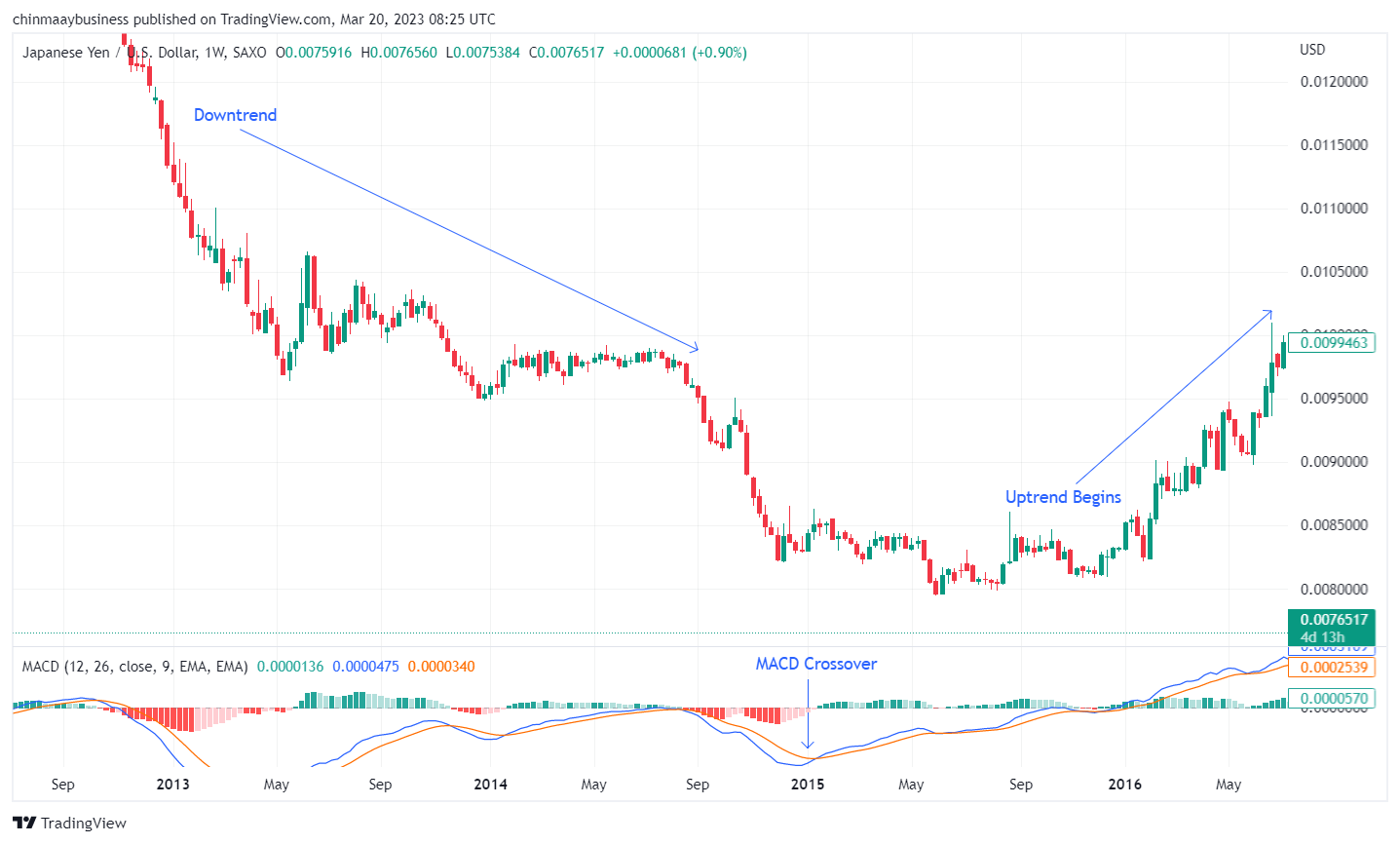
MACD indicator
4. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a widely-used momentum oscillator that can help traders identify potential trend reversals. Developed by J. Welles Wilder in 1978, the RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to determine overbought and oversold conditions in the market. RSI values range from 0 to 100, with levels above 70 typically indicating overbought conditions and levels below 30 suggesting oversold conditions.
To effectively use the RSI for spotting trend reversals, consider the following approach:
Add the RSI indicator to your chart, usually with a default period of 14. You can adjust this parameter based on your trading strategy and preferences
Monitor the RSI values to identify overbought and oversold levels. By default, the RSI uses thresholds of 70 and 30 to indicate overbought and oversold conditions, respectively. However, more extreme levels, such as 80 and 20 or 90 and 10, can provide stronger signals of potential trend reversals
Combining the RSI with other technical analysis tools and techniques is essential to increase the reliability of trend reversal signals. For instance, using support and resistance levels, trend lines, or chart patterns can provide additional confirmation for RSI-based reversal signals. By integrating multiple indicators and approaches, you can enhance the accuracy of your analysis and make more informed trading decisions.
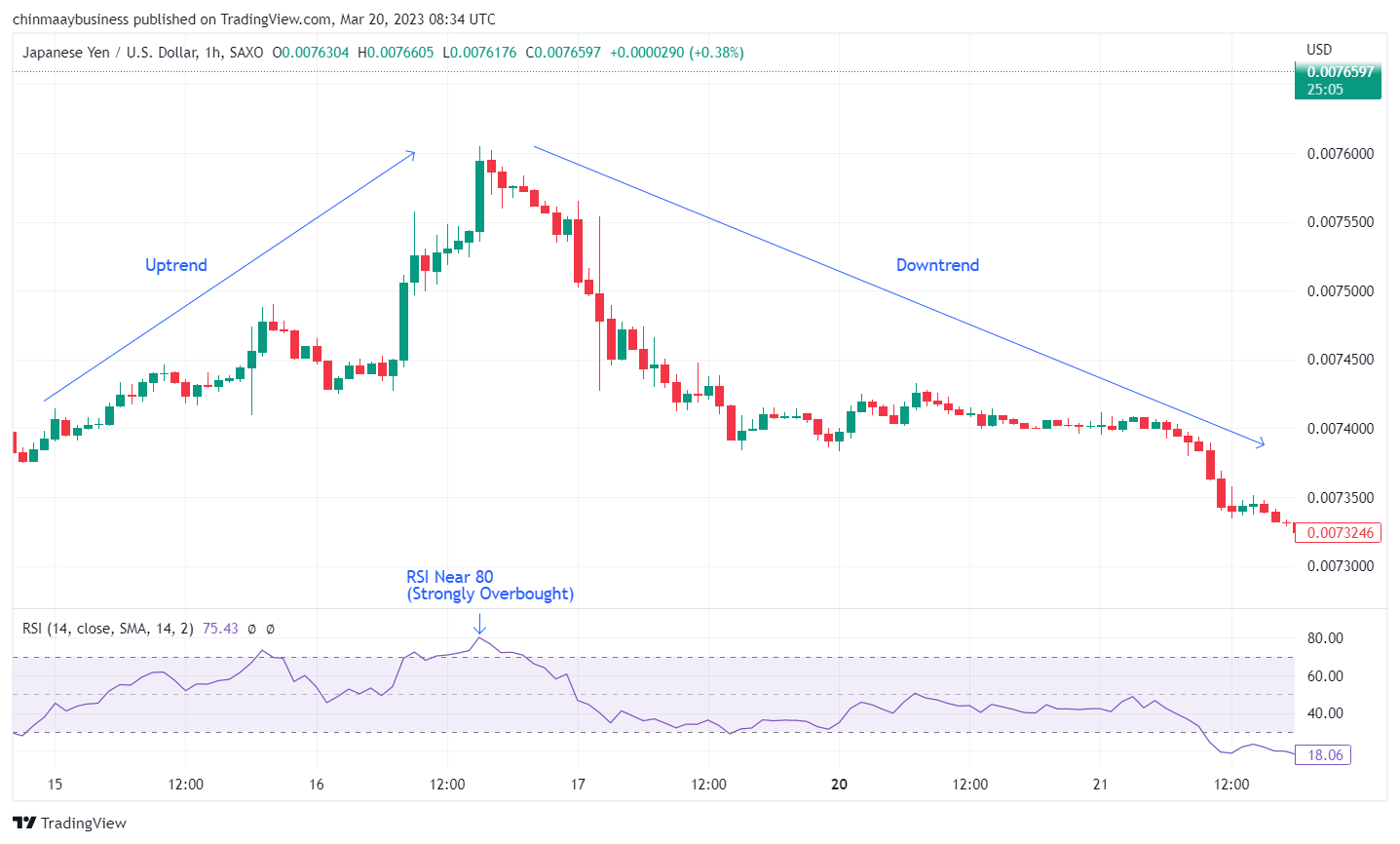
RSI indicator
How to identify trend reversal signals correctly?
To accurately identify trend reversal signals, it is crucial to use a combination of techniques and indicators that complement and confirm one another. Here are some expert tips that may help you improve your ability to spot trend reversals:
Combine multiple indicators: Using a combination of trend reversal indicators, such as moving averages, Bollinger Bands, MACD, and RSI, often generates more reliable signals. Multiple indicators increase the probability of accurately identifying reversals and reduce the risk of false signals.
Look for confirmation from other signals: Always seek additional confirmations from other technical analysis tools before acting on a trend reversal signal. For instance, if you observe a reversal signal from a moving average crossover, confirm it with a complementary indicator like RSI or MACD to strengthen your analysis.
Pay attention to support and resistance levels: Breakouts through key support and resistance levels can provide valuable information about potential trend reversals. When the price breaks through a significant support level during a downtrend, it could indicate a reversal in the bullish trend. Conversely, when the price breaks through a critical resistance level during an uptrend, it could signal a reversal in the bearish trend.
Monitor trend lines: Keep an eye on long-term trend lines, as a break of these lines can provide a strong indication of a trend reversal. A break above a descending trend line during a downtrend could signify a bullish reversal, while a break below an ascending trend line during an uptrend could suggest a bearish reversal.
Trend Reversal vs Retracement - what is the difference?
In trading, it's crucial to differentiate between trend reversals and retracements. These concepts represent changes in an asset's price direction, but they differ in their duration and implications.
Reversal
A reversal is when an asset's price changes direction significantly and maintains this new direction for a longer period. Think of it as a change in the overall trend. For example, if a stock has been increasing in price for months and then starts to consistently decline, this could be a reversal.
Retracement
A retracement, on the other hand, is a temporary price change within a larger trend. It's like a brief pause in the ongoing trend. If a stock has been rising for months and suddenly experiences a minor drop in price before continuing to rise, this short-lived decline is a retracement.
Key differences:
Volume: In retracements, fewer shares are bought and sold, while in reversals, a larger number of shares are traded.
Money Flow: During retracements, people continue to buy and sell the asset, whereas, in reversals, there's a noticeable decrease in buying and selling interest.
Chart Patterns: Retracements display small changes on the price chart, while reversals show more pronounced patterns indicating a change in direction.
Time Frame: Retracements are short-lived events, lasting days to weeks, while reversals can last for weeks or months.
Fundamentals: The underlying factors affecting an asset's value remain the same during a retracement but may change or be speculated to change in a reversal.
Candlesticks: Retracements show indecisive candlestick patterns, while reversals display more specific patterns signaling a change in direction.
Risk management and trend reversal signals
Implementing risk management techniques is crucial when trading based on trend reversal signals. Using risk management tools and the cancellation model, traders can minimize potential losses while maximizing profits. Here's a concise explanation of how to use these tools and models.
Risk management tools
Stop-Loss orders: Automatically close a trade when the asset's price reaches a predetermined level, limiting losses if the market moves against your position.
Position sizing: Allocate a small percentage of your trading capital to each trade (1%-3%) to minimize the impact of a single trade on your portfolio.
Risk-Reward ratio: Determine a suitable risk-reward ratio for your trades (e.g., 1:2 or 1:3), ensuring potential profits outweigh potential losses.
Diversification: Spread your trades across different assets, sectors, or trading styles to reduce the impact of reversals or negative events on your portfolio.
Using the cancellation model
Fill or Kill (FOK) Orders: Automatically cancels an order that cannot be filled in its entirety immediately, preventing partial executions.
Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Orders: Cancels any portion of the order that does not get filled immediately, allowing for partial executions.
One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO) Orders: Consists of two dependent orders; if one order executes, the other order is immediately canceled. This order type reduces risk by ensuring unwanted orders get automatically canceled.
Best Forex brokers
RoboForex is a brokerage company that was founded in 2009. It provides services to financial markets in 169 countries. More than 3.5 million users are RoboForex clients. RoboForex is the leading software developer in the Forex industry.
RoboForex is recognized as a reliable partner by the most respected financial market experts. The company has won numerous prestigious awards. The RoboForex group of companies has an international license to provide services from FSC Belize, and a European license from CySEC (license No. is 191/13 Robomarkets Ltd).
IC Markets
IC Markets is a brokerage company established in 2007 in Sydney, Australia. IC Markets group of companies provides access to financial markets across the world. The group has offices located in different regions enabling IC Markets to work with traders from practically any jurisdiction legally and in compliance with the local law. The companies of the group hold the following licenses: Raw Trading Ltd. is licensed by the SFSA, Seychelles, International Capital Markets Pty Ltd by the ASIC, Australia, and IC Markets (EU) Ltd by the CySEC, Cyprus. IC Markets is also a member of the Financial Commission, an independent organization that deals with disputes and has an insurance fund with up to EUR 20,000 coverage per each trader.
Summary
To sum it up, understanding trend reversal signals is crucial for traders to make informed decisions in the market. Some of the most effective reversal indicators include Moving Averages, Bollinger Bands, MACD, and RSI. By combining these indicators and observing key elements such as support and resistance levels, long-term trendlines, and price action, traders can accurately identify trend reversals. Additionally, differentiating between trend reversals and retracements is essential to avoid making hasty decisions. Finally, implementing risk management strategies, such as using canceled orders, can help minimize losses and improve overall trading performance.
FAQs
What is a trend reversal signal?
A trend reversal signal is an indication that the current price trend of an asset is about to change its direction, either from an uptrend to a downtrend or vice versa.
What is the best indicator for trend reversal?
There is no single best indicator for trend reversal, as it often depends on individual trading styles and preferences. Commonly used indicators include Moving Averages, Bollinger Bands, MACD, and RSI.
How do you identify a trend reversal in trading?
To identify a trend reversal in trading, traders can combine various technical analysis tools such as trend reversal indicators, support and resistance levels, long-term trendlines, and price action patterns.
What are trend reversal strategies?
Trend reversal strategies are trading approaches designed to capitalize on market situations when a prevailing price trend is about to change direction.
Glossary for novice traders
-
1
Broker
A broker is a legal entity or individual that performs as an intermediary when making trades in the financial markets. Private investors cannot trade without a broker, since only brokers can execute trades on the exchanges.
-
2
Trading
Trading involves the act of buying and selling financial assets like stocks, currencies, or commodities with the intention of profiting from market price fluctuations. Traders employ various strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management practices to make informed decisions and optimize their chances of success in the financial markets.
-
3
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands (BBands) are a technical analysis tool that consists of three lines: a middle moving average and two outer bands that are typically set at a standard deviation away from the moving average. These bands help traders visualize potential price volatility and identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market.
-
4
Volatility
Volatility refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the price or value of a financial asset, such as stocks, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, over a period of time. Higher volatility indicates that an asset's price is experiencing more significant and rapid price swings, while lower volatility suggests relatively stable and gradual price movements.
-
5
Risk Management
Risk management is a risk management model that involves controlling potential losses while maximizing profits. The main risk management tools are stop loss, take profit, calculation of position volume taking into account leverage and pip value.
Team that worked on the article
Chinmay Soni is a financial analyst with more than 5 years of experience in working with stocks, Forex, derivatives, and other assets. As a founder of a boutique research firm and an active researcher, he covers various industries and fields, providing insights backed by statistical data. He is also an educator in the field of finance and technology.
As an author for Traders Union, he contributes his deep analytical insights on various topics, taking into account various aspects.
Olga Shendetskaya has been a part of the Traders Union team as an author, editor and proofreader since 2017. Since 2020, Shendetskaya has been the assistant chief editor of the website of Traders Union, an international association of traders. She has over 10 years of experience of working with economic and financial texts. In the period of 2017-2020, Olga has worked as a journalist and editor of laftNews news agency, economic and financial news sections. At the moment, Olga is a part of the team of top industry experts involved in creation of educational articles in finance and investment, overseeing their writing and publication on the Traders Union website.











